Abstract
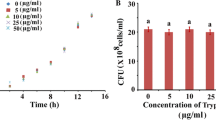
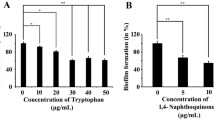
Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive bacterium has been implicated in a plethora of human infections by virtue of its biofilm-forming ability. Inhibition in microbial biofilm formation has been found to be a promising approach towards compromising microbial pathogenesis. In this regard, various natural and synthetic molecules have been explored to attenuate microbial biofilm. In this study, the role of an amino acid, L-tryptophan was examined against the biofilm-forming ability of S. aureus. The compound did not execute any antimicrobial characteristics, instead, showed strong antibiofilm activity with the highest biofilm inhibition at a concentration of 50 µg/mL. Towards understanding the underlying mechanism of the same, efforts were given to examine whether tryptophan could inhibit biofilm formation by interfering with the quorum-sensing property of S. aureus. A molecular docking analysis revealed an efficient binding between the quorum-sensing protein, AgrA, and tryptophan. Moreover, the expression of the quorum-sensing gene (agrA) got significantly reduced under the influence of the test compound. These results indicated that tryptophan could interfere with the quorum-sensing property of the organism thereby inhibiting its biofilm formation. Further study revealed that tryptophan could also reduce the cell surface hydrophobicity of S. aureus by downregulating the expression of dltA. Moreover, the tested concentrations of tryptophan did not show any significant cytotoxicity. Hence, tryptophan could be recommended as a potential antibiofilm agent to manage the biofilm-associated infections caused by S. aureus.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information file. The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Ravaioli S, Montanaro L (2015) Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 5:7
Bronner S, Monteil H, Prévost G (2004) Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:183–220
Ceri H, Olson ME, Stremick C, Read RR, Morck D, Buret A (1999) The Calgary Biofilm Device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J Clin Microbiol 37:1771–1776
Chakraborty P, Joardar S, Ray S, Biswas P, Maiti D, Tribedi P (2018a) 3, 6-Di (pyridin-2-yl)-1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazine (pytz)-capped silver nanoparticles (TzAgNPs) inhibit biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach toward breaking the wall of biofilm through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Folia Microbiol 63:763–772
Chakraborty P, Daware AV, Kumari M, Chatterjee A, Bhattacharyya D, Mitra G, Akhter Y, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2018b) Free tryptophan residues inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach to inhibit the development of microbial biofilm. Arch Microbiol 200:1419–1425
Chakraborty P, Dastidar D, Paul P, Dutta S, Basu D, Sharma S, Basu S, Sarker R, Sen A, Sarkar A, Tribedi P (2020) Inhibition of biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by caffeine: a potential approach for sustainable management of biofilm. Arch Microbiol 202:623–635
Chakraborty P, Paul P, Kumari M, Bhattacharjee S, Singh M, Maiti D, Dastidar DG, Akhter Y, Kundu T, Tribedi DA, P, (2021) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by thymoquinone: an individual and combinatorial study with tetrazine-capped silver nanoparticles and tryptophan. Folia Microbiol 66(2):255–271
Ciofu O, Tolker-Nielsen T (2019) Tolerance and resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to antimicrobial agents-How P. aeruginosa can escape antibiotics. Front Microbiol 10:913
Costa O, Raaijmakers JM, Kuramae EE (2018) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front Microbiol 9:1636
Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, GötzF, (1999) The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun 67:5427–5433
Das MC, Das A, Samaddar S, Daware AV, Ghosh C, Acharjee S, Sandhu P, Jawed JJ, De UC, Majumdar S, Gupta SKD (2018) Vitexin alters Staphylococcus aureus surface hydrophobicity to interfere with biofilm formation. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/301473
Donlan RM (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8:881–890
Dwivedi S, Wahab R, Khan F, Mishra YK, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA (2014) Reactive oxygen species mediated bacterial biofilm inhibition via zinc oxide nanoparticles and their statistical determination. PLoS ONE 9:e111289
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
Gad GFM, El-Feky MA, El-Rehewy MS, Hassan MA, Abolella H, Abd El-Baky RM (2009) Detection of icaA, icaD genes and biofilm production by Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from urinary tract catheterized patients. J Infect Dev Ctries 3(05):342–351
Garrett TR, Bhakoo M, Zhang Z (2008) Bacterial adhesion and biofilms on surfaces. Pro Nat Sci 18:1049–1056
Geisinger E, Muir TW, Novick RP (2009) Agr receptor mutants reveal distinct modes of inhibition by staphylococcal auto inducing peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1216–2122
Ghosh S, Qureshi A, Purohit HJ (2019) D-Tryptophan governs biofilm formation rates and bacterial interaction in P. mendocina and S. aureus. J Biosci 44(1):3
Gilan I, Hadar Y, Sivan A (2004) Colonization, biofilm formation and biodegradation of polyethylene by a strain of Rhodococcus ruber. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:97–104
Goel S, Mishra P (2018) Thymoquinone inhibits biofilm formation and has selective antibacterial activity due to ROS generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(4):1955–1967
Gross M, Cramton SE, Götz F, Peschel A (2001) Key role of teichoic acid net charge in Staphylococcus aureus colonization of artificial surfaces. Infect Immun 69:3423–3426
Gupta P, Sarkar S, Das B, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2016) Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol 198:1–15
Heilmann C, Götz F (1998) Further characterization of Staphylococcus epidermidis transposon mutants deficient in primary attachment or intercellular adhesion. Zentralblattfür Bakteriologie 287:69–83
Heilmann C, Gerke C, Perdreau-Remington F, Götz F (1996) Characterization of Tn917 insertion mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis affected in biofilm formation. Infect Immun 64:277–282
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD—visual molecular dynamics. J Molec Graph 14:33–38
Imlay JA (2003) Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:395–418
Koenig RL, Ray JL, Maleki SJ, Smeltzer MS, Hurlburt BK (2004) Staphylococcus aureus AgrA binding to the RNAIII-agr regulatory region. J Bacteriol 186(22):7549
Kouidhi B, Zmantar T, Hentati H, Bakhrouf A (2010) Cell surface hydrophobicity, biofilm formation, adhesives properties and molecular detection of adhesins genes in Staphylococcus aureus associated to dental caries. Microb Pathog 49:14–22
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lebeaux D, Chauhan A, Rendueles O, Beloin C (2013) From in vitro to in vivo models of bacterial biofilm-related infections. Pathogens 2:288–356
Li H, Ye Y, Ling N, Wu Q, Zhang J (2015) Inhibitory effects of D-Tryptophan on biofilm development by the foodborne Cronobacter sakazakii. Int Dairy J 49:125–129
Lister JL, Horswill AR (2014) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:178
Mack D, Fischer W, Krokotsch A, Leopold K, Hartmann R, Egge H, Laufs R (1996) The intercellular adhesin involved in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis is a linear beta-1, 6-linked glycosaminoglycan: purification and structural analysis. J Bacteriol 178:175–183
Maric S, Vranes J (2007) Characteristics and significance of microbial biofilm formation. Period Biol 109:115–121
Miller MB, Bassler BL (2001) Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:165–199
Moreira CS, Silva ACJA, Novais JS, SáFigueiredo AM, Ferreira VF, Rocha DR, Castro HC (2016) Searching for a potential antibacterial lead structure against bacterial biofilms among new naphthoquinone compounds. J Appl Microbiol 122:651–662
Mukherjee K, Tribedi P, Mukhopadhyay B, Sil AK (2013) Antibacterial activity of long-chain fatty alcohols against Mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 338:177–183
Novick RP (2003) Auto induction and signal transduction in the regulation of Staphylococcal virulence. Mol Microbiol 48:1429–1449
Novick RP, Geisinger E (2008) Auto induction and signal transduction in the regulation of Staphylococcal virulence. Annu Rev Genet 42:541–564
Otto M (2008) Staphylococcal biofilms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 322:207–228
Paharik AE, Horswill AR (2016) The Staphylococcal biofilm: adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0022-2015
Paul P, Chakraborty P, Chatterjee A, Sarker RK, Dastidar DG, Kundu T, Sarkar N, Das A, Tribedi P (2021) 1, 4-Naphthoquinone 1 accumulates reactive oxygen species in Staphylococcus aureus: a promising approach towards effective management of biofilm threat. Arch Microbiol 203(3):1183–1193
Phillips JC, Hardy DJ, Maia JD, Stone JE, Ribeiro JV, Bernardi RC, Buch R, Fiorin G, Hénin J, Jiang W, McGreevy R (2020) Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J Chem Phys 153:044130
Reifsteck F, Wee S, Wilkinson BJ (1987) Hydrophobicity-hydrophilicity of Staphylococci. J Med Microbiol 24:65–73
Rosenberg M, Perry A, Bayer EA, Gutnick DL, Rosenberg E, Ofek I (1981) Adherence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 to human epithelial cells and to hexadecane. Infect Immun 33:29–33
Rybtke M, Hultqvist LD, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2015) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections: community structure, antimicrobial tolerance and immune response. J Mol Biol 427:3628–3645
Sarkar S, Pires MM (2015) d-Amino acids do not inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117613
Sarker RK, Chakraborty P, Paul P, Chatterjee A, Tribedi P (2020) Degradation of low-density poly ethylene (LDPE) by Enterobacter cloacae AKS7: a potential step towards sustainable environmental remediation. Arch Microbiol 202:2117–2125
Su HL, Chou CC, Hung DJ, Lin SH, Pao IC, Lin JH, Huang FL, Dong RX, Lin JJ (2009) The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials 30:5979–5987
Szank T, Kealey C, Brady D (2019) D-Amino acids do no inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus sp. Access Microbiology 1(1A):873
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tribedi P, Sil AK (2014) Cell surface hydrophobicity: a key component in the degradation of polyethylene succinate by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2. J Appl Microbiol 116:295–303
Tribedi P, Gupta AD, Sil AK (2015) Adaptation of Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 in biofilm on low-density polyethylene surface: an effective strategy for efficient survival and polymer degradation. Bioresour Bioprocess 2:1–10
Vuong C, Voyich JM, Fischer ER, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, DeLeo FR, Otto M (2004) Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) protects Staphylococcus epidermidis against major components of the human innate immune system. Cell Microbiol 6(3):269–275
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Sharmistha Das and Ms. Sudipta Chatterjee for a critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PP, PC, RKS, AC, DM, AD and SM performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. DGD, SB and PT conceived the idea, designed the experiments and edited the manuscript critically.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, P., Chakraborty, P., Sarker, R.K. et al. Tryptophan interferes with the quorum sensing and cell surface hydrophobicity of Staphylococcus aureus: a promising approach to inhibit the biofilm development. 3 Biotech 11, 376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02924-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02924-3