Abstract
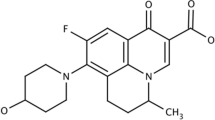
The aim of the present study was to develop and characterize karanjin-loaded ethosomes-based gel formulation for enhanced topical delivery and effective therapy of skin acne. Karanjin-loaded ethosomes (K-ETH) presented a nanometric size of 140.87 ± 2.35 nm, entrapment of 71.41 ± 2.74% and enhanced permeation with 1.9 times increase in the flux and 2.4 times higher skin deposition compared to the hydro-ethanolic solution of karanjin. The DSC analysis confirmed successful entrapment of the karanjin within the ethosomes. The developed ethosomes were incorporated in the carbopol gel for adequate application on the skin surface. The ethosomal gel (K-EGF) also exhibited greater penetration in the rat skin as revealed by CLSM. The optimized K-EGF formulation was non-irritant to the skin as evident by Draize score test and histopathological examination. The highest zone of inhibition, 30.0 ± 1.52 mm and 36.22 ± 0.57 mm was produced by the K-EGF against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis, respectively, indicating substantial antibacterial properties of the K-EGF. DPPH assay indicated its potent antioxidant effects. Substantial anti-inflammatory effects in the carrageenan-induced edema in the rat paw were evident with inhibition of rat paw edema by 66.66% and 70.37% upon application of K-EGF and standard anti-inflammatory agent, respectively. Anti-acne effects were also evident with K-EGF treatment with significant decrease in number and size of sebaceous gland units in dermis. Overall, the above findings vouch for a therapeutic opportunity to improve topical delivery of karanjin in acne treatment employing ethosomal gels as the promising carrier system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulbaqi I, Darwis Y, Khan AK et al (2016) Ethosomal nanocarriers: the impact of constituents and formulation techniques on ethosomal properties, in vivo studies, and clinical trials. IJN. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S105016
Ahmed TA (2015) Preparation of transfersomes encapsulating sildenafil aimed for transdermal drug delivery: Plackett-Burman design and characterization. J Liposome Res 25:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3109/08982104.2014.950276
Arora MK, Yadav A, Saini V (2011) Role of hormones in acne vulgaris. Clin Biochem 44:1035–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.06.984
Arshad N, Rashid N, Absar S, Abbasi M, Saleem S, Mirza B (2013) UV-absorption studies of interaction of karanjin and karanjachromene with ds. DNA: evaluation of binding and antioxidant activity. Open Chem 11:2040–2047
Azimi H, Fallah-Tafti M, Khakshur AA, Abdollahi M (2012) A review of phytotherapy of acne vulgaris: perspective of new pharmacological treatments. Fitoterapia 83:1306–1317
Bragagni M, Mennini N, Maestrelli F, Cirri M, Mura P (2012) Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes and ethosomes as carriers for improving topical delivery of celecoxib. J Drug Deliv 19:354–361
Chandrasekar D, Madhusudhana K, Ramakrishna S, Diwan PV (2006) Determination of DPPH free radical scavenging activity by reversed-phase HPLC: a sensitive screening method for polyherbal formulations. J Pharm Biomed 40:460–464
Chin JM, Goldstein DB (1997) Membrane disordering action of ethanol: variation with membrane cholesterol content and depth of the spin label probe. Mol Pharmacol 13:435–441
Chomnawang MT, Surassmo S, Nukoolkarn VS, Gritsanapan W (2005) Antimicrobial effects of Thai medicinal plants against acne-inducing bacteria. J Ethnopharmacol 101:330–333
Cong T-X, Hao D, Wen X, Li X-H, He G, Jiang X (2019) From pathogenesis of acne vulgaris to anti-acne agents. Arch Dermatol Res 311:337–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01908-x
Draize JH (1944) Methods for the study of irritation and toxicity of substances applied topically to the skin and mucous membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 82:377–390
Dreno B (2004) Topical antibacterial therapy for acne vulgaris. Drugs 64:2389–2397. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200464210-00002
Dubey V, Mishra D, Dutta T, Nahar M, Saraf D, Jain N (2007) Dermal and transdermal delivery of an anti-psoriatic agent via ethanolic liposomes. J Control Release 123:148–154
Fang J-Y, Sung K, Lin H-H, Fang C-L (1999) Transdermal iontophoretic delivery of diclofenac sodium from various polymer formulations: in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Pharm 178:83–92
Fang YP, Tsai YH, Wu PC, Huang YB (2008) Comparison of 5-aminolevulinic acid-encapsulated liposome versus ethosome for skin delivery for photodynamic therapy. Int J Pharm 356:144–152
Fox L, Csongradi C, Aucamp M, du Plessis J, Gerber M (2016) Treatment modalities for acne. Molecules 21:1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081063
Garg BJ, Garg NK, Beg S, Singh B, Katare OP (2016) Nanosized ethosomes-based hydrogel formulations of methoxsalen for enhanced topical delivery against vitiligo: formulation optimization, in vitro evaluation and preclinical assessment. J Drug Target 24:233–246. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2015.1070855
Garg V, Singh H, Bhatia A, Raza K, Singh SK, Singh B, Beg S (2017) Systematic development of transethosomal gel system of piroxicam: formulation optimization, in vitro evaluation, and ex vivo assessment. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 18:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-016-0489-z
Ghosh A, Tiwari GJ (2018) Role of nitric oxide-scavenging activity of Karanjin and Pongapin in the treatment of Psoriasis. 3 Biotech 8:338
Godin B, Touitou E (2004) Mechanism of bacitracin permeation enhancement through the skin and cellular membranes from an ethosomal carrier. J Control Release 94:365–379
Gollnick H, Cunliffe W, Berson D et al (2003) Management of Acne. JAAD 49:S1–S37. https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2003.618
Heng AHS, Chew FT (2020) Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep 10:5754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62715-3
Horita D, Hatta I, Yoshimoto M, Kitao Y, Todo H, Sugibayashi K (2015) Molecular mechanisms of action of different concentrations of ethanol in water on ordered structures of intercellular lipids and soft keratin in the stratum corneum. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1848:1196–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.02.008
Hurler J, Engesland A, Poorahmary KB, Škalko-Basnet N (2012) Improved texture analysis for hydrogel characterization: gel cohesiveness, adhesiveness, and hardness. J Appl Polym Sci 125:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.35414
Ibrahim TM, Abdallah MH, El-Megrab NA, El-Nahas HM (2019) Transdermal ethosomal gel nanocarriers; a promising strategy for enhancement of anti-hypertensive effect of carvedilol. J Liposome Res 29:215–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2018.1529793
International Conference on Harmonization (2003) Q1A (R2), Stability testing of new drug substances and products. In: Presented at the International Conference on Harmonization. International Conference on Harmonization Geneva
Kahraman E, Güngör S, Özsoy Y (2017) Potential enhancement and targeting strategies of polymeric and lipid-based nanocarriers in dermal drug delivery. Ther Del 8:967–985. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde-2017-0075
Kausar H, Mujeeb M, Ahad A, Moolakkadath T, Aqil M, Ahmad A, Akhter MH (2019) Optimization of ethosomes for topical thymoquinone delivery for the treatment of skin acne. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 49:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2018.11.016
Kumar A, Baboota S, Agarwal S, Ali J, Ahuja A (2008) Treatment of acne with special emphasis on herbal remedies. Exp Rev Dermat 3:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1586/17469872.3.1.111
Kumar B, Pathak R, Mary PB, Jha D, Sardana K, Gautam HK (2016) New insights into acne pathogenesis: Exploring the role of acne-associated microbial populations. Dermatol Sin 34:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsi.2015.12.004
Negi LM, Jaggi M, Talegaonkar S (2013) A logical approach to optimize the nanostructured lipid carrier system of irinotecan: efficient hybrid design methodology. Nanotechnology 24:015104. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/1/015104
Orfanos CE, Zouboulis ChC, Almond-Roesler B et al (1997) Current use and future potential role of retinoids in dermatology. Drugs 53:358–388
Patel PP, Trivedi ND (2012) Karanjin ameliorates DSS induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Pharm Sci Res 6:4866–4874
Rani MS, Dayanand C, Shetty J, Vegi PK, Kutty AM (2013) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of pongamia pinnata linn on pathogens of clinical isolates. Am J Phytomed Clin Ther 1:645–651
Ravikumar V, Khan MS, Kumar MM (2011) Development of RP-HPLC method for the quantification of karanjin in the seeds extracts of Pongamia glabra. Int J Pharm Tech 3:1433–1448
Remington JP (2006) Remington: the science and practice of pharmacy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Shahtalebi M, Asghari G, Rahmani F, Shafiee F, Jahanian-Najafabadi A (2018) Formulation of herbal gel of Antirrhinum majus extract and evaluation of its anti-propionibacterium acne effects. Adv Biomed Res 7:53. https://doi.org/10.4103/abr.abr_99_17
Shejawal N, Menon S, Shailajan S (2014) Bioavailability of karanjin from Pongamia pinnata L. in Sprague dawley rats using validated RP-HPLC method. J App Pharm Sci 4:10–14
Singh R, Pandey B (1996) Anti-Inflammatory activity of seed extracts of Ponamia pinnata in Rat. Ind J Phys Pharmacol 40:355–358
Singh A, Jahan I, Sharma M, Rangan L, Khare A, Panda AN (2016) Structural characterization, in silico studies and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of a furanoflavonoid from karanj. Planta Medica Let 3:e91–e95
Srinivasan K, Muruganandan S, Lal J et al (2001) Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Pongamia pinnata leaves in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 78:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00333-6
Tanghetti EA (2013) The role of inflammation in the pathology of acne. J Clin Aesthetic Dermat 6:27
Touitou E, Dayan N, Bergelson L, Godin B, Eliaz M (2000) Ethosomes; novel vesicular carriers for enhanced delivery: characterization and skin penetration properties. J Control Release 65:403–418
Ujwal P, Kumar M, Naika HR, Hosetti B (2007) Antimicrobial activity of different extracts of Pongamia pinnata. Med Aromat Plant Sci Biotechnol 1:285–287
Verma P, Pathak K (2012) Nanosized ethanolic vesicles loaded with econazole nitrate for the treatment of deep fungal infections through topical gel formulation. Nanomedicine 8:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.07.004
Wong A, Zhang B, Jiang M, Gong E, Zhang Y, Lee S (2016) Oxidative stress in acne vulgaris. J Clin Dermatol Ther 3:020
Yang L, Wu L, Wu D, Shi D, Wang T, Zhu X (2017) Mechanism of transdermal permeation promotion of lipophilic drugs by ethosomes. IJN 12:3357–3364. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134708
Yang JH, Hwang EJ, Moon J et al (2019) Clinical efficacy of herbal extracts in treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris: an 8-week, double-blinded, randomized, controlled trial. J Dermatol Treat 16:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1657792
Yeşilada E, Küpeli E (2002) Berberis crataegina DC. root exhibits potent anti-inflammatory, analgesic and febrifuge effects in mice and rats. J Ethnopharmacol 79:237–248
Yi D, Wang Z, Yi L (2015) Development and validation of an LC-MS method for determination of karanjin in rat plasma: application to preclinical pharmacokinetics. J Chromatogr Sci 53:456–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmu064
Yu Z, Lv H, Han G, Ma K (2016) Ethosomes loaded with cryptotanshinone for acne treatment through topical gel formulation. PLoS ONE 11:e0159967. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159967
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Head, Department of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, School of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi, India, for providing necessary research facilities to carry out this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, S.A., Qadir, A., Warsi, M.H. et al. Ethosomes-based gel formulation of karanjin for treatment of acne vulgaris: in vitro investigations and preclinical assessment. 3 Biotech 11, 456 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02978-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02978-3