Abstract
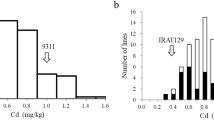
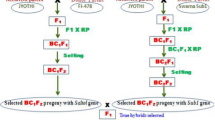
To reduce cadmium (Cd) accumulation in the grains of rice Chuang-5S (C5S), a gene OsHMA3 and a QTL qlGCd3 related to low-Cd accumulation were separately introgressed into the recipient parent C5S (male sterile line) by molecular marker-assisted breeding. The recurrent parent C5S was then replaced by NIL (near-isogenic line)-C5S with the blast resistance gene Pi48 or Pi49 to construct the BC2F1 generation. Finally, two groups of improved materials of C5S, which pyramided the gene/QTL associated with low-Cd accumulation and blast resistance gene, were developed. The Cd accumulation, agronomic traits, genetic background and blast resistance of these improved C5S materials were evaluated. The results showed that the average Cd content of improved C5S material carrying OsHMA3 and qlGCd3 was, respectively, reduced by 52.8% and 50.8% compared with that of C5S, indicating that the gene related to low-Cd accumulation was, successfully, transferred to C5S with stable expression. The main agronomic traits of the improved materials were consistent with those of C5S. Besides, the improved C5S lines showed stronger blast resistance than C5S and more than 88% similarity to the genetic background of C5S. These two groups of improved materials may be further utilized for the breeding of advanced male sterile lines or superior hybrid rice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Nonoue Y, Ono N, Omoteno M, Kuramata M, Fukuoka S, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Ishikawa S (2013) Detection of QTLs to reduce cadmium content in rice grains using LAC23/Koshihikari chromosome segment substitution lines. Breeding Sci 63(3):284–291
Cao Z, Zeng G, Sheng HW, Xiao YH (2013) A simple approach for rapid preparation of rice genomic DNA for PCR analysis. J Hunan Agric Univ 39(1):13–16
Cao Z, Zeng G, Hao M, Sheng HW, Ye NZ, Xiao YH (2015) Improving blast resistance of dual-purpose genic sterile line C815S by using molecular marker-assisted selection. MPB 13(6):1193–1200
Chen LY, Lei DY, Tang WB, Deng HB, Xiao YH, Zhang GL (2015) Review on the methods of hybrid rice breeding. J Hunan Agric Univ 41(1):1–6
Chen XH, Ouyang YN, Fan YC, Qiu BY, Zhang GP, Zeng FR (2018) The pathway of transmembrane cadmium influx via calcium-permeable channels and its spatial characteristics along rice root. J Exp Bot 69(21):5279–5291
Chukwu SC, Rafii MY, Ramlee SI, Ismail SI, Oladosu Y, Okporie E, Onyishi G, Utobo E, Ekwu L, Swaray S, Jalloh M (2019) Marker-assisted selection and gene pyramiding for resistance to bacterial leaf blight disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnol Biotec Equip 33:1–16
Ding YF, Gong SH, Wang Y, Wang FJ, Bao H, Sun JW, Cai C, Yi KK, Chen ZX, Zhu C (2018) MicroRNA166 modulates cadmium tolerance and accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 177:1691–1703
Feng WL, Guo ZH, Xiao XY, Peng C, Shi L, Ran HZ, Xu WX (2019) Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotox Environ Safe 180:160–170
Ishikawa S, Suzui N, Ito-Tanabata S, Ishii S, Igura M, Abe T, Kuramata M, Kawachi N, Fujimaki S (2011) Real-time imaging and analysis of differences in cadmium dynamics in rice cultivars (Oryza sativa) using positron-emitting 107 Cd tracer. BMC Plant Biol 11(1):172
Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramataa M, Abea T, Senourab T, Hased Y, Arao T, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H (2012) Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice. PNAS 109(47):19166–19171
Li YY, Li SC, Li XF (2016) Research progress of molecular marker-assisted selection for pyramiding disease and insect resistance genes in rice. Guangdong Agric Sci 43(6):119–126
Li K, Yu HY, Li TX, Chen GD, Huang F (2017) Cadmium accumulation characteristics of low-cadmium rice (Oryza sativa L.) line and F1 hybrids grown in cadmium-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):1–11
Liu Y (2012) Fine mapping of blast resistance gene Pi48 in rice cultivar Xiangzi 3150, Dissertation, Hunan agricultural University.
Liu LC, Liu SX, Li YC, Min J, Huang HM (2016) Research Progress of Cadmium Accumulation and Regulation in Rice. Chinese Agricultural Sciences Bulletin 32(24):1–5
Luo JS, Huang J, Zeng DL, Peng JS, Zhang GB, Ma HL, Guan Y, Yi HY, Fu YL, Han B, Lin HX, Qian Q, Gong JM (2018) A defensin-like protein drives cadmium efflux and allocation in rice. Nat Commun 9(645):1–9
Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H (2011) OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol 189:190–199
Nie YY, Li X, Mao LH, Yan ML, Yan LA, Cai YH (2016) Improving blast resistance of parental restorer lines R225 by marker-assisted selection. china Rice 22(3):60–63
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Nagato Y, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2011) Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol 53:213–224
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2013) Functional relationship heavy metal P-type ATPases (OsHMA2 and OsHMA3) of rice (Oryza sativa) using RNAi. Plant Biotechnol 30:511–515
Shu ZF, Chen Y, Liu Z, Yuan L, Xiong C, Zhang HQ (2015) Correlation between outcrossing characteristics and stigma feature of 5 PTGMS lines. Crop Res 29(4):343–347
Sun PY, Liu JL, Wang Y, Jiang N, Wang SH, Dai YS, Gao J, Li ZQ, Pan SJ, Wang D, Li W, Liu XL, Xiao YH, Liu EM, Wang GL, Dai LY (2012) Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi49 in the durably resistant rice cultivar Mowanggu. Euphytica 192(1):45–54
Takahashi R, Bashir K, Ishimaru Y, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H (2012) The role of heavy-metal ATPases, HMAs, in zinc and cadmium transport in rice. Plant Signal Behav 7:1605–1607
Takahashi R, Ito M, Katou K, Sato K, Nakagawa S, Tezuka K, Akagi H, Kawamoto T (2016) Breeding and characterization of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) line “Akita 110” for cadmium phytoremediation. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 188(4):1–6
Tan MP, Cheng D, Yang YN, Zhang GQ, Qin MJ, Chen J, Chen YH, Jiang MY (2017) Co-expression network analysis of the transcriptomes of rice roots exposed to various cadmium stresses reveals universal cadmium- responsive genes. Bmc Plant Biol 17(194):1–18
Tang W, Xiao YH (2016) Research progress of physiological and molecular mechanisms of cadmium accumulation in rice. J Anhui Agric Sci 44(27):4–9
Tang L, Mao BG, Li YK, Lv QM, Zhang LP, Chen CY, He HJ, Wang WP, Zeng XF, Shao Y, Pan YL, Hu YY, Peng Y, Fu XQ, Li HQ, Xia ST, Zhao BR (2017) Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Tezuka K, Miyadate H, Katou K, Kodama K, Matsumoto S, Kawamoto T, Masaki S, Satoh H, Yamaguchi M, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H (2010) A single recessive gene controls cadmium translocation in the cadmium hyperaccumulating rice cultivar Cho-Ko-Koku. Theor Appl Genet 120(6):1175–1182
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huanga CF, Andob T, Yanoc M, Ma JF (2010) Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. PNAS 107(38):16500–16505
Ueno D, Koyama E, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2011) Physiological, genetic, and molecular characterization of a high-Cd-accumulating rice cultivar. Jarjan J Exp Bot 62(7):2265–2272
Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Sakamoto T, Kasaia K, Satoc Y, Nagamurac Y, Yoshidab A, Kyozukab J, Ishikawad S, Fujiwaraa T (2011) Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. PNAS 108(52):20959–20964
Wang YB, Hao M, Lei DY, Tang WB, Chen LY (2014) Character of early growth and quick development of genic male sterility lines. Crop Res 28(4):341–344
Wang MA, Yin LH, Pen JX, Nie LL, Li YJ, He J, Zhang W, Ao HJ (2016) Effects of VIP technology on reducing cadmium content in rice. China Rice 22(1):43–47
Wang P, Chen HP, Kopittke PM, Zhao FJ (2019) Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ Pollut 249:1038–1048
Xiong WT, Wang P, Yan TZ, Cao BB, Xu J, Liu DF, Luo MZ (2018) The rice “fruit-weight 2.2-like” gene family member OsFWL4 is involved in the translocation of cadmium from roots to shoots. Planta 247(5):1247–1260
Yang RF, Bai JJ, Fang J, Zeng W, Pu ZZ, Li GX (2015) Establishment of marker-assisted selection system for breeding rice varieties with high resistant starch content. J Nucl Agric Sci 29(12):2259–2267
Zhang L, Zhang X, Li TX, Ji L, Zheng T (2015) Cd uptake and distribution characteristics of Cd pollution-safe rice materials. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 48(1):174–184
Zhao JL, Yang W, Zhang SH, Yang TF, Liu Q, Dong JF, Fu H, Mao XX, Liu B (2018) Genome-wide association study and candidate gene analysis of rice cadmium accumulation in grain in a diverse rice collection. Rice 11:61
Zhu YW, Lin YR, Chen L (2016) Advances in molecular breeding of rice in China. J Xiamen Univ (Natural Science) 55(5):661–671
Funding
We appreciate the funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31171834), National Key Research and Development program (Grant No. 2016YFD0101100), Science and Technology Major Project of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2015NK1001-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Tang, W., Zeng, G. et al. Reduction of cadmium accumulation in the grains of male sterile rice Chuang-5S carrying Pi48 or Pi49 through marker-assisted selection. 3 Biotech 10, 539 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02533-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02533-6