Abstract
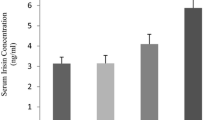
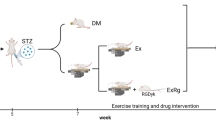
In the present study, we investigated the effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) versus moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) on irisin and expression of myogenic markers (paired box 7 (Pax7), myogenic differentiation 1 (MyoD), myogenin) in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. Eighty-four male Wistar rats (6 weeks of age) were randomly divided into seven groups (n = 12): basic control (Co Basic), 8 weeks control (Co 8w), diabetes mellitus (DM), HIIT, DM + HIIT, MICT, and DM + MICT groups. Diabetes was induced by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ). The \(\dot{V}{\text{o}}_{2\max }\)protocol was characterized by running on a rodent treadmill with moderate intensity (60–70% \(\dot{V}{\text{o}}_{2\max }\)), 60 min per session, 5 days/week, for 6 weeks. HIIT consisted of six 3-min runs at a high intensity (80–90% \(\dot{V}{\text{o}}_{2\max }\)) alternated with 2-min running at low intensity (50% \(\dot{V}{\text{o}}_{2\max }\)), 30 min per session, 5 days/week, for 6 weeks. Results showed that DM decreased myoblast markers compared to Co Basic and Co 8w groups. Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) mRNA decrease was correlated with myoblast markers (Pax7 r = 0.632, p = 0.027; MyoD r = 0.999, p = 0.001; myogenin r = 1.000, p = 0.001) in DM group. DM + MICT significantly increased gene expression of MyoD, myogenin, and FNDC5 compared to DM and DM + HIIT. The results also showed that the intensity and duration of exercise on the treadmill were effective in stimulating irisin and myogenic markers after DM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Experimental data can be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- FNDC5:
-
Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5
- HIIT:
-
High intensity interval training
- MICT:
-
Moderate intensity continuous training
- Pax7:
-
Paired box 7
- MyoD:
-
Myogenic differentiation 1
- FNDC5:
-
Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5
- SCs:
-
Satellite cells
References
Akagawa M, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Ono Y, Yuasa Y, Nagahata I, Sato C, Tsuchie H, Nagasawa H, Hongo M (2018) Effects of activated vitamin D, alfacalcidol, and low-intensity aerobic exercise on osteopenia and muscle atrophy in type 2 diabetes mellitus model rats. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0204857
Almada AE, Wagers AJ (2016) Molecular circuitry of stem cell fate in skeletal muscle regeneration, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(5):267–279
Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Catalano MG, Brignardello E, Danni O, Boccuzzi G (2004) Oxidative stress impairs skeletal muscle repair in diabetic rats. Diabetes 53(4):1082–1088
Baeza-Raja B, Muñoz-Cánoves P (2004) p38 MAPK-induced nuclear factor-κB activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation: role of interleukin-6. Mol Biol Cell 15(4):2013–2026
Bazgir B, Fathi R, Valojerdi MR, Mozdziak P, Asgari A (2017) Satellite cells contribution to exercise mediated muscle hypertrophy and repair. Cell Journal (yakhteh) 18(4):473
Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, Oppliger RA, Gisolfi CV (1979) Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol 47(6):1278–1283
Bell M, Levine C, Downey R, Griffitts C, Mann S, Frye C, Wakshlag J (2016) Influence of endurance and sprinting exercise on plasma adiponectin, leptin and irisin concentrations in racing Greyhounds and sled dogs. Aust Vet J 94(5):154–159
Bentzinger C, von Maltzahn J, Rudnicki MA (2010) Extrinsic regulation of satellite cell specification. Stem Cell Res Ther 1(3):27
Bianchi L, Volpato S (2016) Muscle dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: a major threat to patient’s mobility and independence. Acta Diabetol 53(6):879–889
Bonnefont-Rousselot D (2002) Glucose and reactive oxygen species. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 5(5):561–568
Charan J, Kantharia N (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4(4):303
Cohen S, Nathan JA, Goldberg AL (2015) Muscle wasting in disease: molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 14(1):58–74
de Lade CG, Andreazzi AE, Bolotari M, Costa VMG, Peters VM, de Oliveira GM (2018) Effects of moderate intensity endurance training vs. high intensity interval training on weight gain, cardiorespiratory capacity, and metabolic profile in postnatal overfed rats. Diabetol Metabol Syndr 10(1):70
D’Souza DM, Al-Sajee D, Hawke TJ (2013) Diabetic myopathy: impact of diabetes mellitus on skeletal muscle progenitor cells. Front Physiol 4:379
Farrash W, Brook M, Crossland H, Phillips BE, Cegielski J, Wilkinson DJ, Constantin-Teodosiu D, Greenhaff PL, Smith K, Cleasby M (2020) Impacts of rat hindlimb Fndc5/irisin overexpression on muscle and adipose tissue metabolism. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metabol 318(6):E943–E955
Francesconi C, Niebauer J, Haber P, Weitgasser R, Lackinger C (2019) Lifestyle: physical activity and training as prevetion and therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus (Update 2019). Wien Klin Wochenschr 131(Suppl 1):61–66
Furuichi Y, Kawabata Y, Aoki M, Mita Y, Fujii NL, Manabe Y (2021) Excess glucose impedes the proliferation of skeletal muscle satellite cells under adherent culture conditions. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:341
Ghardashi-Afousi A, Holisaz MT, Shirvani H, Pishgoo B (2018) The effects of low-volume high-intensity interval versus moderate intensity continuous training on heart rate variability, and hemodynamic and echocardiography indices in men after coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized clinical trial study. ARYA Atheroscler 14(6):260
Grant CW, Duclos SK, Moran-Paul CM, Yahalom B, Tirabassi RS, Arreaza-Rubin G, Spain LM, Guberski DL (2012) Development of standardized insulin treatment protocols for spontaneous rodent models of type 1 diabetes. Comp Med 62(5):381–390
Hazrati MS, Souri R, Ravasi A, Gorzi A (2015) Effect of high intensity interval training (HIIT) on level of irisin and insulin resistance index in rats
Heesch MW, Shute RJ, Kreiling JL, Slivka DR (2016) Transcriptional control, but not subcellular location, of PGC-1α is altered following exercise in a hot environment. J Appl Physiol 121(3):741–749
Hong O-K, Son J-W, Kwon H-S, Lee S-S, Kim S-R, Yoo SJ (2018) Alpha-lipoic acid preserves skeletal muscle mass in type 2 diabetic OLETF rats. Nutr Metab 15(1):1–11
Jafari M, Abbasi I, Fathi Aralloo S (2019) The effect of eight weeks high-intensity interval training (HIT) on of irisin levels in obese young men. Thrita 8(2):1–4
Jiang S, Piao L, Ma EB, Ha H, Huh JY (2021) Associations of circulating irisin with FNDC5 expression in fat and muscle in type 1 and type 2 diabetic mice. Biomolecules 11(2):322
Lagha M, Sato T, Bajard L, Daubas P, Esner M, Montarras D, Relaix F, Buckingham M (2008) Regulation of skeletal muscle stem cell behavior by Pax3 and Pax7. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, pp 307–315
Lakshmi PA, Suganthi V (2021) A review on physiological role of IRISIN: in vitro and in vivo studies. Ann Roman Soc Cell Biol 25(6):4814–4829
Leandro CG, Levada AC, Hirabara SM, Manhães-de-Castro R (2007) A program of moderate physical training for Wistar rats based on maximal oxygen consumption. J Strength Cond Res 21(3):751
Lourenco MV, Frozza RL, de Freitas GB, Zhang H, Kincheski GC, Ribeiro FC, Gonçalves RA, Clarke JR, Beckman D, Staniszewski A (2019) Exercise-linked FNDC5/irisin rescues synaptic plasticity and memory defects in Alzheimer’s models. Nat Med 25(1):165
Ma C, Ding H, Deng Y, Liu H, Xiong X, Yang Y (2021) Irisin: a new code uncover the relationship of skeletal muscle and cardiovascular health during exercise. Front Physiol 12:37
Millay DP, O’Rourke JR, Sutherland LB, Bezprozvannaya S, Shelton JM, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2013) Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 499(7458):301
Mirdar S, Kazemzadeh Y, Arabzadeh E, Shirvani H, Hamidian G (2019) The effects of tapering with and without ethanolic extract of Nigella sativa on Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α and exercise-induced bronchial changes. J Mil Med 21(2):131–141
Momenzadeh S, Zamani S, Pourteymourfard-Tabrizi Z, Barreiro C, Jami M-S (2021) Muscles proteome analysis; irisin administration mimics some molecular effects of exercise in quadriceps muscle. Biochimie 189:144–157
Nabeshima Y, Hanaoka K, Hayasaka M, Esuml E, Li S, Nonaka I, Nabeshima Y-i (1993) Myogenin gene disruption results in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature 364(6437):532
Napoli N, Chandran M, Pierroz DD, Abrahamsen B, Schwartz AV, Ferrari SL (2017) Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol 13(4):208
O’Donovan G, Owen A, Bird SR, Kearney EM, Nevill AM, Jones DW, Woolf-May K (2005) Changes in cardiorespiratory fitness and coronary heart disease risk factors following 24 wk of moderate-or high-intensity exercise of equal energy cost. J Appl Physiol 98(5):1619–1625
Papatheodorou K, Papanas N, Banach M, Papazoglou D, Edmonds M (2016) Complications of diabetes 2016. J Diabet Res 69(1):1–3
Passos E, Pereira C, Gonçalves I, Rocha-Rodrigues S, Silva N, Guimaraes J, Neves D, Ascensão A, Magalhães J, Martins M (2015) Role of physical exercise on hepatic insulin, glucocorticoid and inflammatory signaling pathways in an animal model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Life Sci 123:51–60
Pugh JK, Faulkner SH, Turner MC, Nimmo MA (2018) Satellite cell response to concurrent resistance exercise and high-intensity interval training in sedentary, overweight/obese, middle-aged individuals. Eur J Appl Physiol 118(2):225–238
Rahmati-Ahmadabad S, Azarbayjani M-A, Farzanegi P, Moradi L (2021) High-intensity interval training has a greater effect on reverse cholesterol transport elements compared with moderate-intensity continuous training in obese male rats. Eur J Prev Cardiol 28(7):692–701
Reisi J (2016) Effect of 8 weeks resistance training on plasma irisin protein level and muscle FNDC5 and adipose tissue UCP1 genes expression in male rats. Sport Physiol 7(28):117–130
Reza MM, Subramaniyam N, Sim CM, Ge X, Sathiakumar D, McFarlane C, Sharma M, Kambadur R (2017a) Irisin is a pro-myogenic factor that induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and rescues denervation-induced atrophy. Nat Commun 8(1):1104
Reza MM, Subramaniyam N, Sim CM, Ge X, Sathiakumar D, McFarlane C, Sharma M, Kambadur R (2017b) Irisin is a pro-myogenic factor that induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and rescues denervation-induced atrophy. Nat Commun 8(1):1–17
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108
Seale P, Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, Mansouri A, Gruss P, Rudnicki MA (2000) Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell 102(6):777–786
Serrano AL, Baeza-Raja B, Perdiguero E, Jardí M, Muñoz-Cánoves P (2008) Interleukin-6 is an essential regulator of satellite cell-mediated skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell Metab 7(1):33–44
Shirvani H, Arabzadeh E (2020) Metabolic cross-talk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training by regulation of PGC-1α. Eat Weight Disord-Stud Anorexia, Bulimia Obes 25(1):17–24
Smith C, Janney M, Allen RE (1994) Temporal expression of myogenic regulatory genes during activation, proliferation, and differentiation of rat skeletal muscle satellite cells. J Cell Physiol 159(2):379–385
Stein RA, Michielli DW, Glantz MD, Sardy H, Cohen A, Goldberg N, Brown CD (1990) Effects of different exercise training intensities on lipoprotein cholesterol fractions in healthy middle-aged men. Am Heart J 119(2):277–283
Tavassoli H, Heidarianpour A, Hedayati M (2019) The effects of resistance exercise training followed by de-training on irisin and some metabolic parameters in type 2 diabetic rat model. Arch Physiol Biochem 128(1):240–247
Teimourian M, Fatolahi H, Mateenhomaei H (2020) Effect of different exercise mode and ursolic acid supplementation on FNDC5 and UCP1 gene expression and plasma irisin in rats. Int J Sports Exerc Med 6(1):160
Timmons JA, Baar K, Davidsen PK, Atherton PJ (2012) Is irisin a human exercise gene? Nature 488(7413):E9–E10
Tine Kartinah N, Rosalyn SI (2018) The effects of exercise regimens on irisin levels in obese rats model: comparing high-intensity intermittent with continuous moderate-intensity training. BioMed Res Int 27(2):1–8
Usas A, Huard J (2007) Muscle-derived stem cells for tissue engineering and regenerative therapy. Biomaterials 28(36):5401–5406
Vosadi E, Ravasi AA, Soori R, Mazaheri Z, Shabkhiz F (2016) The effect of 4 weeks of endurance exercise on the expression of the muscle Myonectin levels and Insulin resistance in the adult rat. Pathobiol Res 19(2):89–97
Wang XJ, Xiao JJ, Liu L, Jiao HC, Lin H (2017) Excessive glucocorticoid-induced muscle MuRF1 overexpression is independent of Akt/FoXO1 pathway. Biosci Rep 37(6):1–7
Yoon H, Thakur V, Isham D, Fayad M, Chattopadhyay M (2015) Moderate exercise training attenuates inflammatory mediators in DRG of Type 1 diabetic rats. Exp Neurol 267:107–114
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS, EA, and MEZ designed and performed the research, analyzed data, performed histological analysis, and performed western blotting analysis. SRM, GM, and FR designed and performed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and approved the final version. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Research involving animals
The experimental protocol was approved by the local ethics committee of Baqiyatallah University of Medical Science (ethical code: IR.BMSU.REC.1396.632), and was in accordance with the current legislation on animal experimentation (Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, Eighth Edition 2011).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arabzadeh, E., Shirvani, H., Ebadi Zahmatkesh, M. et al. Irisin/FNDC5 influences myogenic markers on skeletal muscle following high and moderate-intensity exercise training in STZ-diabetic rats. 3 Biotech 12, 193 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03253-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03253-9