Abstract
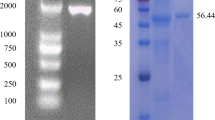
A cellulase encoding gene, Cel PRII, was identified from Mehsani buffalo rumen metagenome, and cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)pLysS. The 1170 bp full length gene encodes a 389 residue polypeptide (Cel PRII) containing a catalytic domain belonging to glycosyl hydrolase (GH) 5 family. The fusion protein consisting of the Cel PRII, thioredoxin tag and 6x Histidine tag with predicted molecular weight of 63 kDa when recovered from inclusion bodies under denaturing conditions, exhibited cellulolytic activity against carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC). Recombinant Cel PRII was stable in the pH range 4.0–10.0 with pH optima 6.0. The optimal reaction temperature of Cel PRII was 30 °C with more than 50% of its activity retained at the temperatures ranging from 0 to 50 °C. Cel PRII exhibited enhanced enzymatic activity in the presence of Mn2+ ions and was inhibited in the presence of chelating agent EDTA. The K m and V max values for CMC were found to be 166 mg/mL and 1292 IU/mg, respectively. Cel PRII identified in the present study may act as an excellent candidate for industrial applications, and may aid in lignocellulosic biomass conversion because of its potential cellulolytic activity, thermostability, and excellent pH stability.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GH:
-
Glycosyl hydrolase
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- DNS:
-
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid
References
Andreaus J, Azevedo H, Cavaco-Paulo A (1999) Effects of temperature on the cellulose binding ability of cellulase enzymes. J Mol Catal B Enzym 7:233–239
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173
Aspeborg H, Coutinho PM, Wang Y, Brumer H, Henrissat B (2012) Evolution, substrate specificity and subfamily classification of glycoside hydrolase family 5 (GH5). BMC Evol Biol 12:186
Bao L, Huang Q, Chang L, Zhou J, Lu H (2011) Screening and characterization of a cellulase with endocellulase and exocellulase activity from yak rumen metagenome. J Mol Catal B Enzym 73:104–110
Bashir Y, Pradeep Singh S, Kumar Konwar B (2014) Metagenomics: an application based perspective. Chin J Biol 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/146030
Bhat M, Bhat S (1997) Cellulose degrading enzymes and their potential industrial applications. Biotechnol Adv 15:583–620
Brulc JM, Antonopoulos DA, Miller MEB, Wilson MK, Yannarell AC, Dinsdale EA, Edwards RE, Frank ED, Emerson JB, Wacklin P (2009) Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:1948–1953
Cheema TA, Jirajaroenrat K, Sirinarumitr T, Rakshit SK (2012) Isolation of a gene encoding a cellulolytic enzyme from swamp buffalo rumen metagenomes and its cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Anim Biotechnol 23:261–277
Daniel R (2005) The metagenomics of soil. Nature Rev Microbiol 3:470–478
Duan CJ, Xian L, Zhao GC, Feng Y, Pang H, Bai XL, Tang JL, Ma QS, Feng JX (2009) Isolation and partial characterization of novel genes encoding acidic cellulases from metagenomes of buffalo rumens. J Appl Microbiol 107:245–256
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Feng Y, Duan C-J, Pang H, Mo X-C, Wu C-F, Yu Y, Hu Y-L, Wei J, Tang J-L, Feng J-X (2007) Cloning and identification of novel cellulase genes from uncultured microorganisms in rabbit cecum and characterization of the expressed cellulases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:319–328
Ferrer M, Golyshina OV, Chernikova TN, Khachane AN, Reyes-Duarte D, Santos VA, Strompl C, Elborough K, Jarvis G, Neef A (2005) Novel hydrolase diversity retrieved from a metagenome library of bovine rumen microflora. Environ Microbiol 7:1996–2010
Ferrer M, Martínez-Martínez M, Bargiela R, Streit WR, Golyshina OV, Golyshin PN (2016) Estimating the success of enzyme bioprospecting through metagenomics: current status and future trends. Microb Biotechnol 9:22–34
Flint HJ, Bayer EA, Rincon MT, Lamed R, White BA (2008) Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nature Rev Microbiol 6:121–131
Franco-Cirigliano MN, Rezende RdC, Gravina-Oliveira MP, Pereira PHF, Do Nascimento RP, Bon EPdS, Macrae A, Coelho RRR (2013) Streptomyces misionensis PESB-25 produces a thermoacidophilic endoglucanase using sugarcane bagasse and corn steep liquor as the sole organic substrates. BioMed Res Int 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/584207
Godfrey T, West S (1996) Textiles. In: Industrial enzymology. Macmillan Press, London, pp 360–371
Gong X, Gruniniger R, Forster R, Teather R, McAllister T (2013) Biochemical analysis of a highly specific, pH stable xylanase gene identified from a bovine rumen-derived metagenomic library. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2423–2431
Gullert S, Fischer MA, Turaev D, Noebauer B, Ilmberger N, Wemheuer B, Alawi M, Rattei T, Daniel R, Schmitz RA, Grundhoff A, Streit WR (2016) Deep metagenome and metatranscriptome analyses of microbial communities affiliated with an industrial biogas fermenter, a cow rumen, and elephant feces reveal major differences in carbohydrate hydrolysis strategies. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:121. doi:10.1186/s13068-016-0534-x
Healy F, Ray R, Aldrich H, Wilkie A, Ingram L, Shanmugam K (1995) Direct isolation of functional genes encoding cellulases from the microbial consortia in a thermophilic, anaerobic digester maintained on lignocellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:667–674
Hess M, Sczyrba A, Egan R, Kim T-W, Chokhawala H, Schroth G, Luo S, Clark DS, Chen F, Zhang T (2011) Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science 331:463–467
Isikgor FH, Becer CR (2015) Lignocellulosic biomass: a sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym Chem 6:4497–4559
Jørgensen H, Kristensen JB, Felby C (2007) Enzymatic conversion of lignocellulose into fermentable sugars: challenges and opportunities. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 1:119–134
Juturu V, Wu JC (2014) Microbial cellulases: engineering, production and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 33:188–203
Källberg M, Wang H, Wang S, Peng J, Wang Z, Lu H, Xu J (2012) Template-based protein structure modeling using the RaptorX web server. Nat Protoc 7:1511–1522
Kim SC, Kang SH, Choi EY, Hong YH, Bok JD, Kim JY, Lee SS, Choi YJ, Choi IS, Cho KK (2016) Cloning and characterization of an endoglucanase gene from Actinomyces sp. Korean native goat 40. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 29:126
Krause DO, Denman SE, Mackie RI, Morrison M, Rae AL, Attwood GT, McSweeney CS (2003) Opportunities to improve fiber degradation in the rumen: microbiology, ecology, and genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:663–693
Kuhad RC, Gupta R, Singh A (2011) Microbial cellulases and their industrial applications. Enzyme Res 2011. doi:10.4061/2011/280696
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Liu L, Feng Y, Duan C-J, Pang H, Tang J-L, Feng J-X (2009) Isolation of a gene encoding endoglucanase activity from uncultured microorganisms in buffalo rumen. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1035–1042
Lorenz P, Eck J (2005) Metagenomics and industrial applications. Nature Rev Microbiol 3:510–516
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Mackie RI (1997) Gut environment and evolution of mutualistic fermentative digestion. In: Mackie RI, White BA (eds) Gastrointestinal microbiology. Springer, New York, pp 13–35
Miller G (1959) Modified DNS method for reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Palackal N, Lyon CS, Zaidi S, Luginbühl P, Dupree P, Goubet F, Macomber JL, Short JM, Hazlewood GP, Robertson DE (2007) A multifunctional hybrid glycosyl hydrolase discovered in an uncultured microbial consortium from ruminant gut. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:113–124
Patel DD, Patel AK, Parmar NR, Shah TM, Patel JB, Pandya PR, Joshi CG (2014) Microbial and carbohydrate active enzyme profile of buffalo rumen metagenome and their alteration in response to variation in the diet. Gene 545:88–94
Pirzadah TB, Malik B, Kumar M, Rehman RU (2014) Lignocellulosic biomass: as future alternative for bioethanol production. In: Hakeem K, Jawaid M, Rashid U (eds) Biomass Bioenergy. Springer, Switzerland, pp 145–163
Pol D, Laxman RS, Rao M (2012) Purification and biochemical characterization of endoglucanase from Penicillium pinophilum MS 20. Indian J Biochem Biophys
Rashamuse K, Visser DF, Hennessy F, Kemp J, Roux-van der Merwe M, Badenhorst J, Ronneburg T, Francis-Pope R, Brady D (2013) Characterisation of two bifunctional cellulase–xylanase enzymes isolated from a bovine rumen metagenome library. Curr Microbiol 66:145–151
Rondon MR, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (1999) The Earth’s bounty: assessing and accessing soil microbial diversity. Trends Biotechnol 17:403–409
Tomme P, Warren R, Gilkes N (1995) Cellulose hydrolysis by bacteria and fungi. Adv Microb Physiol 37:1–81
Voget S, Steele H, Streit W (2006) Characterization of a metagenome-derived halotolerant cellulase. J Biotechnol 126:26–36
Wong DD, Chan VJ, McCormack AA, Batt SB (2010) A novel xyloglucan-specific endo-β-1,4-glucanase: biochemical properties and inhibition studies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1463–1471
Yang J, Dang H (2011) Cloning and characterization of a novel cold-active endoglucanase establishing a new subfamily of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 from a psychrophilic deep-sea bacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 325:71–76
Zhao S, Wang J, Bu D, Liu K, Zhu Y, Dong Z, Yu Z (2010) Novel glycoside hydrolases identified by screening a Chinese Holstein dairy cow rumen-derived metagenome library. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6701–6705
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the supporting staff at Department of Animal Nutrition, Anand Agricultural University, Anand, for their support in sample collection. This work was supported by Niche Area of Excellence project funded by Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi. The first author is also thankful to UGC-CSIR (New Delhi) for providing financial support in the form of fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, R.K., Patel, A.K., Davla, D.M. et al. Molecular cloning, heterologous expression, and functional characterization of a cellulolytic enzyme (Cel PRII) from buffalo rumen metagenome. 3 Biotech 7, 257 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0895-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0895-2