Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of sublingual and vaginal misoprostol in second-trimester termination of pregnancy in 24 and 48 h.
Study Design
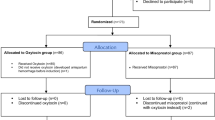
This is a retrospective study of 240 pregnant women seeking termination in second trimester (13–18.5 weeks), in which the patients are subdivided into two groups—first group received 400 mcg of misoprostol sublingually (n = 120), and second group received 400 mcg of misoprostol vaginally (n = 120) every 4 h for a maximum of five doses. The course of misoprostol was repeated if the patient did not abort within 24 h.
Results
The mean induction-to-abortion interval was shorter in sublingual group (10.28 ± 3.1 h) versus 14.68 ± 4.2 h in vaginal group in 24 h (p = 0.0001), and 36.9 ± 4.4 h in sublingual versus 29.7 ± 14 in vaginal group in 48 h (p = 0.0933). Mean dose requirement for misoprostol by sublingual route was low as compared to vaginal misoprostol (1048 ± 301 mg versus 1250 ± 375 mg; p = 0.0001 in 24 h and 1110 ± 833 mg versus 1325 ± 536 mg; p = 0.0231 in 48 h). No significant difference was found in the success rate (both at 24 and 48 h) and in side effects among the two comparison groups.
Conclusion
Misoprostol as such by any route has been proven as an effective abortifacient in second trimester. Both sublingual and vaginal routes are effective for medical abortion. But shorter induction-to-abortion interval in sublingual route, less dose requirement and higher acceptability makes sublingual route as a better choice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wildschut H, Both MI, Medema S, et al. Medical methods for mid-trimester termination of pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(1):CD005216.
The care of women requiring induced abortion. RCOG. https://www.rcog.org.uk/en/guidelines-research-services/guidelines/the-care-of-women-requesting-induced-abortion/. Accessed 13 Oct 2018.
Misoprostol only recommended regimens. https://www.figo.org/sites/default/files/uploads/project-publications/Miso/FIGO_Dosage_Chart%20EN_0.pdf. Accessed 11 Oct 2018.
Nagaria T, Sirmor N. Misoprostol vs mifepristone and misoprostol in second trimester termination of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2011;61(6):659–62.
Milani F, Sharami SH, Arjmandi S. Comparison of sublingual and vaginal misoprostol for second-trimester pregnancy terminations. J Family Reprod Health. 2014;8(1):41–4.
von Hertzen H, Piaggio G, Wojdyla D, et al. Comparison of vaginal and sublingual misoprostol for second trimester abortion: randomized controlled equivalence trial. Hum Reprod. 2009;24(1):106–12.
Tang OS, Schweer H, Seyberth HW, et al. Pharmacokinetics of different routes of administration of misoprostol. Hum Reprod. 2002;17(2):332–6.
Nautiyal D, Mukherjee K, Perhar I, et al. Comparative study of misoprostol in first and second trimester abortions by oral, sublingual, and vaginal routes. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2015;65(4):246–50.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 135: second-trimester abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121(6):1394–406.
Borgatta L, Kapp N. Labor induction abortion in the second trimester. Contraception. 2011;84(1):4–18.
Tanha FD, Golgachi T, Niroomand N, Ghajarzadeh M, Nasr R. Sublingual versus Vaginal misoprostol for second trimester termination: a randomized clinical trial. Arch Gynecolobstet. 2013;287:65–9.
Bhattacharjee N, Saha SP, Ghoshroy SC, et al. A randomised comparative study on sublingual versus vaginal administration of misoprostol for termination of pregnancy between 13 to 20 weeks. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;48(2):165–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interests for any author (financial or otherwise).
Ethical Statement
Ethical committee approval has been obtained before the study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent has been taken.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with animal subjects.
Additional information
Dr. Alka A. Mukherjee MBBS, DGO, FICMCH is a senior consultant and Director of Mukherjee Multispeciality Hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, A.A. Comparison of Effectiveness of Sublingual and Vaginal Misoprostol for Second-Trimester Abortion. J Obstet Gynecol India 69, 246–251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-018-1183-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-018-1183-8