Abstract
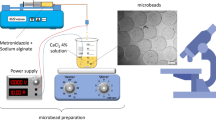
This paper reports a novel, simple, repeatable and cost-effective protocol for producing Ca-alginate beads with controlled sizes ranging from 50–250 μm with a narrow size distribution. The characteristics of the beads depend on the emulsion droplets formed, and the size of the beads can be controlled by manipulating the coalescence factor and the applied mechanical energy, which will also reduce the cost and overall time of the procedure. These results suggest that beads with diameters of 58±5, 69±7, 80±8, 145±11, 195±12 and 225±15 μm (mean diameter ± standard deviation) were easily produced. This was achieved simply by adding a minor amount of Pluronic F-127 (i.e., 0.03%) and controlling the coalescence effect to reduce the stabilization of the emulsion. Therefore, the method has strong potential for mass production on an industrial scale. Furthermore, the solvent evaporation technique successfully evaporated the volatile organic solvent used for emulsification. The beads were proven to be safe via a cell culture study and might be suitable for use in the medical, pharmaceutical and bioengineering field.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Callewaert, J. M. Millot, J. Lesage, D. L. Maquin, and F. E. Levy, Int. J. Pharm., 366, 103 (2009).
A. D. Sezer and J. Akbuga, J. Microencapsulation, 16, 687 (1999).
X. Wang, E. Wenk, X. Hu, G. R. Castro, L. Meinel, X. Wang, C. Li, H. Merkle, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 28, 4161 (2007).
P. K. Suk, J. C. Moon, K. S. Hee, R. M. John, K. G. Son, H. C. Whan, Y. Y. Sun, K. M. Suk, and L. H. Bang, Macromol. Res., 13, 285 (2005).
D. Quong and R. J. Neufeld, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 60, 134 (2000).
K. G. H. Desai, C. Liu, and H. J. Park, J. Microencapsulation, 22, 363 (2005).
G. T. Grant, E. R. Morris, D. A. Rees, and P. J. C. Smith, FEBS Letters, 32, 195 (1973).
L. S. Min, Y. E. Soo, G. H. Do, and L. S. Jeong, Macromol. Res., 17, 168 (2009).
C. Berkland, K. Kim, and D. W. Pack, Pharm. Res., 20, 1055 (2003).
C. Berkland, E. Pollauf, D. W. Pack, and K. Kim, J. Control. Release, 96, 101 (2004).
D. Chicheportiche and G. Reach, Diabetologia, 31, 54 (1988).
I. Jalenjak and T. Kondo, J. Pharm. Sci., 70, 456 (2006).
G. Fundueanu, C. Nastruzzi, A. Carpov, J. Desbrieres, and M. Rinaudo, Biomaterials, 20, 1427 (1999).
T. O. S. Sugiura, Y. Izumida, Y. Aoyagi, M. Satake, A. Ochiai, N. Ohkohchi, and M. Nakajima, Biomaterials, 16, 3327 (2005).
A. M. Chuah, T. Kuroiwa, I. Kobayashi, X. Zhang, and M. Nakajima, Colloids Surf. A, 351, 9 (2009).
J. Tu, S. Bolla, J. Barr, J. Miedema, X. Li, and B. Jasti, Int. J. Pharm., 30, 171 (2005).
L. Capretto, S. Mazzitelli, A. Tosi, and C. Nastruzzi, J. Control. Release, 132, 55 (2008).
D. Poncelet, Ann. Acad. Sci., 944, 74 (2001).
G. Fundueanu, E. Esposito, D. Mihai, A. Carpov, J. Desbrieres, M. Rinaudo, and C. Nastruzzi, Int. J. Pharm., 170, 11 (1998).
J. O. You, S. B. Park, H. Y. Park, S. Haam, C. H. Chung, and W. S. Kim, J. Microencapsulation, 18, 521 (2001).
C. P. Reis, R. J. Neufeld, S. Vilela, A. J. Ribeiro, and F. Veiga, J. Microencapsulation, 23, 245 (2006).
Q. Weia, W. Weia, R. Tiana, L. Wang, Z. Su, and G. Ma, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 323, 267 (2008).
R. Bodmeier and R. W. Mc Ginity, Pharm. Res., 4, 465 (1987).
P. B. Thu, P. Bruheim, T. Espevik, O. Smidsrd, P. S. Shiong, and G. S. Brek, Biomaterials, 17, 1069 (1997).
S. Nilkumhang and A. W. Basit, Int. J. Pharm., 377, 135 (2009).
Y. Fu, Z. Jin, G. Liu, and Y. Yin, Synth. Met., 159, 1744 (2009).
M. Iwata and J. W. Mc Ginity, J. Microencapsulation, 9, 201 (1992).
N. Mofidi, M. A. Moghadam, and M. N. Sarbolouki, Process Biochem., 35, 885 (2000).
Y. Tonga, C. Lib, F. Liangc, J. Chend, H. Zhanga, G. Liua, H. Suna, and J. H. T. Luonge, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B, 266, 5041 (2008).
Office of environmental Health Hazard Assessment (www.oehha.ca.gov/water/phg/pdf/dcm.pdf).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdi, S.I.H., Ng, S.M., Choi, J.Y. et al. Size-controlled microbeads through the influence of the coalescence effect in the emulsification solvent evaporation method. Macromol. Res. 18, 668–673 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-010-0706-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-010-0706-7