Abstract
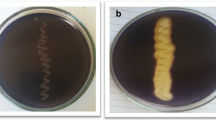
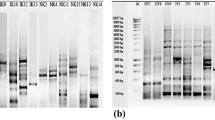
A new bacteria was isolated from hot-spring water of Gazlıgöl, Afyonkarahisar in Turkey. Based on morphological and biochemical tests and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, the isolate belonged to the Anoxybacillus flavithermus species which has 99% similarity with the bacterium DNA. The production of α-amylase by thermophilic Anoxybacillus flavithermus was investigated under solid-state fermentation by using some agricultural waste as substrates. Solid substrates such as rice husk, banana husk, millet, water melon husk, lentil bran, wheat bran and maize oil cake were studied for enzyme production. Of these, rice husk was proved as the best substrate for α-amylase production (1,271 U/mg). The maximum α-amylase production was observed as 1,803 U/mg at 72 h, 1,000 μm particle size, 70% initial moisture content (w/v), and 40% inoculum level (v/w). Among the various nitrogen sources tested, 1% peptone (3,170 U/mg) was found to be the best nitrogen source for α-amylase production. As additional carbon sources, 1% starch (2,364 U/mg) enhanced α-amylase production. The optimum temperature for the activity of α-amylase was found to be 70°C. The enzyme was optimally active at pH 6.0 and stable in the pH range of 6.0–8.0.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1997) Basic Local Aligment Search Tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Anto H, Trivedi U, Patel K (2006) α-Amylase production by Bacillus cereus MTCC 1305 using solid-state fermentation. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:241–245
Arıkan B, Unaldı N, Coral G, Colak Ö, Ashabil A, Osman G (2003) Enzymatic properties of a novel thermostable, thermophilic, alkaline and chelator resistant amylase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. isolate ANT-6. Process Biochem 38:1397–1403
Asgher M, Asad MJ, Rahman SU, Legge RL (2007) A thermostable α-amylase from a moderately thermophilic Bacillus subtilis strain for starch processing. J Food Eng 79:950–955
Babu KR, Satranarayana T (1996) Production of bacterial enzymes by solid-state fermentation. J Sci Indust Res 55:464–467
Babu KR, Satyanarayana T (1995) α-Amylase production by thermophilic Bacillus coagulans in solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem 30:305–309
Baysal Z, Uyar F, Aytekin C (2003) Solid-state fermentation for production of α-amylase by a thermotolerant Bacillus subtilis from hot-spring water. Process Biochem 38:1665–1668
Benson DA, Boguski MS, Lipman DJ et al (1999) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 27:12–17
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, α and β. In: Methods in Enzymology I. Academic, New York
Crabb WD, Mitchinson C (1997) Enzymes involved in the processing of starch to sugar. Trends Biotechnol 15:349–352
Elibol M, Moreira AR (2005) Optimization some factors affecting alkaline protease production by a marine bacterium Teredinobacter turnirae under solid-state substrate fermentation. Process Biochem 40:1951–1956
Gangadharan D, Sivaramakrishnan S, Madhavan K, Pandey N, Pandey A (2006) Solid culturing of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for α-amylase production. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:269–274
Gomes I, Gomes J, Steiner W (2003) Highly thermostable α-amylase and pullulanase of the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Rhodothermus marinus: Production and partial characterization. Bioresour Technol 90:207–214
Goyal N, Gupta JK, Soni SK (2005) A novel raw starch digesting thermostable α-amylase from Bacillus sp. I-3 and its use in the direct hydrolysis of raw potato starch. Enzyme Microb Tech 37:723–734
Hamilton LM, Kelly CT, Fogarty WM (1999) Production and properties of the starch-digesting α-amylase of Bacillus sp. IMD 435. Process Biochem 35:27–31
Kunamneni A, Permaul K, Singh S (2005) Amylase production in solid-state fermentation by the thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus. J Biosci Bioeng 100:168–171
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds). Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Mahanta N, Gupta A, Khare SK (2008) Production of protease and lipase by solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA in solid-state fermentation using Jatropha curcas seed cake as substrate. Bioresour Technol 99:1729–1735
Malhotra R, Noorwes SM, Satyanarayan T (2000) Production and partial characterization of thermostable and calcium-independent α-amylase of an extreme thermophilic Bacillus thermooleovorans NP54. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:378–384
Mamo G, Gessesse A (1999) Purification and characterization of two raw-starch-digesting thermostable α-amylases from a thermophilic Bacillus. Enzyme Microb Tech 25:433–438
Messaoud EB, Ali BM, Elleuch N, Masmoudi NF, Bejar S (2004) Purification and properties of a maltaheptaose-and maltohexaose-forming amylase produced by Bacillus subtilis US116. Enzyme Microb Tech 34:662–666
Narang S, Satyanarayana T (2001) Thermostable α-amylase production by an extreme thermophile Bacillus thermoleovorans. Lett Appl Microbiol 32:31–35
Ooijkaas LP, Weber FJ, Buitelaar RM, Tramper J, Rinzema A (2000) Defined media and inert support: Their potential as solid-state fermentation production systems. Tibtech 18:356–360
Ozdemir S, Güven K, Baysal Z, Uyar F (2009) Screening of Various Organic Substrates and the Development of a Suitable Low-Cost Fermentation Medium for the Production of α-Amylase by Bacillus subtilis. Food Technol Biotechnol 47:364–369
Pandey A (1991) Effect of particle size of substrate on enzyme production in solid-state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 37:169–172
Pandey A (2003) Solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 13:81–84
Pandey A, Soccol CR, Nigam P, Soccol VT (2000) Biotechnological potential of agro-industrial residues: I. Sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour Technol 74:69–80
Rajagopalan G, Krishnan C (2008a) Optimization of medium and process parameters for constitutive α-amylase production from a catabolite derepressed Bacillus subtilis KCC103. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 8:654–661
Rajagopalan G, Krishnan C (2008b) α-Amylase production from catabolite derepressed Bacillus subtilis KCC103 utilizing sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour Technol 99:3044–3050
Ramachandran S, Patel AK, Nampoothiri KM, Francis F, Nagy V, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2004) Coconut oil cake a potential raw material for the production of α-amylase. Bioresour Technol 93:169–174
Ramesh MV, Lonsane BK (1990) Critical importance of moisture content of the medium in alpha-amylase production by Bacillus licheniformis M27 in a solid-state fermentation system. Appl Microbial Biotechnol 33:501–505
Sandhya C, Sumantha A, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2005) Comparative evaluation of neutral protease production by Aspergillus oryzae in submerged and solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem 40:2689–2694
Sivaramakrishnan S, Gangadharan D, Nampoothiri KM, Carlos RS, Pandey A (2006) α-Amylases from Microbial Sources-An Overview on Recent Developments. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:173–184
Soni KS, Kaur A, Gupta JK (2003) A solid-state fermantation based bacterial α-amylase and fungal glucoamylase system and its suitability for hydrolysis of wheat starch. Process Biochem 39:185–192
Studholme DJ, Jackson RA, Leak DJ (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of transformable strains of thermophilic Bacillus species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 172:85–90
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M et al (2007) MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA). Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanyildizi MS, Ozer D, Elibol M (2005) Optimization of α-amylase production by Bacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 40:2291–2296
Tanyildizi MS, Ozer D, Elibol M (2007) Production of bacterial α-amylase by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens under solid substrate fermentation. Biochem Eng J 37:294–297
Ul-Haq I, Idress S, Rajoka MI (2002) Production lipases by Rhizopus oligosporous by solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem 37:637–641
Wind RD, Buitelaar RM, Eggink G, Huizing HJ, Dijkhuizen L (1994) Characterization of a new Bacillus stearothermophilus isolate: A highly thermostable α-amylase producing strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:155–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özdemir, S., Matpan, F., Okumus, V. et al. Isolation of a thermophilic Anoxybacillus flavithermus sp. nov. and production of thermostable α-amylase under solid-state fermentation (SSF). Ann Microbiol 62, 1367–1375 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0385-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0385-4