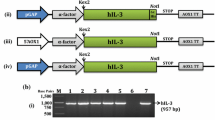
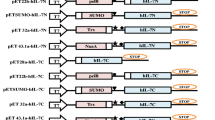
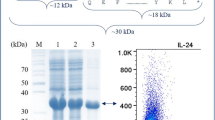
Abstract
Human interleukin-3 (hIL-3) is a clinically important cytokine used to treat hematological malignancies, bone marrow transplantation, cytopenias, and immunological disorders. The cloning of hIL-3 gene was previously reported by our group, where its expression was optimized under methanol-inducible AOX1 promoter having N-terminal α mating factor signal sequence from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This study investigated the role of glycosylation pattern on its molecular stability, secretion efficiency, and biological activity using the mutagenesis approach. The two N-linked glycosylation positions at N15th (Asn15) and N70th (Asn70) were sequentially mutated to generate three recombinant hIL-3 variants, i.e., N15A, N70A, and N15/70A. Asparagine at these positions was replaced with non-polar alanine amino acid (Ala, A). The alteration of N-linked glycosylation sites was disadvantageous to its efficient secretion in Pichia pastoris, where a 52.32%, 36.48%, 71.41% lower production was observed in N15A, N70A, and N15/70A mutants, respectively, as compared to native control. The fully glycosylated native hIL-3 protein showed higher thermal stability over its deglycosylated counterparts. The biological activity of native, N15A, N70A, and N15/70A hIL-3 protein was evaluated, where N15/70A mutant showed slightly higher proliferation efficacy than other combinations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adivitiya B, Mohanty S, Khasa YP (2018) Engineering of deglycosylated and plasmin resistant variants of recombinant streptokinase in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:10561–10577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9402-x
Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H, Schwab H (2014) Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5301–5317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5732-5
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bretthauer RK, Castellino FJ (1999) Glycosylation of Pichia pastoris-derived proteins. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 30(Pt 3):193–200
Curtis BM, Williams DE, Broxmeyer HE et al (1991) Enhanced hematopoietic activity of a human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-interleukin 3 fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:5809–5813
Dagar VK, Adivitiya null, Khasa YP (2016) High-level expression and efficient refolding of therapeutically important recombinant human Interleukin-3 (hIL-3) in E. coli. Protein Expr Purif 131:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2016.11.005
Dagar VK, Khasa YP (2018) Combined effect of gene dosage and process optimization strategies on high-level production of recombinant human interleukin-3 (hIL-3) in Pichia pastoris fed-batch culture. Int J Biol Macromol 108:999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.008
Dagar VK, Adivitiya DN, Khasa YP (2016) Bioprocess development for extracellular production of recombinant human interleukin-3 (hIL-3) in Pichia pastoris. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:1373–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1816-9
Ding H, Griesel C, Nimtz M et al (2003) Molecular cloning, expression, purification, and characterization of soluble full-length, human interleukin-3 with a baculovirus–insect cell expression system. Protein Expr Purif 31:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1046-5928(03)00138-4
Dotsenko AS, Gusakov AV, Volkov PV et al (2016) N-linked glycosylation of recombinant cellobiohydrolase I (Cel7A) from Penicillium verruculosum and its effect on the enzyme activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 113:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25812
Durchschlag H, Christl R, Jaenicke R (1991) Comparative determination of the particle weight of glycoproteins by SDS-PAGE and analytical ultracentrifugation. In: Borchard W (ed) Progress in analytical ultracentrifugation. Steinkopff, Darmstadt, pp 41–56
Freeman JJ, Parr GR, Hecht RI et al (1991) Secondary structure of human interleukin-3. Int J Biochem 23:353–360
Gupta R, Brunak S (2002) Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac Symp Biocomput 7:310–322
Gwen M, Cj L, Ed B, et al (2004) Role of N-linked glycosylation in the secretion and activity of endothelial lipase. J. Lipid Res. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15342690/.
Han M, Wang X, Ding H et al (2014) The role of N-glycosylation sites in the activity, stability, and expression of the recombinant elastase expressed by Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Technol 54:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.09.014
Haraguchi M, Yamashiro S, Furukawa K et al (1995) The effects of the site-directed removal of N-glycosylation sites from beta-1,4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase on its function. Biochem J 312:273–280
Hoffmeister KM, Josefsson EC, Isaac NA et al (2003) Glycosylation restores survival of chilled blood platelets. Science 301:1531–1534. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1085322
Ito K, Ishimaru T, Kimura F, Matsudomi N (2007) Importance of N-glycosylation positioning for secretion and folding of ovalbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.066
Kitamura T, Tange T, Terasawa T et al (1989) Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol 140:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041400219
Klein BK, Olins PO, Bauer SC et al (1999) Use of combinatorial mutagenesis to select for multiply substituted human interleukin-3 variants with improved pharmacologic properties. Exp Hematol 27:1746–1756
Lee J, Park J-S, Moon J-Y et al (2003) The influence of glycosylation on secretion, stability, and immunogenicity of recombinant HBV pre-S antigen synthesized in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:427–432
Li H, Li N, Gao X et al (2011) High level expression of active recombinant human interleukin-3 in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 80:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2011.08.027
Li R, Xie C, Zhang Y et al (2014) Expression of recombinant human IL-4 in Pichia pastoris and relationship between its glycosylation and biological activity. Protein Expr Purif 96:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2014.01.005
Liu W-C, Inwood S, Gong T et al (2019) Fed-batch high-cell-density fermentation strategies for Pichia pastoris growth and production. Crit Rev Biotechnol 39:258–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2018.1554620
Looser V, Bruhlmann B, Bumbak F et al (2015) Cultivation strategies to enhance productivity of Pichia pastoris: a review. Biotechnol Adv 33:1177–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.05.008
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22:249–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1208
Newrzella D, Stoffel W (1996) Functional analysis of the glycosylation of murine acid sphingomyelinase. J Biol Chem 271:32089–32095
Nordén K, Agemark M, Danielson JÅ et al (2011) Increasing gene dosage greatly enhances recombinant expression of aquaporins in Pichia pastoris. BMC Biotechnol 11:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-11-47
Potvin G, Ahmad A, Zhang Z (2012) Bioprocess engineering aspects of heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris: a review. Biochem Eng J 64:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2010.07.017
Radoman B, Grünwald-Gruber C, Schmelzer B et al (2021) The degree and length of O-Glycosylation of recombinant proteins produced in Pichia pastoris depends on the nature of the protein and the process type. Biotechnol J 16:e2000266. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.202000266
Rudd PM, Elliott T, Cresswell P et al (2001) Glycosylation and the immune system. Science 291:2370–2376
Sinclair AM, Elliott S (2005) Glycoengineering: the effect of glycosylation on the properties of therapeutic proteins. J Pharm Sci 94:1626–1635. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20319
Skropeta D (2009) The effect of individual N-glycans on enzyme activity. Bioorg Med Chem 17:2645–2653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2009.02.037
Su Y, Li S-Y, Ghosh S et al (2010) Characterization of variant diphtheria toxin-interleukin-3 fusion protein, DTIL3K116W, for phase I clinical trials. Biol J Int Assoc Biol Stand 38:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biologicals.2009.08.016
Tian B, Chen Y, Ding S (2012) A combined approach for improving alkaline acetyl xylan esterase production in Pichia pastoris, and effects of glycosylation on enzyme secretion, activity and stability. Protein Expr Purif 85:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2012.06.008
Trombetta ES (2003) The contribution of N-glycans and their processing in the endoplasmic reticulum to glycoprotein biosynthesis. Glycobiology 13:77R-91R. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwg075
Wang C, Eufemi M, Turano C, Giartosio A (1996) Influence of the carbohydrate moiety on the stability of glycoproteins. Biochemistry 35:7299–7307. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9517704
Wang XJ, Wang XM, Teng D et al (2014) Recombinant production of the antimicrobial peptide NZ17074 in Pichia pastoris using SUMO3 as a fusion partner. Lett Appl Microbiol 59:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12246
Wang Z, Guo C, Liu L, Huang H (2018) Effects of N-glycosylation on the biochemical properties of recombinant bEKL expressed in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Technol 114:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.03.004
Wang N, Wang KY, Xu F et al (2020) The effect of N-glycosylation on the expression of the tetanus toxin fragment C in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 166:105503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2019.105503
Westers L, Dijkstra DS, Westers H et al (2006) Secretion of functional human interleukin-3 from Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 123:211–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.11.007
Xu G, Wu Y, Zhang Y et al (2019) Role of N-glycosylation on the specific activity of a Coprinopsis cinerea laccase Lcc9 expressed in Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 128:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.05.004
Yang M, Yu X-W, Zheng H et al (2015) Role of N-linked glycosylation in the secretion and enzymatic properties of Rhizopus chinensis lipase expressed in Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Factories 14:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0225-5
Yoshimasu MA, Tanaka T, Ahn J-K, Yada RY (2004) Effect of N-linked glycosylation on the aspartic proteinase porcine pepsin expressed from Pichia pastoris. Glycobiology 14:417–429. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwh024
Zhai Z, Nuylert A, Isobe K, Asano Y (2019) Effects of codon optimization and glycosylation on the high-level production of hydroxynitrile lyase from Chamberlinius hualienensis in Pichia pastoris. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46:887–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02162-w
Funding
The research work was supported by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, New Delhi via Grant No. BT/PR5822/PID/6/684/2012 to Dr. Yogender Pal Khasa (Project Investigator). Vikas Kumar Dagar, acknowledges the financial support from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR, Govt. of India) New Delhi as he received a senior research fellowship (Sanction No. 3/1/3-JRF-2009/MPD-89).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dagar, V.K., Babbal, Mohanty, S. et al. Effect of N-glycosylation on secretion, stability, and biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-3 (hIL-3) in Pichia pastoris. 3 Biotech 12, 221 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03293-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03293-1