Abstract
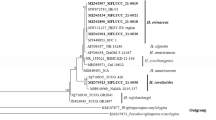
The LW03 strain was isolated from Chinese farmland soil and found to be able to secrete certain enzymes degrading regenerated cellulose films at low temperature. The LW03 strain was systematically identified as Rhizopus arrhizus var. arrhizus by morphological, physiological, and molecular methods. Incubation of regenerated cellulose films with the extracted crude enzyme of LW03 was done to measure morphological changes by using scanning electron microscopy. Microscopic observations showed that the morphology of the regenerated cellulose films changed drastically due to enzymatic hydrolysis. The extracellular hydrolases of LW03 strain incubated on bran medium were also assessed. The predominant activity in the crude enzyme was glucoamylase activity, followed by acid proteinase, phytase and pectinase activity. Interestingly, activities of β-glucosidase, endoglucanase, exoglucanase, and cellulase were also observed, but at a much lower extent. Based on initial evidence, the crude enzyme is most likely to contain some new constituents capable of degrading regenerated cellulose films.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahola S, Turon X, Osterberg M, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of native cellulose nanofibrils and other cellulose model films: effect of surface structure. Langmuir 24:11592–11599
Beauchemin KA, Colombatto D, Morgavi DP, Yang WZ (2003) Use of exogenous fibrolytic enzymes to improve feed utilization by ruminants. J Anim Sci 81:37–47
Cereia M, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Greene LJ, Rosa JC, Polizeli MDLTM (2000) Glucoamylase activity from the thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum. Biochemical and regulatory properties. J Basic Microbiol 40(2):83–92
Chen Y, Zhang LN, Gu JM, Liu J (2004) Physical properties of microporous membranes prepared by hydrolyzing cellulose/soy protein blends. J Membrane Sci 241(2):393–402
Cheng G, Liu Z, Murton JK, Jablin M, Dubey M, Majewski J, Halbert C, Browning J, Ankner J, Akgun B, Wang C, Esker AR, Sale KL, Simmons BA, Kent MS (2011) Neutron reflectometry and QCM-D study of the interaction of cellulases with films of amorphous cellulose. Biomacromolecules 12:2216–2224
Eriksson J, Malmsten M, Tiberg F, Callisen TH, Damhus T, Johansen KS (2005) Enzymatic degradation of model cellulose films. J Colloid Interf Sci 284:99–106
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791
Fernandez-Lahore HM, Auday RM, Fraile ER, Biscoglio de Jimenez Bonino M, Pirpignani L, Machalinski C, Cascone O (1999) Purification and characterization of an acid proteinase from mesophilic Mucor sp. solid-state cultures. J Peptide Res 53(6):599–605
Fierobe HP, Bayer EA, Tardif C, Czjzek M, Mechaly A, Belaich A, Lamed R, Shoham Y, Belaich JP (2002) Degradation of cellulose substrates by cellulosome chimeras: Substrate targeting versus proximity of enzyme components. J Biol Chem 277(51):49621–49630
Gonthier P, Garbelotto M (2011) Amplified fragment length polymorphism and sequence analyses reveal massive gene introgression from the European fungal pathogen Heterobasidion annosum into its introduced congener H. irregulare. Mol Ecol 20:2756–2770
Gunjikar TP, Sawant SB, Joshi JB (2001) Shear deactivation of cellulase, exoglucanase, endoglucanase, and beta-glucosidase in a mechanically agitated reactor. Biotechnol Prog 17(6):1166–1168
Gunnars S, Wagberg L, Stuart MAC (2002) Model films of cellulose: I. Method development and initial results. Cellulose 9:239–249
Himmel ME, Ding SY, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD (2007) Biomass recalcitrance: Engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315(5813):804–807
Jeoh T, Wilson DB, Walker LP (2006) Effect of cellulase mole fraction and cellulose recalcitrance on synergism in cellulose hydrolysis and binding. Biotechnol Prog 22:270–277
Josefsson P, Henriksson G, Wågberg L (2008) The physical action of cellulases revealed by a quartz crystal microbalance study using ultrathin cellulose films and pure cellulases. Biomacromolecules 9(1):249–254
Kargl R, Mohan T, Köstler S, Spirk S, Doliška A, Stana-Kleinschek K, Ribitsch V (2013) Functional patterning of biopolymer thin films using enzymes and lithographic methods. Adv Funct Mater 23:308–315
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequence. J Mol Evol 16(2):111–120
Kleeberg I, Welzel K, VandenHeuvel J, Muller RJ, Deckwer WD (2005) Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters. Biomacromolecules 6(1):262–270
Kosugi A, Murashima K, Doi RH (2001) Characterization of xylanolytic enzymes in Clostridium cellulovorans: Expression of xylanase activity dependent on growth substrates. J Bacteriol 183(24):7037–7043
Li R, Zhang LN, Xu M (2012) Novel regenerated cellulose films prepared by coagulating with water: Structure and properties. Carbohyd Polym 87(1):95–100
Limam F, Chaabouni SE, Ghrir R, Marzouki N (1995) Two cellobiohydrolases of Penicillium occitanis mutant Pol 6: Purification and properties. Enzyme Microb Tech 17:340–346
Liu XY, Huang H, Zheng RY (2007) Molecular phylogenetic relationships within Rhizopus based on combined analyses of ITS rDNA and pyrG gene sequences. Sydowia 59:235–253
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Blol R 66(3):506–577
Medie FM, Davies GJ, Drancourt M, Henrissat B (2012) Genome analyses highlight the different biological roles of cellulases. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(3):227–234
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Mohan T, Kargl R, Doliska A, Ehmann HMA, Ribitsch V, Stana-Kleinschek K (2013) Enzymatic digestion of partially and fully regenerated cellulose model films from trimethylsilyl cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 93:191–198
Molina M, Cenamor R, Nombela C (1987) Exo-1, 3-beta-glucanase activity in Candida albicans: effect of the yeast-to-mycelium transition. J Gen Microbiol 133(3):609–617
Nascimento CV, Souza FHM, Masui DC, Leone FA, Peralta RM, Jorge JA, Furriel RPM (2010) Purification and biochemical properties of a glucose-stimulated β-D-glucosidase produced by Humicola grisea var. thermoidea grown on sugarcane bagasse. J Microbiol 48(1):53–62
Ou KQ, Cheng YQ, Xing Y, Lin L, Nout R, Liang JF (2011) Phytase activity in brown rice during steeping and sprouting. J Food Sci Technol 48(5):598–603
Ramachandran S, Patel AK, Nampoothiri KM, Francis F, Nagy V, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2004) Coconut oil cake - a potential raw material for the production of α-amylase. Bioresour Technol 93(2):169–174
Ricard M, Reid ID (2004) Purified pectinase lowers cationic demand in peroxide-bleached mechanical pulp. Enzyme Microb Technol 34:499–504
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Shieh TR, Ware JH (1968) Survey of microorganisms for the production of extracellular phytase. Appl Microbiol 16(9):1348–1351
Sukharnikov LO, Alahuhta M, Brunecky R, Upadhyay A, Himmel ME, Lunin VV, Zhulin IB (2012) Sequence, structure, and evolution of cellulases in glycoside hydrolase family 48. J Biol Chem 287(49):41068–41077
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Turon X, Rojas OJ, Deinhammer RS (2008) Enzymatic kinetics of cellulose hydrolysis: a QCM-D study. Langmuir 24:3880–3887
Wei JC (1979) Manual of fungi identification. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai (in Chinese)
Wilson BD (2009) Cellulases and biofuels. Curr Opin Biotech 20:295–299
Yang G, Xiong XP, Zhang LN (2002) Microporous formation of blend membranes from cellulose/konjac glucomannan in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J Membrane Sci 201:161–173
Zhang YHP, Lynd LR (2006) A functionally based model for hydrolysis of cellulose by fungal cellulase. Biotechnol Bioeng 94(5):888–898
Zhen Y, Mi TZ, Yu ZG (2008) Detection of Phaeocystis globosa using sandwich hybridization integrated with nuclease protection assay (NPA-SH). J Environ Sci 20(12):1481–1486
Zheng RY, Chen GQ, Huang H, Liu XY (2007) A monograph of Rhizopus. Sydowia 59:273–372
Zyani M, Mortabit D, Mostakim M, Iraqui M, Haggoud A, Ettayebi M, Koraichi SI (2009) Cellulolytic potential of fungi in wood degradation from an old house at the Medina of Fez. Ann Microbiol 59(4):699–704
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. David Peris Navarro and Guo-Rui Huang, University of Wisconsin-Madison, for their revising of our paper. This work was supported by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-46-23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Wang, Q. & Xiong, S. Identification of a fungus able to secrete enzymes that degrade regenerated cellulose films and analyses of its extracellular hydrolases. Ann Microbiol 64, 1041–1048 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0741-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0741-7