Abstract
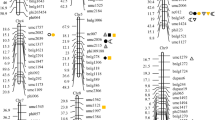
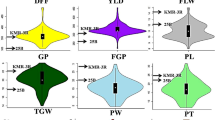
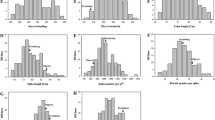
A doubled haploid (DH) population consisting of 125 DHLs derived from the popular rice hybrid, KRH-2 (IR58025A/KMR3R) was utilized for Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) mapping to identify novel genomic regions associated with yield related traits. A genetic map was constructed with 126 polymorphic SSR and EST derived markers, which were distributed across rice genome. QTL analysis using inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) method identified a total of 24 major and minor effect QTLs. Among them, twelve major effect QTLs were identified for days to fifty percent flowering (qDFF12-1), total grain yield/plant (qYLD3-1 and qYLD6-1), test (1,000) grain weight (qTGW6-1 and qTGW7-1), panicle weight (qPW9-1), plant height (qPH12-1), flag leaf length (qFLL6-1), flag leaf width (qFLW4-1), panicle length (qPL3-1 and qPL6-1) and biomass (qBM4-1), explaining 29.95–56.75% of the phenotypic variability with LOD scores range of 2.72–16.51. Chromosomal regions with gene clusters were identified on chromosome 3 for total grain yield/plant (qYLD3-1) and panicle length (qPL3-1) and on chromosome 6 for total grain yield/plant (qYLD6-1), flag leaf length (qFLL6-1) and panicle length (qPL6-1). Majority of the QTLs identified were observed to be co-localized with the previously reported QTL regions. Five novel, major effect QTLs associated with panicle weight (qPW9-1), plant height (qPH12-1), flag leaf width (qFLW4-1), panicle length (qPL3-1) and biomass (qBM4-1) and three novel minor effect QTLs for panicle weight (qPW3-1 and qPW8-1) and fertile grains per panicle (qFGP5-1) were identified. These QTLs can be used in breeding programs aimed to yield improvement after their validation in alternative populations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama HA, Eizenga GC, Yan W (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breed 19:341–356
Alam MM, Tanaka T, Nakamura H, Ichikawa H, Kobayashi K, Yaeno T, Yamaoka N, Shimomoto K, Takayama K, Nishina H, Nishiguchi M (2015) Overexpression of a rice heme activator protein gene (OsHAP2E) confers resistance to pathogens, salinity and drought, and increases photosynthesis and tiller number. Plant Biotechnol J 13:85–96
Bai XF, Luo LJ, Yan WH, Kovi MR, Xing YZ (2011) Quantitative trait loci for rice yield-related traits using recombinant inbred lines derived from two diverse cultivars. J Genet 90(2):209–215
Balachandran SM, Sarma NP, Siddiq E (1999) Inheritance of anther culture response in rice. Curr Sci 77:962–964
Balakrishnan D, Subrahmanyam D, Badri J, Raju AK, RaoYV BK, Mesapogu S, Surapaneni M, PonnuswamyR PG, Babu VR, Neelamraju S (2016) Genotype × environment interactions of yield traits in backcross introgression lines derived from Oryza sativa cv Swarna/Oryza Nivara. Front Plant Sci 7:1530
Balakrishnan D, Surapaneni M, Yadavalli VR et al (2020) Detecting CSSLs and yield QTLs with additive, epistatic and QTL×environment interaction effects from Oryza sativa × O. nivara IRGC81832 cross. Sci Rep 10:7766. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64300-0
Bernier J, Kumar A, Ramaiah V, Spaner D, Atlin G (2007) A large-effect QTL for grain yield under reproductive-stage drought stress in upland rice. Crop Sci 47:505–516
Bing Y, Xue WY, Luo LJ, Xing YZ (2006) QTL analysis for flag leaf characteristics and their relationships with yield and yield traits in rice. Acta Genet Sin 3(9):824–832
Brondani C, Rangel PHN, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2002) QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203
Calayugan MIC, Formantes AK, Amparado A, Descalsota-Empleo GI, Nha CT et al (2020) Genetic analysis of agronomic traits and grain iron and zinc concentrations in a doubled haploid population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Rep 10:2283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59184
Cho TG, Kang HJ, Lee JS, Lee YT, Lim SJ, Gauch H, Eun MY, McCouch SR (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci in rice for yield, yield components, and agronomic traits across years and locations. Crop Sci 47:2403–2417
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196
Collard BCY, Cruz CMV, McNally KL, Virk PS, Mackill DJ (2008) Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: Current status and future considerations. Int J Plant Genom. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/524847
Dellaporta SL, Jonathan W, James BH (1983) A plant DNA mini preparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1(4):19–21
Descalsota-Empleo GI, Amparado A, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Tesoroa F, Stangoulisc J, Reinkea R, MallikarjunaSwamy BP (2019) Genetic mapping of QTL for agronomic traits and grain mineral elements in rice. Crop J 7(4):560–572
Donde R, Kumar J, Gouda G, Gupta M, Mukherjee M et al (2019) Assessment of genetic diversity of drought tolerant and susceptible rice genotypes using microsatellite markers. Rice Sci 26:239–247
Dutta P, Dutta PN, Borua PK (2013) Morphological trait as selection indices in rice: a statistical view. Univ J Agric Res 1(3):85–96
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4 ed. Longman, Harlow
Fiyaz RA, Yadav AK, Krishnan SG, Ellur RK, Bashyal BM et al (2016) Mapping quantitative trait loci responsible for resistance to Bakanae disease in rice. Rice 9:3–10
George D, Mallery P (2010) SPSS for windows step by step: a simple guide and reference 17.0 update 10th edition. Pearson, Boston
Golam F, Yin YH, Masitah A, Afnierna N, Majid NA, Khalidn OM (2011) Analysis of aroma and yield components of aromatic rice in Malaysian tropical environment. Aust J Crop Sci 5(11):1318–1325
Gouda G, Gupta MK, Donde R, Kumar J, Vadde R, Mohapatra T, Behera L (2019) Computational approach towards understanding structural and functional role of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase 2 (CKX2) in enhancing grain yield in rice plant. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38(4):1158–1167
Gramaje LV, Caguiat JD, Oscar SJ, dela Cruz QD, Millas RA, Carampatana JE, Tabanao DAA (2020) Heterosis and combining ability analysis in CMS hybrid rice. Euphytica 216(14):1–22
Gravetter F, Wallnau L (2014) Essentials of statistics for the behavioral sciences. In: 8th Edition, Wadsworth, Belmont
Guo L, Gao Z, Qian Q (2014) Application of resequencing to rice genomics, functional genomics and evolutionary analysis. Rice 7(1):4
Han H, Huang (1987) Application of pollen-derived plants to crop improvement. Int Rev Cytol 107:293–313
He P, Li JZ, Zheng XW, Shen LS, Lu CF, Chen Y, Zhu LH (2001) Comparison of molecular linkage maps and agronomic trait loci between DH and RIL populations derived from the same rice cross. Crop Sci 41:1240–1246
Hittalmani S, Huang N, Courtois B, Venuprasad R, Shashidhar HE, Zhuang JY, Zheng KL, Liu GF, Wang GC, Sidhu JS, Srivantaneeyaku S, Singh VP, Bagali PG, Prasanna HC, McLaren G, Khush GS (2003) Identification of QTL for growth and grain yield-related traits in rice across nine locations of Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:679–690
Huang R, Jiang L, Zheng J, Wang T, Wang H, Huang Y et al (2013) Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci 18:218–226
IRRI. Standard Evaluation System for Rice (SES) Los Banos. Philippines: International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). In: 4 ed.2002; p. 15–16
Iwamoto M, Higo K, Takano M (2009) Circadian clock- and phytochrome-regulated Dof-like gene, Rdd1, isassociated with grain size in rice. Plant Cell Environ 32:592–603
Jaikishan I, Rajendrakumar P, Ramesha M, Viraktamath B, Balachandran S, Neeraja CN, Sujatha K, SrinivasaRao K, Natarajkumar P, Hari Y, Sakthivel K, Ramaprasad AS, Sundaram RM (2009) Prediction of heterosis for grain yield in rice using ‘key’ informative EST-SSR markers. Plant Breed 129:108–111
Jiang S, Wang D, Yan S, Liu S, Liu B, Kang H, Wang GL et al (2019) Dissection of the genetic architecture of rice tillering using a genome-wide association study. Rice 12(43):1–11
Johnson HW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimation of genetic and environmental variability in soyabeans. Agron J 47:314–318
Khush GS (1999) Green revolution: preparing for the 21st century. Genome 42(4):646–655
Khush GS (2003) Productivity improvements in rice. Nutr Rev 61:S114–S116
Kim CK, Chu SH, Park HY, Seo J, Kim B, Lee G, Koh HJ, Chin JH (2017) Identification of heterosis QTLs for yield and yield-related traits in Indica-Japonica recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed Biotech 5(4):371–389
Kinoshita N, Kato M, Koyasaki K, Kawashima T, Nishimura T, Hirayama Y, Takamure I, Sato T, Kato K (2017) Identification of quantitative trait loci for rice grain quality and yield-related traits in two closely related Oryza sativa L. subsp. japonica cultivars grown near the northernmost limit for rice paddy cultivation. Breed Sci 67:191–206
Kohnaki ME, Kiani G, Nematzadeh G (2013) Relationship between morphological traits in rice restorer lines at F3 generation using multivariate analysis. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 1(6):572–577
Konate AK, Zongo A, Kam H, Sanni A, Audebert A (2016) Genetic variability and correlation analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L.) inbred lines based on agromorphological traits. Afr J Agric Res 11(35):3340–3346
Koumoto T, Shimada H, Kusano H, She K-C, Iwamoto M, Takano M (2013) Rice monoculm mutation moc2, which inhibits outgrowth of the second tillers, is ascribed to lack of a fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Plant Biotechnol 30:47–56
Kulkarni SR, Ulaganathan K, Sundaram RM, Hari Prasad AS, Abdul Fiyaz R, Balachandran SM (2020a) Production of doubled haploids from rice hybrid KRH-2 through anther culture and their evaluation for agro-morphological traits. J Rice Res 13(1):33–50
Kulkarni SR, Balachandran SM, Ulaganathan K, Balakrishnan D, Praveen M et al (2020b) Molecular mapping of QTLs for yield related traits in recombinant inbred line (RIL) population derived from the popular rice hybrid KRH-2 and their validation through SNP genotyping. Sci Rep 10:13695. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70637-3
Kumar A, Singh VJ, Krishnan SG, Vinod KK, Bhowmick PK, Nagarajan M, Ellur RK, Bollinedi H, Singh AK (2019) WA-CMS-based iso-cytoplasmic restorers derived from commercial rice hybrids reveal distinct population structure and genetic divergence towards restorer diversification. 3 Biotech 9(299):1–15
Lee DK, Kim HI, Jang G, Chung PJ, Jeong JS, Kim YS et al (2015) The NF-YA transcription factor OsNF-YA7 confers drought stress tolerance of rice in an abscisic acid independent manner. Plant Sci 241:199–210
Li D, Sun C, Yongcai F, Li C, Zhu Z, Chen L, Cai H, Wang X (2002) Identification and mapping of genes for improving yield from Chinese common wild rice (O. rufipogon Griff.) using advanced backcross QTL analysis. Chin Sci Bull 47(18):1533–1537
Li X, Qian Q, Fu Z, Wang Y, Xiong G, Zeng D, Wang X, Liu X, Teng S, Hiroshi F, Yuan M, Luo D, Han B, Li J (2003) Control of tillering in rice. Nature 422:618–621
Lin H, Wang RX, Qian Q, Yan MX, Meng XB, Fu Z, Yan C, Jiang B, Su Z, Li J, Wang Y (2009) DWARF27, an iron-containing protein required for the biosynthesis of strigolactones, regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth. Plant Cell 21:1512–1525
Liu WZ, Chao W, Fu YP, Hu GC, Si HM, Zhu Li, Luan WJ, He ZQ, Sunet ZX (2009) Identification and characterization of HTD2: a novel gene negatively regulating tiller bud outgrowth in rice. Planta 230:649–658
Liu LH, Xie TT, Peng P, Qiu HY, Li XY (2017) Mutations in the MIT3 gene encoding a caroteniod isomerase lead to increased tiller number in rice. Plant Sci 267:1–10
Lu K, Wu BW, Wang J, Zhu W, Nie HP, Qian J, Huang W, Fang Z (2018) Blocking amino acid transporter OsAAP3 improves grain yield by promoting outgrowth buds and increasing tiller number in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1710–1722
Ma X, Feng F, Zhang Y, Eid I, Xu K, Li T, Mei H, Liu H, Gao N, Chen C, Luo L, Yu S (2019) A novel rice grain size gene OsSNB was identified by genome-wide association study in natural population. PLoS Genet 15:e1008191
Mahadevappa M (2004) Rice production in India-relevance of hybrid and transgenic technologies. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 64:1–4
Marathi B, Guleria S, Mohapatra T, Parsad R, Mariappan N, Kurungara VK, Atwal SS, Prabhu KV, Singh NK, Singh AK (2012) QTL analysis of novel genomic regions associated with yield and yield related traits in new plant type based recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 12:137
Matsubara K, Yamamoto E, Kobayashi N, Ishii T, Tanaka J, Tsunematsu H, Yoshinaga S, Matsumura O, Yonemaru J, Mizobuchi R, Yamamoto T, Kato H, Yano M et al (2016) Improvement of rice biomass yield through QTL-based selection. PLoS One 11:e0151830
McCouch SR (2008) Gene Nomenclature System for Rice. Rice 1(1):72–84
Mena M, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Schmidt RJ, Carbonero P (1998) An endosperm-specific DOF protein from barley, highly conserved in wheat, binds to and activates transcription from the prolamin-box of a native Bhordein promoter in barley endosperm. Plant J 16:53–62
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283
Mishra R, Rao GJN, Rao RN, Kaushal P (2015) Development and characterization of elite doubled haploid lines from two indica rice hybrids. Rice Sci 22(6):290–299
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song XJ, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M (2010) OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet 42:545–549
Miura K, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2011) The role of QTLs in the breeding of high-yielding rice. Trends Plant Sci 16:319–326
Nan J, Feng X, Wang C, Zhang X, Wang R, Liu J, Yuan Q, Jiang G, Lin S (2018) Improving rice grain length through updating the GS3 locus of an elite variety Kongyu 131. Rice 11(1):21
Nor Aishah H, Harun AR, MohdRafii Y, Norain MN, NurIzzah J (2014) Correlation analysis on agronomic characters in F1 population derived from a cross of PongsuSeribu 2 and MR 264. In: Research and Development Seminar 2014; Bangi (Malaysia); 14–16 Oct 2014; INIS-MY–2015–2016; INS. 46
Ogunbayo SA, Sie M, Ojo DK, Sanni KA, Akinwale MG, Toulou B, Shittu A, Idehen EO, Popoola AR, Daniel IO, Gregorio GB (2014) Genetic variation and heritability of yield and related traits in promising rice genotypes (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Breed Crop Sci 6(11):153–159
Oladosu Y, Rafii MY, Samuel C, Fatai A, Magaji U, Kareem I, Kamarudin ZS, Muhammad I, Kolapo K (2019) Drought resistance in rice from conventional to molecular breeding: a review. Int J Mol Sci 20(14):3519
Peng JY, Virmani SS (1991) Heterosis in some inter-varietal crosses of rice. Oryza 28:31–36
Pranathi K, Viraktamath BC, Neeraja CN, Balachandran SM, Prasad ASH et al (2016) Development and validation of candidate gene-specific markers for the major fertility restorer genes, Rf4, and Rf3, in rice. Mol Breed 36(10):145
Qi X, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhao Q, Zhu D, Yu J (2017) ZmDof3, a maize endosperm-specific Dof protein gene, regulates starch accumulation and aleurone development in maize endosperm. Plant Mol Biol. 93:7–20
Rafii MY, Zakiah MZ, Asfaliza R, Iffah HMD, Latif MA, Malek MA (2014) Grain quality performance and heritability estimation in selected F1 rice genotypes. Sains Malays 43(1):1–7
Raghavan C, Mauleon R, Lacorte V, Jubay M, Zaw H (2017) Approaches in characterizing genetic structure and mapping in a rice multiparental population. G3: Genes Genom Genet 7:1721–1730
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M (2008) Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:209–214
Segami S, Yamamoto T, Oki K, Noda T, Kanamori H, Sasaki H et al (2016) Detection of novel QTLs regulating grain size in extra-large grain rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines. Rice 9:34
Senadhira D, Zapata-Arias FJ, Gregorio GB, Alejar MS, De La Cruz HC, Padolina TF, Galvezcet AM (2002) Development of the first salt tolerant rice cultivar through indica/indica anther culture. Field Crops Res 76:103–110
Senguttuvel P, Revathi P, Kemparaju KB, Sruthi K, Sadath Ali M, KoteswaraRao P, Hari Prasad AS (2019) Rice hybrids released in India. In: Compendium No. 103/2019.ICAR-IIRR, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030. India. p. 127
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis E, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Shakiba E, Edwards JD, Jodari F, Duke SE, Baldo AM, Korniliev P, McCouch SR, Eizenga GC (2017) Genetic architecture of cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) determined through high resolution genome-wide analysis. PLoS One 12:e0172133
Sheeba NK, Viraktamath BC, Sivaramakrishnan S, Gangashetti MG, Khera P, Sundaram RM (2009) Validation of molecular markers linked to fertility restorer gene (s) for WA-CMS lines of rice. Euphytica 167:217–227
Shinji I, Masahiko M, Tomotsugu A, Kazumitsu O, Itsuro T, Junko K (2005) Suppression of tiller bud activity in tillering dwarf mutants of rice. Plant Cell Physiol 46:79–86
Singh N, Majumder S, Singh ON, Vikram P, Singh A, Singh S (2015) A large-effect QTL for grain weight in rice on chromosome 10. Aust J Crop Sci 9(5):372–377
Singh A, Carandang J, Gonzaga ZJC, Collard BCY, Ismail AM, Septiningsih EM (2017) Identification of QTLs for yield and agronomic traits in rice under stagnant flooding conditions. Rice 10:15
Spielman DJ, Kolady DE, Ward PS (2013) The prospects for hybrid rice in India. Food Sec 5:651–665
Sruthi K, Divya B, Senguttuvel P, Revathi P, Kemparaju KB, Koteswararao P, Sundaram RM et al (2019) Evaluation of genetic diversity of parental lines for development of heterotic groups in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 29:236–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-019-00529-9
Suh JP, Cho YC, Won Y-J, Ahn EK, Baek MK, Kim MK, Kim BK, Jena KK (2015) Development of resistant gene-pyramided japonica rice for multiple biotic stresses using molecular marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed Biotech 3:333–345
Suriyan C, Bootsaya S, Aussanee P, Chalermpol K (2009) An efficient procedure for embryogenic callus induction and doubled haploid plant regeneration through anther culture of Thai aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp indica.). In Vitro Cell. Dev Biol Plant 45(2):171–179
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Reddy GA, Viraktamath BC, Sarla N (2014) Mapping and introgression of QTL for yield and related traits in two backcross populations derived from Oryza sativa cv. Swarna and two accessions of O. nivara. J Genet 93:643–654
Thalapati S, Haritha G, Naga DN, Prasad BA, Surendhar RC, Swamy BPM, Batchu AK, Basava RK, Viraktamath BC, Neelamraju S (2015) Heterosis and combining ability in rice as influenced by introgressions from wild species Oryza rufipogon including qyld2.1 sub-QTL into the restorer line KMR3. Euphytica 202:81–95
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in advanced back cross population between Oryza rufipogon and Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Tinker NA, Mather DE, Rossnagel BG, Kasha KJ, Kleinhof A, Hayes PM, Falk DE, Ferguson T, Shugar LP, Legge WG, Irvine RB, Choo TM, Briggs KG, Ullrich SE, Franckowiak JD, Blake TK, Graf RJ, Dofing SM, Saghai-Maroof MA, Scoles GJ, Hoffman D, Dahleen LS, Killan A, Chen F, Biyashev RM, Kudrna DA, Steffenson BJ (1996) Regions of the genome that affect agronomic performance in two-row barley. Crop Sci 36(4):1053–1062
Virmani SS (1996) Hybrid rice. Advagron 57:378–462
Virmani SS, Mao CX, Hardy B (2003) Hybrid rice for food security, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 May 2002. International Rice Research Institute, Los Ban˜os, Philippines, p 407
Wang J (2009) Inclusive composite interval mapping of quantitative trait genes. Acta Agronom Sin 35:239–245
Wang YH, Li JY (2011) Branching in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:94–99
Wang Z, Taramino G, Yong D, Liu G, Tingey SV, Miao GL, Wang GL (2001) Rice ESTs with disease-resistance gene or defense-response gene-like sequences mapped to regions containing major resistance genes or QTLs. Mol Genet Genom 265(2):302–310
Wang Y, Wang J, Zhai L, Liang C, Chen K, Xu J (2020) Identify QTLs and candidate genes underlying source, sink and grain yield-related traits in rice by integrated analysis of bi-parental and natural populations. PLoS One 15(8):e0237774
Wanjari RH, Mandal KG, Ghosh PK, Adhikari T, Rao N (2006) Rice in India: present status and strategies to boost its production through hybrids. J Sustain Agric 28:19–39
Xing Y, Zhang Q (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:421–442
Xu M, Zhu L, Shou HX, Wu P (2005) A PIN1 family gene, OsPIN1, involved in auxin-dependent adventitious root emergence and Tillering in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol 46(10):1674–1681
Xu Y, Li P, Yang Z, Xu C (2017) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in crops. Crop J 5:175–184
Yeh SY, Chen HW, Ng CY, Lin CY, Tseng TH, Li WH, Ku MSB (2015) Down regulation of Cytokinin oxidase 2 expression increases tiller number and improves rice yield. Rice 8(1):36
Zapata-Arias FJ (2003) Laboratory protocol for anther culture technique in rice. In: Mauszynski M, Kasha KJ, Forster BP (eds) Doubled haploid production in crop plants, a manual. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 109–116
Zaw H, Raghavan C, Pocsedio A, Swamy M, Jubay ML, Singh RK, Bonifacio J, Mauleon R, Hernandez JE, Mendioro MS, Gregorio GB, Leung H (2019) Exploring genetic architecture of grain yield and quality traits in a 16-way indica by japonica rice MAGIC global population. Sci Rep 9:19605
Zhang ZH, Li P, Wang LX, Hua ZL, Zhu LH, Zhua YG (2004) Genetic dissection of the relationships of biomass production and partitioning with yield and yield related traits in rice. Plant Sci 167:1–8
Zhu YJ, Huang DR, Fan YY, Zhang ZH, Ying JZ, Zhuang JY (2016) Detection of QTLs for yield heterosis in rice using a RIL population and its testcross population. Int J Genom. Article ID 2587823
Acknowledgements
First author is grateful to DST INSPIRE Fellowship Division, New Delhi for providing the financial assistance (Grant # DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2013/1146, February 2014-March 2019). All authors are grateful to the Director, ICAR-IIRR for providing the infrastructural facilities for carrying out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMB, RMS, SRK, conceptualized the study; SMB, RMS, DB guided with methodology; SRK, DB carried out the investigation and completed the formal analysis; SRK prepared the original draft of the manuscript; SMB, RMS, DB, KU, guided with the critical review and editing of the manuscript; ASHP provided with the initial material for the development of doubled haploid population; GR, MBVNK, SKH, RRK, DA, MA, EP, TD, KP, MAD, MS, KC, PS helped with the recording of agro-morphological data of the doubled haploid data in the field for three consecutive seasons.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulkarni, S.R., Balachandran, S.M., Ulaganathan, K. et al. Mapping novel QTLs for yield related traits from a popular rice hybrid KRH-2 derived doubled haploid (DH) population. 3 Biotech 11, 513 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03045-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03045-7