Abstract
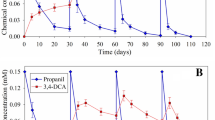
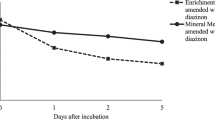
An enrichment culture method was applied to the isolation of a bacterial strain responsible for biodegradation of methidathion residues, from a methidathion-treated orchard. The strain (SPL-2) was identified as Serratia sp. according to its physiological characteristics and 16S rRNA gene phylogenetic analysis. Serratia sp. was able to grow in a poor medium consisting of mineral salts and using methidathion as the sole carbon source at a concentrations of 50–150 mg/L. The effects of multifactors on degradation of methidathion in pure cultures by Serratia sp. were investigated using an orthogonal experimental design L9 (34). On the basis of range analysis and ANOVA results, the most significant factors were temperature and inoculum size. The optimal conditions for methidathion biodegradation in pure cultures were a temperature in 30 °C, an inoculum size of 10 %, pH = 7 and an aeration rate of 200 rpm. Two different concentrations of strain SPL-2 fermenting liquids (OD600 = 0.2 and OD600 = 0.4) were prepared and applied to remove methidathion residues from agricultural products, and this process can be described by a first order rate model. In contrast to controls, the DT50 of methidathion was shortened by 35.7 %, 8.2 % and by 62.3 %, 57.5 % on OD600 = 0.2 and OD600 = 0.4 treated haricot beans and peaches, respectively. These results suggest that the isolated bacterial strain may have potential for use in bioremediation of methidathion-contaminated crops.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi M, Mostafalou S, Pournourmohammadi S, Shadnia S (2004) Oxidative stress and cholinesterase inhibition in saliva and plasma of rats following subchronic exposure to malathion. Comp Biochem Physiol C 137:29–34
Altuntas I, Delibas N, Demirci M, Kilinc I, Tamer N (2002) The effects of methidathion on lipid peroxidation and some liver enzymes: role of vitamins E and C. Arch Toxicol 76:470–473
Araujo DM, Yoshida MI, Takahashi JA, Carvalho CF, Stapelfeldt F (2010) Biodegradation studies on fatty amines used for reverse flotation of iron ore. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 64:151–155
Bidlan R, Manonmani HK (2002) Aerobic degradation of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) by Serratia marcescens DT-1P. Process Biochem 38:49–56
Blasco C, Font G, Pico Y (2006) Evaluation of 10 pesticide residues in oranges and tangerines from Valencia (Spain). Food Control 17:841–846
Bouaid A, Martin-Esteban A, Fernandez P, Camara C (2000) Microwave-assisted extraction method for the determination of atrazine and four organophosphorus pesticides in oranges by gas chromatography (GC). Fresenius J Anal Chem 367:291–294
Burkhard N, Guth JA (1979) Photolysis of organophosphorus insecticides on soil surfaces. Pestic Sci 10:313–319
Cervera MI, Medina C, Portoles T, Pitarch E, Beltran J, Serrahima E, Pineda L, Munoz G, Centrich F, Hernandez F (2010) Multi-residue determination of 130 multiclass pesticides in fruits and vegetables by gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:2873–2891
Cycon M, Wojcik M, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2009) Biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide diazinon by Serratia sp and Pseudomonas sp and their use in bioremediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 76:494–501
Das BK, Mukherjee SC (2000) Chronic toxic effects of quinalphos on some biochemical parameters in Labeo rohita (Ham.). Toxicol Lett 114:11–18
Dejonckheere WP, Kips RH (1974) Photodecomposition of methidathion. J Agric Food Chem 22:959–968
Feng Z, Cui KY, Li XD, Fu JA, Sheng GY (2004) Biodegradation kinetics of phthalate esters by Pseudomonas fluoresences FS1. Process Biochem 39:1125–1129
Fuentes E, Baez ME, Quinones A (2008) Suitability of microwave-assisted extraction coupled with solid-phase extraction for organophosphorus pesticide determination in olive oil. J Chromatogr A 1207:38–45
Getzin L (1970) Persistence of methidathion in soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 5:104–110
Ghanem I, Orfi M, Shamma M (2007) Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos by Klebsiella sp. isolated from an activated sludge sample of waste water treatment plant in Damascus. Folia Microbiol 52:423–427
Gonzalez-Lopez J, Martinez-Toledo M, Salmeron V (1992) Effect of the insecticide methidathion on agricultural soil microflora. Biol Fertil Soils 13:173–175
Hartley D, Kidd H (1987) The agrochemicals handbook, 2nd edn. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Hong Q, Zhang ZH, Hong YF, Li SP (2007) A microcosm study on bioremediation of fenitrothion-contaminated soil using Burkholderia sp.FDS-1. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:55–61
Jaiswal PK, Thakur IS (2007) Isolation and characterization of dibenzofuran-degrading Serratia marcescens from alkalophilic bacterial consortium of the chemostat. Curr Microbiol 55:447–454
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Kyriakidis NB, Athanasopoulos P, Georgitsanakou I (2000) Effect of storage temperature on degradation of Methidathion in fortified orange and peach juices. J AOAC Int 83:967–971
Leahy JG, Colwell RR (1990) Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 54:305
Li MT, Hao LL, Sheng L, Xu JB (2008) Identification and degradation characterization of hexachlorobutadiene degrading strain Serratia marcescens HL1. Bioresour Technol 99:6878–6884
Liang B, Lu P, Li HH, Li R, Li SP, Huang X (2009) Biodegradation of fomesafen by strain Lysinibacillus sp ZB-1 isolated from soil. Chemosphere 77:1614–1619
Montpas S, Samson J, Langlois E, Lei JY, Piche Y, Chenevert R (1997) Degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by Serratia marcescens. Biotechnol Lett 19:291–294
Quest JA, Copley MP, Hamernik KL, Rinde E, Fisher B, Engler R, Burnam WL, Fenner-Crisp PA (1990) Evaluation of the carcinogenic potential of pesticides: 2. Methidathion. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 12:117–126
Ramadan MA, El-Tayeb OM, Alexander M (1990) Inoculum size as a factor limiting success of inoculation for biodegradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1392
Rani MS, Lakshmi KV, Devi PS, Madhuri RJ, Aruna S, Jyothi K, Narasimha G, Venkateswarlu K (2008) Isolation and characterization of a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium from agricultural soil and its growth response. Afr J Microbiol Res 2:026–031
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406
Sanchez L, Mingorance MD, Pena A (2000) Microwave assisted process for methidathion in water samples for physicochemical studies. Analyst 125:1199–1203
Sanchez L, Pena A, Sanchez-Rasero F, Romero E (2003) Methidathion degradation in soil amended with biosolids and a cationic surfactant: use of different kinetic models. Biol Fertil Soils 37:319–323
Singh S, Chandra R, Patel DK, Rai V (2007) Isolation and characterization of novel Serratia marcescens (AY927692) for pentachlorophenol degradation from pulp and paper mill waste. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1747–1754
Singh S, Singh BB, Chandra R, Patel DK, Rai V (2009) Synergistic biodegradation of pentachlorophenol by Bacillus cereus (DQ002384), Serratia marcescens (AY927692) and Serratia marcescens (DQ002385). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1821–1828
Smith CA, Iwata Y, Gunther FA (1978) Conversion and disappearance of methidathion on thin layers of dry soil. J Agric Food Chem 26:959–962
Sulak O, Altuntas I, Karahan N, Yildirim B, Akturk O, Yilmaz HR, Delibas N (2005) Nephrotoxicity in rats induced by organophosphate insecticide methidathion and ameliorating effects of vitamins E and C. Pestic Biochem Physiol 83:21–28
Sutcu R, Altuntas I, Yildirim B, Karahan N, Demirin H, Delibas N (2006) The effects of subchronic methidathion toxicity on rat liver: role of antioxidant vitamins C and E. Cell Biol Toxicol 22:221–227
Tao YG, Wang YM, Yan SL, Ye LB (2008) Optimization of omethoate degradation conditions and a kinetics model. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62:239–243
Verma P, Madamwar D (2003) Decolourization of synthetic dyes by a newly isolated strain of Serratia marcescens. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:615–618
Vorkamp K, Kellner E, Taube J, Moller KD, Herrmann R (2002) Fate of methidathion residues in biological waste during anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 48:287–297
Wang X, Chu XQ, Yu YL, Fang H, Chen J, Song FM (2006) Characteristics and function of Bacillus latersprorus DSP in degrading chlorpyrifos. Acta Pedologica Sin 43:648–654
Xu XR, Gu JD, Li HB, Li XY (2005) Kinetics of di-n-butyl phthalate degradation by a bacterium isolated from mangrove sediment. J Microbiol Biotechnol 15:946–951
Yavuz T, Delibas N, Yildirim B, Altuntas I, Candir O, Cora A, Karahan N, Ibrisim E, Kutsal A (2005) Vascular wall damage in rats induced by organophosphorus insecticide methidathion. Toxicol Lett 155:59–64
Zambonin CG, Quinto M, De Vietro N, Palmisano F (2004) Solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography mass spectrometry: a fast and simple screening method for the assessment of organophosphorus pesticides residues in wine and fruit juices. Food Chem 86:269–274
Zhang C, Jia L, Wang SH, Qu J, Li K, Xu LL, Shi YH, Yan YC (2010) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by two Serratia spp. with different cell surface hydrophobicity. Bioresour Technol 101:3423–3429
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by the NSFC (No.41171253), the National 863 High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2006AA06Z361), Science and Technology Supportive Project of Sichuan Province, China (No. 2009SZ0204), Science and Technology project of Chengdu (10GGYB472SF-023) and Science and Technology Development Project of Longquanyi District Aro-technical Extension Centre, Chengdu. The authors wish to thank Professor Dong Yu from Sichuan University for laboratory assistance with the procedure of pesticide determination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Lan, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Biodegradation of methidathion by Serratia sp. in pure cultures using an orthogonal experiment design, and its application in detoxification of the insecticide on crops. Ann Microbiol 63, 451–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0489-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0489-5