Abstract
Aim
The aim of the present study is to compare between sublingual administration of misoprostol and vaginal administration in the management of missed abortion.
Materials and Methods
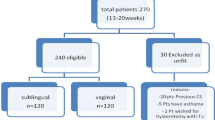
The study was conducted in El-Shatby Maternity Hospital on 160 patients diagnosed as missed abortion by ultrasonographic examination. Cases were divided into two groups according to the methods of misoprostol administration, whether sublingual or vaginal. Patients of the two groups were observed for the times of uterine colic starting, cervical dilation, and conceptus expulsion, along with recording of any side effects.
Result
During the follow-up of our cases we found that sublingual route is more effective than vaginal route in the management of missed abortion. The difference between the two groups in percentage of conceptus expulsion was statistically significant. The most common side effects were nausea which was present in 55 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 40 % of cases in group II (vaginal) then severe pain in 25 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 20 % of cases in group II (vaginal) and hyperpyrexia in 15 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 5 % of cases in group II (vaginal).
Conclusion
Sublingual administration of misoprostol is more effective than its vaginal administration in missed abortion management. Side effect of misoprostol as nausea, vomiting, fever is more common with sublingual administration in comparison with its vaginal administration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberma E, Grudzinskas G, Chardt G. Spontaneous abortion: diagnosis and treatment. London: Springer; 1992. p. 9–20.
Grimes DA, Stuart G. Abortion jabberwocky: the need for better terminology. Contraception. 2010;81(2):93–6.
Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, Halvorson LM, et al. First-trimester abortion. In: Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, editors. Williams Gynecology. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008.
Geyman JP, Oliver LM, Sullivan SD. Expectant, medical, or surgical treatment of spontaneous abortion in first trimester of pregnancy? A pooled quantitative literature evaluation. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1999;12(1):55–64.
Chung TK, Cheung LP, Sahota DS, et al. Spontaneous abortion: short-term complications following either conservative or surgical management. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;38(1):61–4.
Scroggins KM, Smucker WD, Krishen AE. Spontaneous pregnancy loss: evaluation, management, and follow-up counseling. Prim Care. 2000;27(1):153–67.
Kripke C. Expectant management vs. surgical treatment for miscarriage. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(7):1125–6.
Davies NM, Longstreth J, Jamali F. Misoprostol therapeutics revisited. Pharmacotherapy. 2001;21(1):60–73.
Denison FC, Calder AA, Kelly RW. The action of prostaglandin E2 on the human cervix: stimulation of interleukin 8 and inhibition of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180(3 Pt 1):614–20.
Shah N, Azam SI, Khan NH. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol in the management of missed miscarriage. J Pak Med Assoc. 2010;60(2):113–6.
Doubilet PM, Benson CB, Bourne T, et al. Diagnostic criteria for nonviable pregnancy early in the first trimester. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(15):1443–51.
Weeks AD, Fiala C, Safar P. Misoprostol and the debate over off-label drug use. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2005;112:269–72.
El-Sayed MM, Mohammed SA, Jones MH. Expectant management of first-trimester miscarriage. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;29(8):681–5.
Chia KV, Ogbo VI. Medical termination of missed abortion. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;22(2):184–6.
Tanha FD, Feizi M, Shariat M. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for the management of missed abortion. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2010;36(3):525–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
It meets ethical guidelines as the manuscript has been approved by ethics committee of Alexandria medical school, and a written consent has been taken from all patients about participation in research.
Additional information
Dr. Hossam Hassan Aly Hassan El Sokkary is Lecturer of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt. He was Obstetrics and Gynaecology Residents, El Shatby Alexandria University Hospital, Alexandria, Egypt in 20 October 1996 to 19 October 1999. He was Assistant Lecturer in 4 January 2004 to 22 September 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Sokkary, H.H.A.H. Comparison Between Sublingual and Vaginal Administration of Misoprostol in Management of Missed Abortion. J Obstet Gynecol India 66 (Suppl 1), 24–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-015-0757-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-015-0757-y