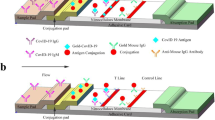
Abstract
Fv-antibodies against the nucleocapsid protein (NP) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were screened from an Fv-antibody library, and a one-step immunoassay was performed to detect SARS-CoV-2 using real viral samples. The Fv-antibody library was prepared using site-directed mutagenesis of the CDR3 region, which was composed of 11 amino acids. To screen the target Escherichia coli from the Fv-antibody library, the expressed probes [N-terminal domain (NTD) labeled with GFP and C-terminal domain (CTD) labeled with GFP] were reacted separately with the Fv-antibody library. After oligonucleotide sequencing, two clones for each probe were selected as the final clones. The screened Fv-antibodies with the binding affinity to NTD (or CTD) were expressed as soluble proteins, and the affinity constant (KD) was calculated to be 25.4 nM for NTD and 26.9 nM for CTD. The expressed Fv-antibodies were used for the one-step immunoassay based on switching-peptides, which were bound to the expressed Fv-antibodies. The one-step immunoassay based on Fv-antibodies could be used for the linear detection of SARS-CoV-2 NP, and the limit of detection (LOD) was estimated to be 9.6 nM (438 ng/mL) for Anti-NTD and 14.1 nM (639 ng/mL) for Anti-CTD. For the demonstration of one-step immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2, NATtrol™ SARS-CoV-2 real sample was used, and the LOD was estimated to be 29.7 copies/mL (Ct = 39.5) using Anti-NTD and 117.8 copies/mL (Ct = 38.0) using Anti-CTD. The measured LOD for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a one-step immunoassay based on the switching-peptide was considered feasible for the medical diagnosis of COVID-19. Finally, the interaction between the screened Fv-antibodies and SARS-CoV-2 NP was investigated using docking simulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Wuertz, K.M., Barkei, E.K., Chen, W.-H., Martinez, E.J., Lakhal-Naouar, I., Jagodzinski, L.L., Paquin-Proulx, D., Gromowski, G.D., Swafford, I., Ganesh, A.: A SARS-CoV-2 spike ferritin nanoparticle vaccine protects hamsters against Alpha and Beta virus variant challenge. NPJ Vaccines 6, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-021-00392-7
Zhang, Q., Xiang, R., Huo, S., Zhou, Y., Jiang, S., Wang, Q., Yu, F.: Molecular mechanism of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and host cells and interventional therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6, 233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00653-w
Kim, S., Lee, J.-H.: Current advances in paper-based biosensor technologies for rapid COVID-19 diagnosis. BioChip J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00078-9
Jung, J., Sung, J.S., Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Kwon, S., Bae, H.E., Kang, M.-J., Jose, J., Lee, M., Shin, H.-J.: One-step immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 using screened Fv-antibodies and switching peptides. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115834
Sun, C., Chen, L., Yang, J., Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Yang, J., Zhang, J., Xie, L.: SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV spike-RBD structure and receptor binding comparison and potential implications on neutralizing antibody and vaccine development. Biorxiv (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.16.951723
Feng, W., Xiang, Y., Wu, L., Chen, Z., Li, Q., Chen, J., Guo, Y., Xia, D., Chen, N., Zhang, L.: Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 is a potential target for developing new generation of vaccine. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 36, e24479 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24479
Schnurra, C., Reiners, N., Biemann, R., Kaiser, T., Trawinski, H., Jassoy, C.: Comparison of the diagnostic sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein and glycoprotein-based antibody tests. J. Clin. Virol. 129, 104544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104544
Raïch-Regué, D., Muñoz-Basagoiti, J., Perez-Zsolt, D., Noguera-Julian, M., Pradenas, E., Riveira-Muñoz, E., Giménez, N., Carabaza, A., Giménez, F., Saludes, V.: Performance of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests for Omicron and other variants of concern. Front. Microbiol. 13, 810576 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.810576
Ha, Y., Kim, I.: Recent developments in innovative magnetic nanoparticles-based immunoassays: from improvement of conventional immunoassays to diagnosis of COVID-19. BioChip J. 16, 351–365 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00064-1
Xu, J.L., Davis, M.M.: Diversity in the CDR3 region of VH is sufficient for most antibody specificities. Immunity 13, 37–45 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00006-6
Jung, J., Bong, J.-H., Sung, J.S., Park, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Kwon, S., Kang, M.-J., Jose, J., Pyun, J.-C.: Immunoaffinity biosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-1 using screened Fv-antibodies from an autodisplayed Fv-antibody library. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115439
Xie, S., Wang, J., Yu, X., Peng, T., Yao, K., Wang, S., Liang, D., Ke, Y., Wang, Z., Jiang, H.: Site-directed mutations of anti-amantadine scFv antibody by molecular dynamics simulation: prediction and validation. J. Mol. Model. 26, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-4286-y
Sung, J.S., Bong, J.-H., Lee, S.J., Jung, J., Kang, M.-J., Lee, M., Shim, W.-B., Jose, J., Pyun, J.-C.: One-step immunoassay for food allergens based on screened mimotopes from autodisplayed FV-antibody library. Biosens. Bioelectron. 202, 113976 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113976
Jung, J., Bong, J.-H., Sung, J.S., Lee, S.J., Lee, M., Kang, M.-J., Jose, J., Pyun, J.-C.: Fluorescein and rhodamine B-binding domains from autodisplayed Fv-antibody library. Bioconj. Chem. 32, 2213–2223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00376
Jung, J., Bong, J.-H., Lee, S.J., Kim, M.-J., Sung, J.S., Lee, M., Kang, M.-J., Song, J., Jose, J., Pyun, J.-C.: Screening of Fv antibodies with specific binding activities to monosodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals for the diagnosis of gout and pseudogout. ACS Appl. Biomater. 4, 3388–3397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c01680
Sung, J.S., Bong, J.-H., Yun, T.G., Han, Y., Park, Y., Jung, J., Lee, S.J., Kang, M.-J., Jose, J., Lee, M.: Antibody-mediated screening of peptide inhibitors for monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) from an autodisplayed FV library. Bioconj. Chem. 33, 1166–1178 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00107
Lee, S.J., Bong, J.-H., Jung, J., Sung, J.S., Kang, M.-J., Jose, J., Pyun, J.-C.: Screening of biotin-binding FV-antibodies from autodisplayed FV-library on E. coli outer membrane. Anal. Chim. Acta (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338627
Matsuo, T.: Viewing SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in terms of molecular flexibility. Biology 10, 454 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060454
Bong, J.-H., Kim, H.-R., Jung, J., Park, J.-H., Sung, J.S., Lee, C.K., Choi, K.-H., Shin, S.-S., Kang, M.-J., Kim, H.O.: Switching-peptides for one-step immunoassay and its application to the diagnosis of human hepatitis B. Biosens. Bioelectron. 178, 112996 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.112996
Kim, T.-H., Bong, J.-H., Kim, H.-R., Shim, W.-B., Kang, M.-J., Pyun, J.-C.: One-step immunoassay based on switching peptides for analyzing ochratoxin A in wines. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 13, 1–12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-022-00352-3
Lee, C.K., Jung, J., Kim, H.-R., Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Park, J.-H., Kwon, S., Kang, M.-J., Pyun, J.-C.: One-step immunoassay for the detection of food-poisoning related bacteria using a switching peptide. Analyst 147, 5363–5371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2an00940d
Park, J.-H., Song, Z., Bong, J.-H., Kim, H.-R., Kim, M.-J., Choi, K.-H., Shin, S.-S., Kang, M.-J., Lee, D.Y., Pyun, J.-C.: Electrochemical one-step immunoassay based on switching peptides and pyrolyzed carbon electrodes. ACS Sens. 7, 215–224 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c01998
Rabaan, A.A., Tirupathi, R., Sule, A.A., Aldali, J., Mutair, A.A., Alhumaid, S., Muzaheed, G.N., Koritala, T., Adhikari, R.: Viral dynamics and real-time RT-PCR Ct values correlation with disease severity in COVID-19. Diagnostics 11, 1091 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061091
Engelmann, I., Alidjinou, E.K., Ogiez, J., Pagneux, Q., Miloudi, S., Benhalima, I., Ouafi, M., Sane, F., Hober, D., Roussel, A.: Preanalytical issues and cycle threshold values in SARS-CoV-2 real-time RT-PCR testing: should test results include these? ACS Omega 6, 6528–6536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00166
Kifaro, E.G., Kim, M.J., Jung, S., Noh, J.-Y., Song, C.-S., Misinzo, G., Kim, S.K.: Direct reverse transcription real-time PCR of viral RNA from saliva samples using hydrogel microparticles. BioChip J. 16, 409–421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00065-0
Corman, V.M., Landt, O., Kaiser, M., Molenkamp, R., Meijer, A., Chu, D.K., Bleicker, T., Brünink, S., Schneider, J., Schmidt, M.L.: Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eur. Surveill. 25, 2000045 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Huang, W.E., Lim, B., Hsu, C.C., Xiong, D., Wu, W., Yu, Y., Jia, H., Wang, Y., Zeng, Y., Ji, M.: RT-LAMP for rapid diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb. Biotechnol. 13, 950–961 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13586
Fozouni, P., Son, S., de León Derby, M.D., Knott, G.J., Gray, C.N., D’Ambrosio, M.V., Zhao, C., Switz, N.A., Kumar, G.R., Stephens, S.I.: Amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas13a and mobile phone microscopy. Cell 184, 323–333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.001
Zhao, H., Liu, F., Xie, W., Zhou, T.-C., OuYang, J., Jin, L., Li, H., Zhao, C.-Y., Zhang, L., Wei, J.: Ultrasensitive supersandwich-type electrochemical sensor for SARS-CoV-2 from the infected COVID-19 patients using a smartphone. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 327, 128899 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128899
Białobrzeska, W., Ficek, M., Dec, B., Osella, S., Trzaskowski, B., Jaramillo-Botero, A., Pierpaoli, M., Rycewicz, M., Dashkevich, Y., Łęga, T.: Performance of electrochemical immunoassays for clinical diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 based on selective nucleocapsid N protein detection: Boron-doped diamond, gold and glassy carbon evaluation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 209, 114222 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114222
Peng, T., Dong, L., Feng, X., Yang, Y., Wang, X., Niu, C., Liang, Z., Qu, W., Zou, Q., Dai, X.: Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and N gene and its application in antigen testing kits evaluation. Talanta 258, 124462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124462
Duell, J., Dittrich, M., Bedke, T., Mueller, T., Eisele, F., Rosenwald, A., Rasche, L., Hartmann, E., Dandekar, T., Einsele, H.: Frequency of regulatory T cells determines the outcome of the T-cell-engaging antibody blinatumomab in patients with B-precursor ALL. Leukemia 31, 2181–2190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.41
Liu, M., Wang, B., Wang, F., Yang, Z., Gao, D., Zhang, C., Ma, L., Yu, X.: Soluble expression of single-chain variable fragment (scFv) in Escherichia coli using superfolder green fluorescent protein as fusion partner. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 6071–6079 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09925-6
Pédelacq, J.-D., Cabantous, S., Tran, T., Terwilliger, T.C., Waldo, G.S.: Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 79–88 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1172
Eberhardt, J., Santos-Martins, D., Tillack, A.F., Forli, S.: AutoDock Vina 1.2. 0: New docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 61, 3891–3898 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203
Wei, S., Suryawanshi, H., Djandji, A., Kohl, E., Morgan, S., Hod, E.A., Whittier, S., Roth, K., Yeh, R., Alejaldre, J.C.: Field-deployable, rapid diagnostic testing of saliva for SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84792-8
Park, J.-H., Lee, G.-Y., Song, Z., Bong, J.-H., Chang, Y.W., Cho, S., Kang, M.-J., Pyun, J.-C.: Capacitive biosensor based on vertically paired electrodes for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 202, 113975 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113975
Jung, J., Bong, J.-H., Kim, H.-R., Park, J.-H., Lee, C.K., Kang, M.-J., Kim, H.O., Pyun, J.-C.: Anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein antibodies derived from pig serum with a controlled specificity. BioChip J. 15, 195–203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00019-y
Jung, J., Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Sung, J.S., Lee, C., Kang, M.-J., Kim, H.O., Shin, H.-J., Pyun, J.-C.: Isolation of antibodies against the spike protein of SARS-CoV from pig serum for competitive immunoassay. BioChip J. 15, 396–405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00033-0
Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Jung, J., Lee, S.J., Sung, J.S., Lee, C.K., Kang, M.-J., Kim, H.O., Pyun, J.-C.: Competitive immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 using pig sera-derived anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. BioChip J. 15, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00011-6
Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Jung, J., Lee, S.J., Sung, J.S., Lee, C.K., Kang, M.-J., Kim, H.O., Pyun, J.-C.: Pig sera-derived anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in surface plasmon resonance biosensors. BioChip J. 14, 358–368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-020-4404-z
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of Korea [HV22C0131] and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea [NRF-2020R1A5A101913111, RS-2023-00209053, and NRF-2021R1A2C209370611], and Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry (IPET) [122010022SB010].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that may have influenced the work reported in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, J., Sung, J.S., Kim, TH. et al. One-Step Immunoassay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Using Screened Fv-Antibodies. BioChip J (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00151-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00151-5