Abstract
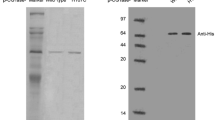
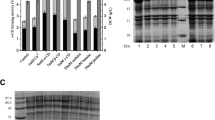
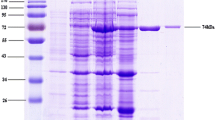
To meet the growing demand of β-cyclodextrin (CD), innovative approaches are being developed to improve the production of β-CD by β-cyclodextrin glucose-transferase (CGTase). Considering the low production and efficacy of wild-type β-CGTase-producing strains, to obtain the strains suitable for industrial production of β-CGTase, the recombinant engineered bacteria strain DF257 is constructed by transfecting with the plasmid expressing His tagged β-CGTase. The fermentation of β-CGTase-expressing DF257 was optimized in the presence of different metal ions, amino acids, and incubated at a certain temperature and pH condition. The results showed that when Mg2+ and isoleucine were added into the culture medium at 0.5 mM and 0.5 g/L, respectively, the enzyme activity of β-CGTase increased significantly after incubation at 37 °C with the initial pH of 7.5. In addition, the optimal temperature for β-CGTase with the addition of Mg2+ and isoleucine was also determined. The T half of β-CGTase under 50, 55, 60 and 65 °C was 9.5, 8.8, 6.2 and 1.2 h, respectively. Further investigation showed that β-CGTase kept stable under the pH 6.0–10.0, and pH 7.5 was identified as the optimal pH condition of β-CGTase. With the addition of Mg2+ and isoleucine, the kinetic properties of β-CGTase in the cyclization reaction had a similar form with Michaelis equation under 50 °C and pH 7.5, and Vmax, Km, and Kcat was 3.74 mg/mL/min, 3.28 mg/mL, and 31.17/s, respectively. The possible underlying mechanism by which Mg2+ and isoleucine synergistically improved the thermostability of β-CGTase was investigated by the surface hydrophobicity index analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis. The results indicated that addition of Mg2+ and isoleucine maintained the spatial structure and enhanced the thermostability of β-CGTase. These findings provided a theoretical basis for realizing the industrialization application of β-CGTase in promoting the generation of β-CD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented in this study is available from the correspoding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bezerra FM, Lis MJ, Firmino HB, Dias da Silva JG, Curto Valle RCS, Borges Valle JA, Scacchetti FAP, Tessaro AL (2020) The role of beta-cyclodextrin in the textile industry-review. Molecules 25(16):3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163624
Chodankar D, Vora A, Kanhed A (2022) beta-cyclodextrin and its derivatives: application in wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29(2):1585–1604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17014-3
Hirano K, Ishihara T, Ogasawara S, Maeda H, Abe K, Nakajima T, Yamagata Y (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel gamma-CGTase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(2):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0041-7
Jacob S, Nair AB (2018) Cyclodextrin complexes: perspective from drug delivery and formulation. Drug Dev Res 79(5):201–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21452
Karthic A, Roy A, Lakkakula J, Alghamdi S, Shakoori A, Babalghith AO, Emran TB, Sharma R, Lima CMG, Kim B, Park MN, Safi SZ, de Almeida RS, Coutinho HDM (2022) Cyclodextrin nanoparticles for diagnosis and potential cancer therapy: a systematic review. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:984311. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.984311
Lee M, Dey KP, Lee YS (2020) Complexation of methyl salicylate with beta-cyclodextrin and its release characteristics for active food packaging. Food Sci Biotechnol 29(7):917–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00749-z
Liu Y, Qiu C, Li X, McClements DJ, Wang C, Zhang Z, Jiao A, Long J, Zhu K, Wang J, Jin Z (2022) Application of starch-based nanoparticles and cyclodextrin for prebiotics delivery and controlled glucose release in the human gut: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63:6126–6137. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2028127
Muankaew C, Loftsson T (2018) Cyclodextrin-based formulations: a non-invasive platform for targeted drug delivery. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 122(1):46–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12917
Nik-Pa NIM, Sobri MFM, Abd-Aziz S, Ibrahim MF, Kamal Bahrin E, Mohammed Alitheen NB, Ramli N (2020) Combined optimization of codon usage and glycine supplementation enhances the extracellular production of a beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus sp. NR5 UPM in Escherichia coli. Int J Mol Sci 21(11):3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113919
Pawar S, Shende P (2020) A Comprehensive patent review on beta-cyclodextrin cross-linked nanosponges for multiple applications. Recent Pat Nanotechnol 14(1):75–89. https://doi.org/10.2174/1872210513666190603083930
Petitjean M, Garcia-Zubiri IX, Isasi JR (2021) History of cyclodextrin-based polymers in food and pharmacy: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(4):3465–3476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01244-5
Pishtiyski I, Popova V, Zhekova B (2008) Characterization of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase produced by Bacillus megaterium. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 144(3):263–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8009-y
Rosso AM, Ferrarotti SA, Krymkiewicz N, Nudel BC (2002) Optimisation of batch culture conditions for cyclodextrin glucanotransferase production from Bacillus circulans DF 9R. Microb Cell Fact 1(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-1-3
Sakellaropoulou A, Siamidi A, Vlachou M (2022) Melatonin/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: a review. Molecules 27(2):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020445
Stella VJ, He Q (2008) Cyclodextrins. Toxicol Pathol 36(1):30–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623307310945
Tian B, Hua S, Liu J (2020) Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems for chemotherapeutic anticancer drugs: a review. Carbohydr Polym 232:115805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115805
Topuz F, Uyar T (2018) Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functional nanofibers for drug delivery applications. Pharmaceutics 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010006
Upadhyay D, Sharma S, Shrivastava D, Kulshreshtha NM (2019) Production and characterization of beta-cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from Bacillus sp. ND1. J Basic Microbiol 59(2):192–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201800390
Wang H, Zhou W, Li H, Rie B, Piao C (2017) Improved activity of beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus sp. N-227 via mutagenesis of the conserved residues. 3 Biotech 7(2):149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0725-6
Wang H, Zhou W, Li H, Bu R (2018) Optimization of the fermentation conditions for the mutant strain of beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase H167C to produce cyclodextrins. 3 Biotech 8(3):165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1182-6
Yadav M, Thakore S, Jadeja R (2022) A review on remediation technologies using functionalized Cyclodextrin. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29(1):236–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15887-y
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (2019MS03079, 2021BS0824), Research Program of science and technology at Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (NJZY19149), The Research Ability Enhancement program for Young Teachers of Inner Mongolia Minzu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HW, WZ: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing-original draft. YZ, CW, CL, JX, ZZ, HL, JL, YM: methodology, formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhou, W., Zhang, Y. et al. The synergistic effect of metal ions and amino acids on the fermentation of β-CGTase-producing statin DF257. 3 Biotech 14, 53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03900-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03900-9