Abstract
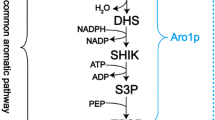
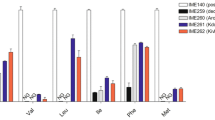
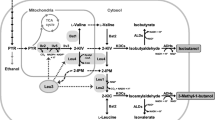
In this study, we applied a series of genetic modifications to wild-type S. cerevisiae strain BY4741 to address the bottlenecks in the l-tyrosine pathway. A tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) gene from Rhodobacter capsulatus, which can catalyze conversion of l-tyrosine into p-coumaric acid, was overexpressed to facilitate the analysis of l-tyrosine and test the strain’s capability to synthesize heterologous derivatives. First, we enhanced the supply of precursors by overexpressing transaldolase gene TAL1, enolase II gene ENO2, and pentafunctional enzyme gene ARO1 resulting in a 1.55-fold increase in p-coumaric acid production. Second, feedback inhibition of 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase and chorismate mutase was relieved by overexpressing the mutated feedback-resistant ARO4K229L and ARO7G141S, and a 3.61-fold improvement of p-coumaric acid production was obtained. Finally, formation of byproducts was decreased by deleting pyruvate decarboxylase gene PDC5 and phenylpyruvate decarboxylase gene ARO10, and p-coumaric acid production was increased 2.52-fold. The best producer—when TAL1, ENO2, ARO1, ARO4K229L, ARO7G141S, and TAL were overexpressed, and PDC5 and ARO10 were deleted—increased p-coumaric acid production by 14.08-fold (from 1.4 to 19.71 mg L−1). Our study provided a valuable insight into the optimization of l-tyrosine metabolic pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinwumi BC, Bordun KAM, Anderson HD (2018) Biological activities of stilbenoids. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/Ijms19030792
Borodina I, Nielsen J (2014) Advances in metabolic engineering of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of chemicals. Biotechnol J 9(5):609–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201300445
Braus GH (1991) Aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a model system for the regulation of a eukaryotic biosynthetic pathway. Microbiol Rev 55(3):349–370
Choo JH, Han C, Lee DW, Sim GH, Moon HY, Kim JY, Song JY, Kang HA (2018) Molecular and functional characterization of two pyruvate decarboxylase genes, PDC1 and PDC5, in the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(8):3723–3737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8862-3
Chougule M, Patel AR, Sachdeva P, Jackson T, Singh M (2011) Anticancer activity of Noscapine, an opioid alkaloid in combination with Cisplatin in human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 71(3):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.06.002
Donnez D, Jeandet P, Clement C, Courot E (2009) Bioproduction of resveratrol and stilbene derivatives by plant cells and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 27(12):706–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.09.005
Duncan K, Edwards RM, Coggins JR (1988) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARO1 gene. An example of the co-ordinate regulation of five enzymes on a single biosynthetic pathway. FEBS Lett 241(1–2):83–88
Gietz RD, Woods RA (2002) Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Method Enzymol 350:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(02)50957-5
Gold ND, Gowen CM, Lussier FX, Cautha SC, Mahadevan R, Martin VJJ (2015) Metabolic engineering of a tyrosine-overproducing yeast platform using targeted metabolomics. Microb Cell Fact 14:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0252-2
Graham LD, Gillies FM, Coggins JR (1993) Over-expression of the yeast multifunctional arom protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1216(3):417–424
Hartmann M, Schneider TR, Pfeil A, Heinrich G, Lipscomb WN, Braus GH (2003) Evolution of feedback-inhibited beta/alpha barrel isoenzymes by gene duplication and a single mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(3):862–867. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0337566100
Hegemann JH, Heick SB (2011) Delete and repeat: a comprehensive toolkit for sequential gene knockout in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Mol Biol 765:189–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-197-0_12
Iraqui I, Vissers S, Cartiaux M, Urrestarazu A (1998) Characterisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARO8 and ARO9 genes encoding aromatic aminotransferases I and II reveals a new aminotransferase subfamily. Mol Gen Genet 257(2):238–248
Jiang H, Morgan JA (2004) Optimization of an in vivo plant P450 monooxygenase system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 85(2):130–137. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10867
Karsten WE, Reyes ZL, Bobyk KD, Cook PF, Chooback L (2011) Mechanism of the aromatic aminotransferase encoded by the Aro8 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys 516(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2011.09.008
Koopman F, Beekwilder J, Crimi B, van Houwelingen A, Hall RD, Bosch D, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT, Daran JM (2012) De novo production of the flavonoid naringenin in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 11:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-11-155
Krivoruchko A, Nielsen J (2015) Production of natural products through metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Opin Biotechnol 35:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.004
Kyndt JA, Meyer TE, Cusanovich MA, Van Beeumen JJ (2002) Characterization of a bacterial tyrosine ammonia lyase, a biosynthetic enzyme for the photoactive yellow protein. FEBS Lett 512(1–3):240–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02272-X
Li MJ, Kildegaard KR, Chen Y, Rodriguez A, Borodina I, Nielsen J (2015) De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 32:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.08.007
Liu D, Li BZ, Liu H, Guo XJ, Yuan YJ (2017) Profiling influences of gene overexpression on heterologous resveratrol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front Chem Sci Eng 11(1):117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meteno.2015.09.001
Liu QL, Liu HJ, Yang YY, Zhang XM, Bai YL, Qiao MQ, Xu HJ (2014) Scarless gene deletion using mazF as a new counter-selection marker and an improved deletion cassette assembly method in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Appl Microbiol 60(2):89–93. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.60.89
Luttik MA, Vuralhan Z, Suir E, Braus GH, Pronk JT, Daran JM (2008) Alleviation of feedback inhibition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae aromatic amino acid biosynthesis: quantification of metabolic impact. Metab Eng 10(3–4):141–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2008.02.002
Mao JW, Liu QL, Song XF, Wang HSY, Feng H, Xu HJ, Qiao MQ (2017) Combinatorial analysis of enzymatic bottlenecks of l-tyrosine pathway by p-coumaric acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 39(7):977–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2322-5
Ohashi K, Chaleckis R, Takaine M, Wheelock CE, Yoshida S (2017) Kynurenine aminotransferase activity of Aro8/Aro9 engage tryptophan degradation by producing kynurenic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci Rep 7(1):12180. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12392-6
Paravicini G, Mosch HU, Schmidheini T, Braus G (1989) The general control activator protein GCN4 is essential for a basal level of ARO3 gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 9(1):144–151
Rodriguez A, Kildegaard KR, Li MJ, Borodina I, Nielsen J (2015) Establishment of a yeast platform strain for production of p-coumaric acid through metabolic engineering of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis. Metab Eng 31:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.08.003
Romagnoli G, Knijnenburg TA, Liti G, Louis EJ, Pronk JT, Daran JM (2015) Deletion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARO8 gene, encoding an aromatic amino acid transaminase, enhances phenylethanol production from glucose. Yeast 32(1):29–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3015
Sato F, Inui T, Takemura T (2007) Metabolic engineering in isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 8(4):211–218. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920107781387438
Sauer B (1987) Functional expression of the cre-lox site-specific recombination system in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 7(6):2087–2096
Silva S, Costa EM, Calhau C, Morais RM, Pintado ME (2017) Anthocyanin extraction from plant tissues: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57(14):3072–3083. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1087963
Strucko T, Magdenoska O, Mortensen UH (2015) Benchmarking two commonly used Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for heterologous vanillin-β-glucoside production. Metab Eng Commun 2:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meteno.2015.09.001
Vuralhan Z, Luttik MA, Tai SL, Boer VM, Morais MA, Schipper D, Almering MJ, Kotter P, Dickinson JR, Daran JM, Pronk JT (2005) Physiological characterization of the ARO10-dependent, broad-substrate-specificity 2-oxo acid decarboxylase activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(6):3276–3284. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.6.3276-3284.2005
Xu P, Bhan N, Koffas MAG (2013) Engineering plant metabolism into microbes: from systems biology to synthetic biology. Curr Opin Biotech 24(2):291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2012.08.010
Yao LH, Jiang YM, Shi J, Tomas-Barberan FA, Datta N, Singanusong R, Chen SS (2004) Flavonoids in food and their health benefits. Plant Food Hum Nutr 59(3):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-004-0049-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Tianjin Key Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology [17JCZDJC32200]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [31770102]; the Sino-Swiss Scientific and Technological Cooperation Project supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China [2015DFG32140].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study, performing experimental assessments, drafting the articles, and revising it. All authors have contributed, seen and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Mao, J., Song, X. et al. Optimization of the l-tyrosine metabolic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by analyzing p-coumaric acid production. 3 Biotech 10, 258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02223-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02223-3