Abstract
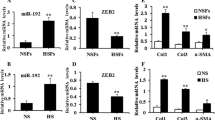
Elucidating the molecular mechanism of the microRNAs in skin fibrosis is critical for identifying a novel therapeutic strategy for hypertrophic scar (HS). In this study, it was shown that miR-210-5p is induced by TGFβ, and that overexpression of miR-210-5p promoted the differentiation of human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) into myofibroblasts. STAT5A is required for TGFβ-induced STAT3 activity. Here, we show that miR-210-5p attenuated TGFβ-induced STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing the expression of STAT5A. Taken together, the present study suggests that TGFβ-induced miR-210-5p reduced STAT5A expression, leading to aberrant activation of STAT3, and facilitate skin fibrosis in HDFs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu El Makarem MA, El-Sagheer GM, Abu El-Ella MA (2018) The role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 and transforming growth factor-β1 in hepatic fibrosis induced by chronic hepatitis c virus infection in egyptian patients. Med Princ Pract Int J Kuwait Univ Health Sci Cent 27:115–121
Adegboyega PA, Mifflin RC, DiMari JF, Saada JI, Powell DW (2002) Immunohistochemical study of myofibroblasts in normal colonic mucosa, hyperplastic polyps, and adenomatous colorectal polyps. Arch Pathol Lab Med 126:829–836
Berman B, Perez OA, Konda S, Kohut BE, Viera MH, Delgado S, Zell D, Li Q (2007) A review of the biologic effects, clinical efficacy, and safety of silicone elastomer sheeting for hypertrophic and keloid scar treatment and management. Dermatol Surg off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 33:1291–1302
Bernasconi A, Marino R, Ribas A, Rossi J, Ciaccio M, Oleastro M, Ornani A, Paz R, Rivarola MA, Zelazko M et al (2006) Characterization of immunodeficiency in a patient with growth hormone insensitivity secondary to a novel STAT5b gene mutation. Pediatrics 118:e1584-1592
Bloemen MC, van der Veer WM, Ulrich MM, van Zuijlen PP, Niessen FB, Middelkoop E (2009) Prevention and curative management of hypertrophic scar formation. Burns J Int Soc Burn Inj 35:463–475
Bodempudi V, Hergert P, Smith K, Xia H, Herrera J, Peterson M, Khalil W, Kahm J, Bitterman PB, Henke CA (2014) miR-210 promotes IPF fibroblast proliferation in response to hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L283-294
Cui Y, Hosui A, Sun R, Shen K, Gavrilova O, Chen W, Cam MC, Gao B, Robinson GW, Hennighausen L (2007) Loss of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 leads to hepatosteatosis and impaired liver regeneration. Hepatology 46:504–513
Cumaraswamy AA, Gunning PT (2012) Progress towards direct inhibitors of Stat5 protein. Horm Mol Biol Clin Invest 10:281–286
Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:103–111
Fan Z, Hao C, Li M, Dai X, Qin H, Li J, Xu H, Wu X, Zhang L, Fang M et al (2015) MKL1 is an epigenetic modulator of TGF-beta induced fibrogenesis. Biochem Biophys Acta 1849:1219–1228
Fasanaro P, D’Alessandra Y, Di Stefano V, Melchionna R, Romani S, Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC, Martelli F (2008) MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J Biol Chem 283:15878–15883
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Lorenzi M, Pescatori M, Brioschi M, Kulshreshtha R, Banfi C, Stubbs A, Calin GA, Ivan M et al (2009) An integrated approach for experimental target identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J Biol Chem 284:35134–35143
Feng H, Wu R, Zhang S, Kong Y, Liu Z, Wu H, Wang H, Su Y, Zhao M, Lu Q (2020) Topical administration of nanocarrier miRNA-210 antisense ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice. J Dermatol 47:147–154
Fernando J, Faber TW, Pullen NA, Falanga YT, Kolawole EM, Oskeritzian CA, Barnstein BO, Bandara G, Li G, Schwartz LB et al (2013) Genotype-dependent effects of TGF-β1 on mast cell function: targeting the Stat5 pathway. J Immunol (baltimore, Md: 1950) 191:4505–4513
Grosso S, Doyen J, Parks SK, Bertero T, Paye A, Cardinaud B, Gounon P, Lacas-Gervais S, Noël A, Pouysségur J et al (2013) MiR-210 promotes a hypoxic phenotype and increases radioresistance in human lung cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis 4:e544
Hoelbl A, Kovacic B, Kerenyi MA, Simma O, Warsch W, Cui Y, Beug H, Hennighausen L, Moriggl R, Sexl V (2006) Clarifying the role of Stat5 in lymphoid development and Abelson-induced transformation. Blood 107:4898–4906
Hosui A, Hennighausen L (2008) Genomic dissection of the cytokine-controlled STAT5 signaling network in liver. Physiol Genomics 34:135–143
Hosui A, Kimura A, Yamaji D, Zhu BM, Na R, Hennighausen L (2009) Loss of STAT5 causes liver fibrosis and cancer development through increased TGF-{beta} and STAT3 activation. J Exp Med 206:819–831
Hou SX, Zheng Z, Chen X, Perrimon N (2002) The Jak/STAT pathway in model organisms: emerging roles in cell movement. Dev Cell 3:765–778
Hu B, Phan SH (2016) Notch in fibrosis and as a target of anti-fibrotic therapy. Pharmacol Res 108:57–64
Hu S, Huang M, Li Z, Jia F, Ghosh Z, Lijkwan MA, Fasanaro P, Sun N, Wang X, Martelli F et al (2010) MicroRNA-210 as a novel therapy for treatment of ischemic heart disease. Circulation 122:S124-131
Imada K, Bloom ET, Nakajima H, Horvath-Arcidiacono JA, Udy GB, Davey HW, Leonard WJ (1998) Stat5b is essential for natural killer cell-mediated proliferation and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med 188:2067–2074
Kim S, Kim Y, Lee Y, Chung JH (2008) Ceramide accelerates ultraviolet-induced MMP-1 expression through JAK1/STAT-1 pathway in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Lipid Res 49:2571–2581
Kofoed EM, Hwa V, Little B, Woods KA, Buckway CK, Tsubaki J, Pratt KL, Bezrodnik L, Jasper H, Tepper A et al (2003) Growth hormone insensitivity associated with a STAT5b mutation. Nengl J Med 349:1139–1147
Li G, Zhou R, Zhang Q, Jiang B, Wu Q, Wang C (2016) Fibroproliferative effect of microRNA-21 in hypertrophic scar derived fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 345:93–99
Li Y, Zhang J, Lei Y, Lyu L, Zuo R, Chen T (2017a) MicroRNA-21 in skin fibrosis: potential for diagnosis and treatment. Mol Diagn Ther 21:633–642
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang W, Liu Y, Li Y, Wang K, Zhang Y, Yang C, Li X, Shi J et al (2017b) MicroRNA-192 regulates hypertrophic scar fibrosis by targeting SIP1. J Mol Histol 48:357–366
Martin P (1997) Wound healing–aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276:75–81
Nakajima H, Liu XW, Wynshaw-Boris A, Rosenthal LA, Imada K, Finbloom DS, Hennighausen L, Leonard WJ (1997) An indirect effect of Stat5a in IL-2-induced proliferation: a critical role for Stat5a in IL-2-mediated IL-2 receptor alpha chain induction. Immunity 7:691–701
Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J, Kon M (1999) On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a review. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1435–1458
Ogawa C, Tone Y, Tsuda M, Peter C, Waldmann H, Tone M (2014) TGF-β-mediated Foxp3 gene expression is cooperatively regulated by Stat5, Creb, and AP-1 through CNS2. J Immunol (baltimore, Md: 1950) 192:475–483
O’Shea JJ, Plenge R (2012) JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity 36:542–550
Owens BM, Simmons A (2013) Intestinal stromal cells in mucosal immunity and homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol 6:224–234
Park GS, An MK, Yoon JH, Park SS, Koh SH, Mauro TM, Cho EB, Park EJ, Kim KH, Kim KJ (2019) Botulinum toxin type a suppresses pro-fibrotic effects via the JNK signaling pathway in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res 311:807–814
Pedroza M, To S, Assassi S, Wu M, Tweardy D, Agarwal SK (2018) Role of STAT3 in skin fibrosis and transforming growth factor beta signalling. Rheumatology 57:1838–1850
Piersma B, Wouters OY, Bank RA (2018) alphaII-spectrin and betaII-spectrin do not affect TGFbeta1-induced myofibroblast differentiation. Cell Tissue Res 374:165–175
Qin Q, Furong W, Baosheng L (2014) Multiple functions of hypoxia-regulated miR-210 in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 33:50
Shoji T, Nakasa T, Yamasaki K, Kodama A, Miyaki S, Niimoto T, Okuhara A, Kamei N, Adachi N, Ochi M (2012) The effect of intra-articular injection of microRNA-210 on ligament healing in a rat model. Am J Sports Med 40:2470–2478
Sun L, Fan Z, Chen J, Tian W, Li M, Xu H, Wu X, Shao J, Bian Y, Fang M et al (2016) Transcriptional repression of SIRT1 by protein inhibitor of activated STAT 4 (PIAS4) in hepatic stellate cells contributes to liver fibrosis. Sci Rep 6:28432
Varga J, Jimenez SA (1986) Stimulation of normal human fibroblast collagen production and processing by transforming growth factor-beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 138:974–980
Watany MM, Hagag RY, Okda HI (2018) Circulating miR-21, miR-210 and miR-146a as potential biomarkers to differentiate acute tubular necrosis from hepatorenal syndrome in patients with liver cirrhosis: a pilot study. Clin Chem Lab Med 56:739–747
Zhang X, Sai B, Wang F, Wang L, Wang Y, Zheng L, Li G, Tang J, Xiang J (2019) Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol Cancer 18:40
Zhou R, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Fu S, Wang C (2015) Aberrant miR-21 and miR-200b expression and its pro-fibrotic potential in hypertrophic scars. Exp Cell Res 339:360–366
Zhu Y, Wang J, Meng X, Xie H, Tan J, Guo X, Han P, Wang R (2017) A positive feedback loop promotes HIF-1alpha stability through miR-210-mediated suppression of RUNX3 in paraquat-induced EMT. J Cell Mol Med 21:3529–3539
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, S., Qiu, Y. MiR-210-5p regulates STAT3 activation by targeting STAT5A in the differentiation of dermal fibroblasts. 3 Biotech 11, 243 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02777-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02777-w