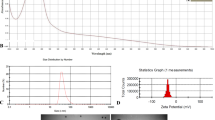
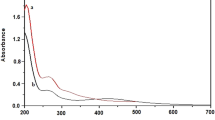
Abstract
Zinc oxide nanoparticles and curcumin are excellent antimicrobial agents. They have the potential to be used as alternative to antibiotics in wound infection management. In this study, ZnO–curcumin nanocomposite was synthesized and characterized. Physical adsorption of the nanocomposite onto collagen skin wound dressing was conducted and structural investigation was carried out by SEM. Antimicrobial assay, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and viability assays of different concentrations of nanocomposite loaded collagen membrane were conducted against clinically isolated methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci (MRCoNS), such as S. epidermidis, S. hemolyticus, and S. saprophyticus. The nanocomposite showed excellent anti-CoNS activity on time kill assay with the MIC value of 195 µg/mL against S. epidermidis, S. hemolyticus and 390 µg/mL against S. saprophyticus. The nanocomposite loaded collagen membrane also showed excellent in vitro antistaphylococcal activity. This study may lead to the development of antibiotic alternate strategies to control and limit the MRCoNS in wound-related infections.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Surh Y-J, Shishodia S (2007) The molecular targets and therapeutic uses of curcumin in health and disease. Springer, Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5
Augustine R, Malik HN, Singhal DK, Mukherjee A, Malakar D, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S (2014) Electrospun polycaprolactone/ZnO nanocomposite membranes as biomaterials with antibacterial and cell adhesion properties. J Polym Res 21:1. doi:10.1007/s10965-013-0347-6
Babu SS, Mathew S, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S (2016) Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, and microbial barrier properties of poly (ε-caprolactone)/cloisite 30B thin films 3. Biotechnology 6:249
Bradshaw CE (2011) An in vitro comparison of the antimicrobial activity of honey, iodine and silver wound dressings. Biosci Horiz 4:61–70. doi:10.1093/biohorizons/hzr008
Deepachitra R, Ramnath V, Sastry TP (2014) Graphene oxide incorporated collagen–fibrin biofilm as a wound dressing material. RSC Adv 4:62717–62727. doi:10.1039/c4ra10150b
Dhivya R, Ranjani J, Rajendhran J, Rajasekaran M, Annaraj J (2015) pH responsive curcumin/ZnO nanocomposite for drug delivery. Adv Mater Lett 6:505–512
Esawy MA, Awad GE, Wahab WAA, Elnashar MM, El-Diwany A, Easa SM, Fawkia M (2016) Immobilization of halophilic Aspergillus awamori EM66 exochitinase on grafted k-carrageenan-alginate beads 3. Biotechnology 6:29
Gopal J, Muthu M, Chun SC (2015) One-step, ultrasonication-mobilized, solvent-free extraction/synthesis of nanocurcumin from turmeric. RSC Adv 5:48391–48398. doi:10.1039/c5ra06002h
Gunes H, Gulen D, Mutlu R, Gumus A, Tas T, Topkaya AE (2013) Antibacterial effects of curcumin: an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration study. Toxicol Ind Health 32:246–250. doi:10.1177/0748233713498458
Guo G et al (2011) Preparation of curcumin loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers and their in vitro antitumor activity against Glioma 9L cells. Nanoscale 3:3825–3832
Jin T, Sun D, Su JY, Zhang H, Sue HJ (2009) Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide quantum dots against Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Enteritidis, and Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Sci 74:M46–M52. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.01013.x
John JF, Harvin AM (2007) History and evolution of antibiotic resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci: Susceptibility profiles of new anti-staphylococcal agents. Ther Clin Risk Manag 3:1143
Kumar H, Rani R (2013) Structural and optical characterization of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by microemulsion route. Int Lett Chem Phys Astron 14:26–36
Lim MM, Sultana N (2016) In vitro cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of silver-coated electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatine nanofibrous scaffolds 3. Biotechnology 6:211
Mei L, Wang Y, Tong A, Guo G (2016) Facile electrospinning of an efficient drug delivery system. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13:741–753
Mohanty C, Das M, Sahoo SK (2012) Sustained wound healing activity of curcumin loaded oleic acid based polymeric bandage in a rat model. Mol Pharma 9:2801–2811. doi:10.1021/mp300075u
Moussawi RN, Patra D (2016) Modification of nanostructured ZnO surfaces with curcumin: fluorescence-based sensing for arsenic and improving arsenic removal by ZnO. RSC Adv 6:17256–17268
Mun S-H et al (2013) Synergistic antibacterial effect of curcumin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytomedicine 20:714–718. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2013.02.006
Mun S-H et al (2014) Curcumin reverse methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 19:18283–18295. doi:10.3390/molecules191118283
Panchatcharam M, Miriyala S, Gayathri VS, Suguna L (2006) Curcumin improves wound healing by modulating collagen and decreasing reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell Biochem 290:87–96
Patra P, Mitra S, Debnath N, Pramanik P, Goswami A (2014) Ciprofloxacin conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticle: a camouflage towards multidrug resistant bacteria. Bull Mater Sci 37:199–206. doi:10.1007/s12034-014-0637-6
Piette A, Verschraegen G (2009) Role of coagulase-negative staphylococci in human disease. Vet Microbiol 134:45–54. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.09.009
Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG (2010) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deli 7:1063–1077
Reddy KM, Feris K, Bell J, Wingett DG, Hanley C, Punnoose A (2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl Phys Lett 90:213902. doi:10.1063/1.2742324
Sanphui P, Goud NR, Khandavilli UR, Bhanoth S, Nangia A (2011) New polymorphs of curcumin. Chem Commun 47:5013–5015
Sirelkhatim A et al (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano Micro Lett 7:219–242. doi:10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x
Soumya KR, Thomas SA, Sugathan S, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan EK (2013) Antibiotic susceptibility and multiplex PCR analysis of coagulase negative staphylococci isolated from laboratory workers. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 2:266–272
Soumya KR, Sugathan S, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan E (2016) Studies on coexistence of mec gene, IS256 and novel sasX gene among human clinical coagulase-negative staphylococci 3. Biotechnology 6:233
Tan TY, Ng SY, Ng WX (2006) Clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci recovered from nonsterile sites. J Clin Microbiol 44:3413–3414. doi:10.1128/jcm.00757-06
Thomas R, Soumya KR, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan EK (2015) Inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticle fabricated urinary catheter on colonization efficiency of coagulase negative staphylococci. J Photochem Photobiol B 149:68–77. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.04.034
Tocco I, Zavan B, Bassetto F, Vindigni V (2012) Nanotechnology-based therapies for skin wound regeneration. J Nanomater 2012:1–11. doi:10.1155/2012/714134
Voicu G, Oprea O, Vasile B, Andronescu E (2013) Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide-gentamicin hybrid material. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct (DJNB) 8(3):1191–1203
Zhou J, Zhao F, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yang L (2007) Size-controlled synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photoluminescence properties. J Lumin 122–123:195–197. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2006.01.089
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Indian Council of Medical Research, Government of India for the funded project on Coagulase-negative staphylococci. We acknowledge Director, School of Chemical Science and School of Pure and Applied Physics, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam, for the help. We also thank the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, for DBT RGYI and DBT—MSUB—IPLSARE Programs in School of Biosciences, Mahatma Gandhi University for providing instrumentation facilities. We are grateful to the Dean and laboratory staffs of the MOSC Medical College, Kolenchery.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soumya, K.R., Snigdha, S., Sugathan, S. et al. Zinc oxide–curcumin nanocomposite loaded collagen membrane as an effective material against methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci. 3 Biotech 7, 238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0861-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0861-z