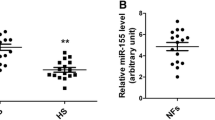
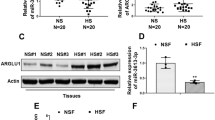
Abstract
Hypertrophic scar (HS) is a fibro-proliferative disorder which is characterized by excessive deposition of collagen and accumulative activity of myofibroblasts. Increasing evidences have demonstrated miRNAs play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of HS. MiR-192 is closely associated with renal fibrosis, but its effect on HS formation and skin fibrosis remains unknown. In the study, we presented that miR-192 was up-regulated in HS and HS derived fibroblasts (HSFs) compared to normal skin (NS) and NS derived fibroblasts (NSFs), accompanied by the reduction of smad interacting protein 1 (SIP1) expression and the increase of Col1, Col3 and α-SMA levels. Furthermore, we confirmed SIP1 was a direct target of miR-192 by using luciferase reporter assays. Meanwhile, the overexpression of miR-192 increased the levels of Col1, Col3 and α-SMA. The synthesis of collagen and more positive α-SMA staining were also observed in bleomycin-induced dermal fibrosis model of BALB/c mice treated with subcutaneous miR-192 mimics injection, whereas the inhibition of miR-192 decreased the expression of Col1, Col3 and α-SMA. Moreover, SIP1 siRNA could enhance the levels of Col1, Col3 and α-SMA, showing that the effect of knockdown SIP1 was similar to miR-192 mimics, and the phenomenon manifested miR-192 regulated HS fibrosis by targeting SIP1. Together, our results indicated that miR-192 was a critical factor of HS formation and facilitated skin fibrosis by targeting directly SIP1.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HS:
-
Hypertrophic scar
- HSFs:
-
Hypertrophic scar derived fibroblasts
- NS:
-
Normal skin
- NSFs:
-
Normal skin derived fibroblasts
- SIP1:
-
Smad interacting protein 1
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- 3′-UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated regions
- α-SMA:
-
α-smooth muscle actin
References
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Botla SK, Savant S, Jandaghi P, Bauer AS, Mucke O, Moskalev EA, Neoptolemos JP, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Scarpa A, Gaida MM, Buchler MW, Strobel O, Hackert T, Giese NA, Augustin HG, Hoheisel JD (2016) Early epigenetic downregulation of microrna-192 expression promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Res 76:4149–4159
Brown BD, Naldini L (2009). Exploiting and antagonizing microRNA regulation for therapeutic and experimental applications. Nat Rev Genet 10:578–585
Brown BC, McKenna SP, Siddhi K, McGrouther DA, Bayat A (2008) The hidden cost of skin scars: quality of life after skin scarring. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:1049–1058
Deshpande SD, Putta S, Wang M, Lai JY, Bitzer M, Nelson RG, Lanting LL, Kato M, Natarajan R (2013) Transforming growth factor-beta-induced cross talk between p53 and a microRNA in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 62:3151–3162
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79:351–379
Garavelli L, Donadio A, Zanacca C, Banchini G, Della Giustina E, Bertani G, Albertini G, Rossi C Del, Zweier C, Rauch A, Zollino M, Neri G (2003) Hirschsprung disease, mental retardation, characteristic facial features, and mutation in the gene ZFHX1B (SIP1): confirmation of the Mowat–Wilson syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 116A:385–388
Gibbs JR, Singleton A (2006) Application of genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism typing: simple association and beyond. PLoS Genet 2:e150
Gras C, Ratuszny D, Hadamitzky C, Zhang H, Blasczyk R, Figueiredo C (2015) miR-145 Contributes to hypertrophic scarring of the skin by inducing myofibroblast activity. Mol Med 21:296–304
Hino K, Tsuchiya K, Fukao T, Kiga K, Okamoto R, Kanai T, Watanabe M. (2008). Inducible expression of microRNA-194 is regulated by HNF-1alpha during intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. RNA 14:1433–1442
Imamichi Y, Konig A, Gress T, Menke A (2007) Collagen type I-induced Smad-interacting protein 1 expression downregulates E-cadherin in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 26:2381–2385
Jiang X, Tsitsiou E, Herrick SE, Lindsay MA (2010) MicroRNAs and the regulation of fibrosis. FEBS J 277:2015–2021
Kathju S, Gallo PH, Satish L (2012) Scarless integumentary wound healing in the mammalian fetus: molecular basis and therapeutic implications. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 96:223–236
Kato M, Zhang J, Wang M, Lanting L, Yuan H, Rossi JJ, Natarajan R (2007) MicroRNA-192 in diabetic kidney glomeruli and its function in TGF-beta-induced collagen expression via inhibition of E-box repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3432–3437
Kato M, Putta S, Wang M, Yuan H, Lanting L, Nair I, Gunn A, Nakagawa Y, Shimano H, Todorov I, Rossi JJ, Natarajan R (2009) TGF-beta activates Akt kinase through a microRNA-dependent amplifying circuit targeting PTEN. Nat Cell Biol 11:881–889
Kato M, Arce L, Wang M, Putta S, Lanting L, Natarajan R (2011) A microRNA circuit mediates transforming growth factor-beta1 autoregulation in renal glomerular mesangial cells. Kidney Int 80:358–368
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, Lee TJ, Jeon YJ, Volinia S, Pineau P, Marchio A, Palatini J, Suh SS, Alder H, Liu CG, Dejean A, Croce CM (2011). p53 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med 208:875–883
Krupa A, Jenkins R, Luo DD, Lewis A, Phillips A, Fraser D (2010) Loss of MicroRNA-192 promotes fibrogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:438–447
Kwan P, Ding J, Tredget EE (2015) MicroRNA 181b regulates decorin production by dermal fibroblasts and may be a potential therapy for hypertrophic scar. PLoS ONE 10:e0123054
Lee JY, Park MK, Park JH, Lee HJ, Shin DH, Kang Y, Lee CH, Kong G (2014) Loss of the polycomb protein Mel-18 enhances the epithelial–mesenchymal transition by ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression through the downregulation of miR-205 in breast cancer. Oncogene 33:1325–1335
Li P, He QY, Luo CQ (2014) Overexpression of miR-200b inhibits the cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts in vitro. J Dermatol 41:903–911
Li Y, Yang L, Zheng Z, Shi J, Wu X, Guan H, Jia Y, Tao K, Wang H, Han S, Gao J, Zhao B, Su L, D Hu (2015) MRP1 knockdown down-regulates the deposition of collagen and leads to a reduced hypertrophic scar fibrosis. J Mol Histol 46:357–364
Li G, Zhou R, Zhang Q, Jiang B, Wu Q, Wang C (2016) Fibroproliferative effect of microRNA-21 in hypertrophic scar derived fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 345:93–99
Liu J, Wang Y, Pan Q, Su Y, Zhang Z, Han J, Zhu X, Tang C, Hu D (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin pathway forms a negative feedback loop during TGF-beta1 induced human normal skin fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition. J Dermatol Sci 65:38–49
Lv LL, Cao YH, Ni HF, Xu M, Liu D, Liu H, Chen PS, Liu BC (2013) MicroRNA-29c in urinary exosome/microvesicle as a biomarker of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F1220–F1227
Mejlvang J, Kriajevska M, Vandewalle C, Chernova T, Sayan AE, Berx G, Mellon JK, Tulchinsky E (2007) Direct repression of cyclin D1 by SIP1 attenuates cell cycle progression in cells undergoing an epithelial mesenchymal transition. Mol Biol Cell 18:4615–4624
Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J, Kon M (1999) On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a review. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1435–1458
Ong CT, Khoo YT, Tan EK, Mukhopadhyay A, Do DV, Han HC, Lim IJ, Phan TT (2007). Epithelial–mesenchymal interactions in keloid pathogenesis modulate vascular endothelial growth factor expression and secretion. J Pathol 211:95–108
Parrizas M, Brugnara L, Esteban Y, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Canivell S, Murillo S, Gordillo-Bastidas E, Cusso R, Cadefau JA, Garcia-Roves PM, Servitja JM, Novials A (2015). Circulating miR-192 and miR-193b are markers of prediabetes and are modulated by an exercise intervention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E407–E415
Putta S, Lanting L, Sun G, Lawson G, Kato M, Natarajan R (2012) Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:458–469
Rosa-Rosa JM, Pita G, Gonzalez-Neira A, Milne RL, Fernandez V, Ruivenkamp C, van Asperen CJ, Devilee P, Benitez J (2009) A 7 Mb region within 11q13 may contain a high penetrance gene for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118:151–159
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, Fricke E, Luber B, Busch R, Hofler H, Becker KF (2002) Differential expression of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition regulators snail, SIP1, and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol 161:1881–1891
Sideek MA, Teia A, Kopecki Z, Cowin AJ, Gibson MA (2016) Co-localization of LTBP-2 with FGF-2 in fibrotic human keloid and hypertrophic scar. J Mol Histol 47:35–45
Tazawa H, Kagawa S, Fujiwara T (2011) MicroRNAs as potential target gene in cancer gene therapy of gastrointestinal tumors. Expert Opin Biol Ther 11:145–155
Tyack Z, Simons M, Spinks A, Wasiak J (2012) A systematic review of the quality of burn scar rating scales for clinical and research use. Burns 38:6–18
van Grunsven LA, Michiels C, Van de Putte T, Nelles L, Wuytens G, Verschueren K, Huylebroeck D (2003) Interaction between Smad-interacting protein-1 and the corepressor C-terminal binding protein is dispensable for transcriptional repression of E-cadherin. J Biol Chem 278:26135–26145
Verschueren K, Remacle JE, Collart C, Kraft H, Baker BS, Tylzanowski P, Nelles L, Wuytens G, Su MT, Bodmer R, Smith JC, Huylebroeck D (1999) SIP1, a novel zinc finger/homeodomain repressor, interacts with Smad proteins and binds to 5′-CACCT sequences in candidate target genes. J Biol Chem 274:20489–20498
Wang XW, Heegaard NH, Orum H (2012) MicroRNAs in liver disease. Gastroenterology 142:1431–1443
Witkos TM, Koscianska E, Krzyzosiak WJ (2011). Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr Mol Med 11:93–109
Zhang ZF, Zhang YG, Hu DH, Shi JH, Liu JQ, Zhao ZT, Wang HT, Bai XZ, Cai WX, Zhu HY, Tang CW (2011). Smad interacting protein 1 as a regulator of skin fibrosis in pathological scars. Burns 37:665–672
Zhou R, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Fu S, Wang C (2015) Aberrant miR-21 and miR-200b expression and its pro-fibrotic potential in hypertrophic scars. Exp Cell Res 339:360–366
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81171811, 81372069, 81571914 and 81272098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Yan Li, Julei Zhang and Wei Zhang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, W. et al. MicroRNA-192 regulates hypertrophic scar fibrosis by targeting SIP1. J Mol Hist 48, 357–366 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-017-9734-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-017-9734-3