Abstract
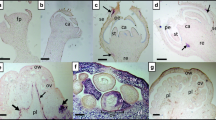
Summer squash is one of the important vegetable crops and its production is hampered by various abiotic and biotic stresses. Of the different biotic stresses, viral infections are responsible for causing great losses to this crop. Diseases caused by begomoviruses are becoming a major constraint in the cultivation of summer squash. Samples from summer squash plants exhibiting severe yellow mosaic and leaf curl symptoms were collected from the Varanasi district of Uttar Pradesh (India) and begomovirus associated with these plants was transmitted through whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci) to healthy squash plants. The relationship between causal virus and whitefly vector was determined. The minimum acquisition access period (AAP) and inoculation feeding period (IFP) required by B. tabaci to transmit the virus was determined to be 10 min and female insects have greater efficiency in transmitting virus than male insects. The partial genome of the virus was amplified by PCR (1.2 kb), cloned and sequenced from the ten infected plant samples collected from field. Partial genome sequence analysis (1.2 kb) obtained from the ten samples revealed that they are associated with begomovirus species closely related to the Indian strain of Squash leaf curl China virus (SLCCNV). Therefore, one representative sample (Sq-1) was selected and complete genome of the virus was amplified by rolling circle amplification (RCA) method. Sequence analysis by Sequence Demarcation Tool (SDT) showed that the current isolate has maximum nucleotide (nt) identity of 93.7–98.4% and 89–98.1% with respect to DNA A DNA B, respectively with Indian strains of SLCCNV infecting cucurbits in India. Recombination analysis of genomes (DNA A and DNA B components) showed that a major part of genomes likely to be originated from already known begomoviruses (ToLCNDV, SLCCNV-CN and SLCCNV-IN) are infecting cucurbitaceous crops. Serological assays such as triple antibody sandwich-enzyme-linked immune-sorbent (TAS-ELISA) assay, dot blot immunobinding assay (DIBA), immuno-capture polymerase chain reaction (IC-PCR) were developed for the detection of SLCCNV.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Knowles NJ, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Mushegian AR (2017) Changes to taxonomy and the international code of virus classification and nomenclature ratified by the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Arch Virol 162:2505–2538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3358-5
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Brown JK, Nelson MR (1987) Host range and vector relationships of Cotton leaf crumple virus. Plant Dis 71:522–524. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-71-0522
Chan YL, Lee LM, Shih SL, Kuo FH, Kenyon L (2019) Survey of virus diseases affecting squash (Cucurbita moschata) in Taiwan. Acta Hortic. 1257:23–28. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2019.1257.4
Cohen S, Duffus JE, Larsen RC, Liu HY, Flock RA (1983) Purification, serology, and vector relationships of Squash leaf curl virus, a whitefly-transmitted geminivirus. Phytopathol 73:1669–1673. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-73-1669
Czosnek H, Ghanim M, Morin S, Rubinstein G, Fridman V, Zeidan M (2001) Whiteflies; vectors, and victims (?) of geminiviruses. Adv Virus Res 57:291–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-3527(01)57006-2
Davino S, Napoli C, Dellacroce C, Miozzi L, Noris E, Davino M, Accotto GP (2009) Two new natural begomovirus recombinants associated with the tomato yellow leaf curl disease co-exist with parental viruses in tomato epidemics in Italy. Virus Res 143:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2009.03.001
Dinsdale A, Cook L, Riginos C, Buckley Y, De Barro PJ (2010) Refined global analysis of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Aleyrodoidea) mitochondrial CO1 to identify species level genetic boundaries. Ann Entomol Soc Am 103:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1603/AN09061
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15. https://doi.org/10.2307/2419362
Fiallo-Olive E, Pan LL, Liu SS, Navas-Castillo J (2020) Transmission of begomoviruses and other whitefly-borne viruses: dependence on the vector species. Phytopathol 110:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-07-19-0273-FI
Frohlich DR, Torres-Jerez I, Bedford ID, Markham PG, Brown JK (1999) A phylogeographical analysis of Bemisia tabaci species complex based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Mol Ecol 8:1683–1691. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00754.x
Garcia-Arenal F, Fraile A, Malpica JM (2001) Variability and genetic structure of plant virus populations. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:157–186. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.157
Ghanem GAM (2003) Okra leaf curl virus: a monopartite begomovirus infecting okra crop in Saudi Arabia. Arab J Biotechol 6(1):139–152
Gray SM, Banerjee N (1999) Mechanisms of arthropod transmission of plant and animal viruses. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:128–148. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.63.1.128-148.1999
Haible D, Kober S, Jeske H (2006) Rolling circle amplification revolutionizes diagnosis and genomics of geminiviruses. J Virol Methods 135(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2006.01.017
Hong Y, Wang X, Tian B, Cai, (1995) Chinese squash leaf curl virus: a new whitefly-transmitted geminivirus. Sci China Bull 8(2):179–186
Hui-jie WU, Meng LI, Hong Ni, Peng B, Qin-sheng GU (2020) Molecular and biological characterization of melon-infecting Squash leaf curl China virus in China. J Integr Agric 19(2):570–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62642-0
Ito T, Ogawa T, Samretwanich K, Sharma P, IkegamiM, (2007) Yellow leaf curl disease of pumpkin in Thailand is associated with Squash leaf curl China virus. Plant Pathol 57:766. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01803.x
Jones DR (2003) Plant virus transmitted by whiteflies. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:195–219. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022846630513
Kanakala S, Ghanim M (2019) Global genetic diversity and geographical distribution of Bemisia tabaci and its bacterial endosymbionts. PLoS ONE 14(3):e0213946. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213946
Kon T, Dolores M, Bajet NB, Hase S, Takahashi H, Ikegami M (2003) Molecular characterization of a strain of Squash leaf curl China virus from the Philippines. J Phytopathol 151:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0434.2003.00764.x
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Liao JY, Hu CC, Lin TK, Chang CA, Deng TC (2007) Identification of Squash leaf curl Philippines virus on Benincasa hispida in Taiwan. Plant Pathol Bull 16:11–18
Lima ATM, Sobrinho RR, Gonzalez-Aguilera J, Rocha CS, Silva SJC, Xavier CAD, Silva FN, Duffy S, Zerbini FM (2013) Synonymous site variation due to recombination explains higher genetic variability in begomovirus populations infecting non-cultivated hosts. J Gen Virol 94:418–431. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.047241-0
Maina S, Edwards OR, de Almeida L, Ximenes A, Jones RAC (2017) First complete Squash leaf curl China virus genomic segment DNA-A sequence from East Timor. Genome Announc 5:e00483-e517. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00483-17
Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M, Khoosal A, Muhire B (2015) RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 1(1):vev003. https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/vev003
Muhire BM, Varsani A, Martin DP (2014) SDT: a virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108277. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108277
Muniyappa V, Venkatesh HM, Ramappa HK, Kulkarni RS, Zeidan M, Tarba C-Y, Ghanim M, Czosnek H (2000) Tomato leaf curl virus from Bangalore (ToLCV-Ban4): sequence comparison with Indian ToLCV isolates, detection in plants and insects, and vector relationships. Arch Virol 145:1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050070078
Muniyappa V, Maruthi MN, Babitha CR, Colvin J, Briddon RW, Rangaswamy KT (2003) Characterization of Pumpkin yellow vein mosaic virus from India. Ann Appl Biol 142:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00257.x
Navas-Castillo J, Fiallo-Olive E, Sanchez-Campos S (2011) Emerging virus diseases transmitted by whiteflies. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49:219–248. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-072910-095235
Palmer KE, Schnippenkoetter WH, Rybicki EP (1998) Geminivirus Isolation and DNA Extraction. In: Foster G.D., Taylor S.C. (eds) Plant Virology Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 81. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-385-6:41
Paris HS (1986) A proposed subspecific classification for Cucurbita pepo. Phytologia 61:133–138
Patil CV, Ramdas SV, Premchand U, Shankarappa KS (2017) Survey, symptomatology, transmission, host range and characterization of begomovirus associated with yellow mosaic disease of ridge gourd from southern India. Virus Dis 28(2):146–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-017-0376-6
Polston JE, Hiebert E, McGovern RJ, Stansly PA, Schster DJ (1993) Host range of tomato mottle virus, a new geminivirus infecting tomato in Florida. Plant Dis 77:1181–1184. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-77-1181
Polston JE, De Barro P, Boykin LM (2014) Transmission specificities of plant viruses with the newly identified species of the Bemisia tabaci species complex. Pest Manag Sci 70:1547–1552. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3738
Powell CA (1987) Detection of three plant viruses by dot immune-binding assay. Phytopathology 77:306–369. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-77-306
Power AG (2000) Insect transmission of plant viruses: a constraint on virus variability. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:336–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00090-x
Retuerma ML, Pableo GO, Price WC (1971) Preliminary study of the transmission of Philippine tomato leaf curls virus by Bemisia tabaci. Philipp Phytopathol 7:29–34
Revill PA, Ha CV, Porchum SC, Vu MT, Dale JL (2003) The complete nucleotide sequence of two distinct Geminiviruses infecting Cucurbits in Vietnam. Arch Virol 148:1523–1541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-003-0109-6
Riyaz SM, Deepan S, Dharanivasan G, Jesse MI, Raja M, Kathiravan K (2013) The first report on a variant of Squash leaf curl China virus (SLCCNV) infecting Benincasa hispida in India. New Dis Rep 28:20. https://doi.org/10.5197/j.2044-0588.2013.028.020
Riyaz SM, Deepan S, Jesse M, Dharanivasan G, Kathiravan K (2015) New record of bipartite Squash leaf curl China virus (SLCCNV) and Croton yellow vein mosaic beta satellite associated with yellow vein disease of ash gourd in India. New Dis Rep 31:3. https://doi.org/10.5197/j.2044-0588.2015.031.003
Rocha CS, Castillo-Urquiza GP, Lima ATM, Silva FN, Xavier CAD, Hora-Junior BT, Beserra-Junior JEA, Malta AWO, Martin DP, Varsani A, Alfenas-Zerbini P, Mizubuti ESG, Zerbini FM (2013) Brazilian begomovirus populations are highly recombinant, rapidly evolving, and segregated based on geographical location. J Virol 87:5784–5799. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00155-13
Rojas MR, Gilbertson RL, Russell DR, Maxwell DP (1993) Use of degenerate primers in the polymerase chain reaction to detect whitefly-transmitted geminiviruses. Plant Dis 77:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-77-0340
Saritha RK, Bag TK, Loganathan M, Rai AB, Rai M (2011) First report of Squash leaf curl China virus causing mosaic symptoms on summer squash (Cucurbita pepo) grown in Varanasi district of India. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 44(2):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235400902952301
Seepiban C, Charoenvilaisiri S, Warin N, Bhunchoth A, Phironrit N, Phuangrat B, Chatchawankanphanich O, Attathom S, Gajanandana O (2017) Development and application of triple antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for begomovirus detection using monoclonal antibodies against Tomato yellow leaf curl Thailand virus. Virol J 14:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-017-0763-z
Silva FN, Lima ATM, Rocha CS, Castillo-Urquiza GP, Alves-Junior M, Zerbini FM (2014) Recombination and pseudorecombination driving the evolution of the begomoviruses Tomato severe rugose virus (ToSRV) and Tomato rugose mosaic virus (ToRMV): two recombinant DNA A components sharing the same DNA B. Virol J 11:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-11-66
Simon C, Frati F, Beckembach A, Crespi B, Liu B, Flook P (1994) Evolution, weighting and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann Entomol Soc Am 87:651–701. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/87.6.651
Singh JAS, Sahi Mann HS, Kapur SP (1994) Studies on whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Genn) transmitted Cotton leaf curl virus disease in Punjab. J Insect Sci 7:194–198
Singh R, Raj SK, Prasad V (2008) Molecular characterization of a strain of Squash leaf curl China virus from north India. J Phytopathol 156(4):222–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.2007.01347.x
Singh AK, Mishra KK, Chattopadhyay B, Chakraborty S (2009) Biological and molecular characterization of a begomovirus associated with yellow mosaic vein mosaic disease of pumpkin from Northern India. Virus Genes 39:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-009-0396-4
Tahir M, HaiderMS BRW (2010) First report of Squash leaf curl China virus in Pakistan. Australas Plant Dis Notes 5:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1071/DN10009
Van der Walt E, Rybicki EP, Varsani A, Polston JE, Billharz R, Donaldson L, Monjane AL, Martin DP (2009) Rapid host adaptation by extensive recombination. J Gen Virol 90:734–746. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.007724-0
Varma A, Malathi VG (2003) Emerging geminivirus problems: a serious threat to crop production. Ann Appl Biol 142:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00240.x
Venkataravanappa V, Reddy CNL, Jalali S, Krishna Reddy M (2012) Molecular characterization of distinct bipartite begomovirus infecting bhendi (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) in India. Virus Genes 44:522–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0732-y
Venkataravanappa V, Swarnalatha P, Reddy CNL, Chauhan N, Krishna Reddy M (2016) Association of recombinant Chilli leaf curl virus with enation leaf curl disease of tomato: a new host for chilli begomovirus in India. Phytoparasitica 44:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-016-0510-9
Venkataravanappa V, Kodandaram MH, Reddy CNL, Shankarappa KS, Krishna Reddy M (2017) Comparative transmission of Bhendi yellow vein mosaic virus by two cryptic species of the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). 3 Biotech 7:331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0970-8
Whitaker TW, Bemis WP (1975) Origin and evolution of the cultivated Cucurbita. Bull Torrey Bot Club 102:362–368. https://doi.org/10.2307/2484762
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Director, Indian Institute of Vegetable Research, Varanasi, for providing research facilities and his keen interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We declare that all authors participated in the research and article preparation. VV design of the experiments and drafted the article. CNLR designed the study and revision of the manuscript, KSS participated in analysis of the data, HDV and MN participated in the collection of the data. MKR guided and designed the study and revised the article. All authors approved the submitted version of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkataravanappa, V., Reddy, C.N.L., Nandan, M. et al. Transmission, characterization and occurrence of recombination in Indian strain of squash leaf curl China virus associated with yellow mosaic and leaf curl disease of Summer squash. 3 Biotech 11, 265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02821-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02821-9