Abstract
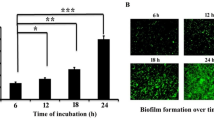
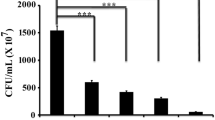
Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive opportunistic microorganism, promotes pathogenicity in the human host through biofilm formation. Microorganisms associated with biofilm often exhibit drug-resistance property that poses a major threat to public healthcare. Thus, the exploration of new therapeutic approaches is the need of the hour to manage biofilm-borne infections. In the present study, efforts are put together to test the antimicrobial as well as antibiofilm activity of 1,4-naphthoquinone against Staphylococcus aureus. The result showed that the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of this compound was found to be 100 µg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus. In this regard, an array of experiments (crystal violet, biofilm protein measurement, and microscopic analysis) related to biofilm assay were conducted with the sub-MBC concentrations (1/20 and 1/10 MBC) of 1,4-naphthoquinone. All the results of biofilm assay demonstrated that these tested concentrations (1/20 and 1/10 MBC) of the compound (1,4-naphthoquinone) showed a significant reduction in biofilm development by Staphylococcus aureus. Moreover, the tested concentrations (1/20 and 1/10 MBC) of the compound (1,4-naphthoquinone) were able to reduce the microbial motility of Staphylococcus aureus that might affect the development of biofilm. Further studies revealed that the treatment of 1,4-naphthoquinone to the organism was found to increase the cellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that resulted in the inhibition of biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus. Hence, it can be concluded that 1,4-naphthoquinone might be considered as a promising compound towards biofilm inhibition caused by Staphylococcus aureus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babula P, Adam V, Havel L, Kizek R (2007) Naphthoquinones and their pharmacological properties. Ceska Slov Farm 56(3):114–120
Boles BR, Horswill AR (2011) Staphylococcal biofilm disassembly. Trends Microbiol 19(9):449–455
Chakraborty P, Joardar S, Ray S, Biswas P, Maiti D, Tribedi P (2018) 3, 6-Di (pyridin-2-yl)-1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazine (pytz)-capped silver nanoparticles (TzAgNPs) inhibit biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach toward breaking the wall of biofilm through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Folia Microbiol 63(6):763–772
Chakraborty P, Daware AV, Kumari M, Chatterjee A, Bhattacharyya D, Mitra G, Akhter Y, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2018) Free tryptophan residues inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach to inhibit the development of microbial biofilm. Arch Microbiol 200(10):1419–1425
Chakraborty P, Dastidar D, Paul P, Dutta S, Basu D, Sharma S, Basu S, Sarker R, Sen A, Sarkar A, Tribedi P (2020) Inhibition of biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by caffeine: a potential approach for sustainable management of biofilm. Arch Microbiol 202(3):623–635
Conrad A, Suutari MK, Keinänen MM, Cadoret A, Faure P, Mansuy-Huault L, Block JC (2003) Fatty acids of lipid fractions in extracellular polymeric substances of activated sludge flocs. Lipids 38(10):1093–1105
Cortes ME, Consuegra J, Sinisterra RD (2011) Biofilm formation, control, and novel strategies for eradication. Sci Against Microbial Pathog Commun Curr Res Technol Adv 2:896–905
Costa O, Raaijmakers JM, Kuramae EE (2018) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front Microbiol 9:1636
Das A, Gopalakrishnan B, Voss OH, Doseff AI, Villamena FA (2012) Inhibition of ROS-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells by nitrone spin traps via induction of phase II enzymes and suppression of mitochondria-dependent pro-apoptotic signaling. Biochem Pharmacol 84(4):486–497
Das MC, Paul S, Gupta P, Tribedi P, Sarkar S, Manna D, Bhattacharjee S (2016) 3-Amino-4-aminoximidofurazan derivatives: small molecules possessing antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 120(4):842–859
Das A, Narayanam MK, Paul S, Mukherjee P, Ghosh S, Dastidar DG, Chakrabarty S, Ganguli A, Basu B, Pal M, Chatterji U, Banerjee SK, Karmakar P, Kumar D, Chakrabarti G (2019) A novel triazole, NMK-T-057, induces autophagic cell death in breast cancer cells by inhibiting γ-secretase-mediated activation of Notch signaling. J Biol Chem 294(17):6733–6750
Davies D (2003) Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(2):114–122
Dwivedi S, Wahab R, Khan F, Mishra YK, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA (2014) Reactive oxygen species-mediated bacterial biofilm inhibition via zinc oxide nanoparticles and their statistical determination. PLoS ONE 9(11):e111289
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(9):623–633
Garrett TR, Bhakoo M, Zhang Z (2008) Bacterial adhesion and biofilms on surfaces. Prog Nat Sci 18(9):1049–1056
Gupta P, Sarkar S, Das B, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2016) Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention-a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol 198(1):1–15
Imlay JA (2003) Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu Rev Microbiol 57(1):395–418
Kaito C, Sekimizu K (2007) Colony spreading in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol Res 189(6):2553–2557
Kumar L, Chhibber S, Harjai K (2013) Zingerone inhibits biofilm formation and improve antibiofilm efficacy of ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Fitoterapia 90:73–78
Lee JH, Park JH, Cho MH, Lee J (2012) Flavone reduces the production of virulence factors, staphyloxanthin, and α-hemolysin Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Microbiol 65(6):726–732
Lewis K (2005) Persister cells and the riddle of biofilm survival. Biochemistry (Moscow) 70(2):267–274
Lister JL, Horswill AR (2014) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:178
Liu GY, Essex A, Buchanan JT, Datta V, Hoffman HM, Bastian JF, Fierer J, Nizet V (2005) Staphylococcus aureus golden pigment impairs neutrophil killing and promotes virulence through its antioxidant activity. J Exp Med 202(2):209–215
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maric S, Vranes J (2007) Characteristics and significance of microbial biofilm formation. Period Biol 109:115–121
Masuda K, Funayama S, Komiyama K, Unezawa I, Ito K (1987) Constituents of Tritoniacrocosmaeflora, I. Tricrozarin A, a novel antimicrobial naphthazarin derivative. J Nat Prod 50(3):418–421
Mukherjee K, Tribedi P, Mukhopadhyay B, Sil AK (2013) Antibacterial activity of long-chain fatty alcohols against mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 338(2):177–183
Paharik AE, Horswill AR (2016) The Staphylococcal biofilm: adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec
Papageorgiou VP, Assimopoulou AN, Couladouros EA, Hepworth D, Nicolaou KC (1999) The chemistry and biology of alkannin, shikonin, and related naphthazarin natural products. Angew Chem Int Ed 38(3):270–301
Pelz A, Wieland KP, Putzbach K, Hentschel P, Albert K, Götz F (2005) Structure and biosynthesis of staphyloxanthin from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem 280(37):32493–32498
Pollitt E, Crusz S, Diggle S (2016) Staphylococcus aureus forms spreading dendrites that have characteristics of active motility. Sci Rep 5(1):1–12
Ribeiro LM, Fumagalli F, Mello RB, Froes TQ, da Silva MV, Gomes SV, Barros TF, Emery FS, Castilho MS (2020) Structure-activity relationships and mechanism of action of tetragomycin derivatives as inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureusstaphyloxanthin biosynthesis. Microb Pathog 144:104127
Sharma BK, Saha A, Rahaman L, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2015) Silver inhibits the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adv Microbiol 5(10):677
Spormann AM (1999) Gliding motility in bacteria: insights from studies of Myxococcusxanthus. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(3):621–641
Sun F, Qu F, Ling Y, Mao P, Xia P, Chen H, Zhou D (2013) Biofilm-associated infections: antibiotic resistance and novel therapeutic strategies. Future Microbiol 8(7):877–886
Thomson RH (1971) Naturally occuring quinones. Acad Prf SS, New York
Tribedi P, Gupta AD, Sil AK (2015) Adaptation of Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 in biofilm on low-density polyethylene surface: an effective strategy for efficient survival and polymer degradation. Bioresour Bioprocess 2(1):14
Yarwood JM, Schlievert PM (2003) Quorum sensing in Staphylococcus infections. J Clin Invest 112(11):1620–1625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, P., Chakraborty, P., Chatterjee, A. et al. 1,4-Naphthoquinone accumulates reactive oxygen species in Staphylococcus aureus: a promising approach towards effective management of biofilm threat. Arch Microbiol 203, 1183–1193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02117-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02117-1