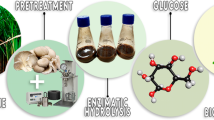
Abstract
Lignocelluloses from agricultural, industrial, and forest residues constitute a majority of the total biomass present in the world. Environmental concerns of disposal, costly pretreatment options prior to disposal, and increased need to save valuable resources have led to the development of value-added alternate technologies such as bioethanol production from lignocellulosic wastes. In the present study, biologically pretreated (with the fungus, Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1) and chemically pretreated (with mild acid or dilute alkali) wheat straw (WS) and banana stem (BS) were subsequently subjected to enzymatic saccharification (with mixture of 6.0 U/g of filter paper cellulase and 17 U/g of β-glucosidase) and were evaluated for bioethanol production using Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCIM 3570. Biological and chemical pretreatments removed up to 4.0–49.2 % lignin from the WS and BS which was comparatively higher than that for cellulose (0.3–12.4 %) and for hemicellulose (0.7–21.8 %) removal with an average 5.6–49.5 % dry matter loss. Enzymatic hydrolysis yielded 64–306.6 mg/g (1.5–15 g/L) reducing sugars from which 0.15–0.54 g/g ethanol was produced from Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCIM 3570.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Industrial bioconversion of renewable resources to bioethanol is a promising alternative to petroleum-based chemical synthesis (Volynets and Dahman 2011). In this context, lignocelluloses, the most abundant source of sugars, are a potential candidate for obtaining energy in the form of charcoal, hydrogen, ethanol, and biogas; the last three of which require hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic material. Production of biofuel and other bioproducts from lignocellulose is expected to promote rural economies, enhance energy security, and alleviate environmental pollution (Espino et al. 2011).
The use of lignocelluloses as a raw material is particularly convenient because it results in a significant reduction in the cost of production of value-added products viz. enzymes, organic acids, etc. However, for the establishment of lignocellulose-based biofuel economy, saccharification of these materials is necessary (Espino et al. 2011). The phenyl propanoid polymers in the lignin prevents access to the cellulose and hemicellulose polymer for the efficient release of sugars, and subsequent fermentation to bioethanol, and hence the lignin must be removed first (Espino et al. 2011). During the last decade, considerable developments in pretreatment techniques for improving the rate of release and total yield of sugars in the hydrolysis step have been made (Hendriks and Zeeman 2009) and using these processes substantial amounts of lignin and hemicelluloses have been hydrolyzed and transformed into value-added products (Dashtban et al. 2009). The pretreatment techniques can be classified as physical, chemical, and biological and can be used individually or in combination, such as mechanical and thermal or chemical and thermal (Talebnia et al. 2010). The overall efficiency of any pretreatment process can be correlated to a good balance between low inhibitor formation and high substrate digestibility.
Biological pretreatment comprises the use of microorganisms especially brown rot, soft rot and/or white-rot fungi to selectively degrade lignin and hemicellulose. Of these, white-rot fungi seem to be the most effective as they are potential producers of laccase (E.C.1.10.3.2), manganese peroxidase (MnP; E.C.1.11.1.13), and lignin peroxidase (LiP; E.C.1.11.1.14), enzymes that modify lignin. Various researchers have reported the use of many white-rot fungi (Pleurotus ostreatus, Trametes versicolor, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus) for the depolymerization of lignin and hemicellulosic compounds (Kuhar et al. 2008; Shrivastava et al. 2011). The selection of fungi is based on their higher affinity to degrade lignin rather than the carbohydrate moieties. Though the use of biological pretreatment is considered safe, environmentally friendly and less energy consuming compared to other pretreatment methods, the rate of hydrolysis is low and needs improvement to make it a commercially viable proposition.
The objective of the present work was to evaluate and compare the effect of fungal pretreatment with the chemical pretreatments on Wheat straw (WS) and banana stem (BS) and to improve the enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain higher reducing sugar for bioethanol production.
Materials and methods
Lignocellulosic substrates
Wheat straw (WS) and banana stem (BS) were collected locally and ground to an approximate particle size of 1–2 mm. For analytical purposes, the untreated and pretreated substrates were milled to 30 mesh size.
Microorganisms and culture conditions
Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1 (GenBank accession no. EU420068) was grown and maintained on 2 % Malt Extract Agar (MEA) medium agar plates. MEA contained (g/L) Malt extract 30.0, Peptone 3.0, and Agar 15.0 (pH 5.0) at 30 °C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCIM 3570 was procured from National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (NCIM), National Chemical Laboratory (NCL), Pune, India and was maintained on agar slants containing (g/L) Peptone 10.0, Glucose 40.0, NaCl 5.0, and agar 20.0 (pH 5.5) at 30 °C. Both isolates were stored at 4 °C and sub-cultured every fortnight.
The inoculum of Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1 was prepared in 50 ml 2 % Malt Extract Broth (MEB) in 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks. MEB had the same composition as MEA but lacked agar. The flasks were inoculated with 5 mycelial discs (7 mm diameter each) which had been prepared from 8-day-old fungal culture grown on MEA and incubated on a rotatory shaker (150 rpm) at 30 °C for 8 days. The inoculum of S. cerevisiae was prepared by growing the culture at 30 °C for 24 h under static condition in a medium containing (g/L) Peptone 10.0, Glucose 40.0, and NaCl 5.0 (pH 5.5).
Pretreatment of substrates
Chemical pretreatment
WS and BS were subjected to two chemical pretreatment regimes prior to enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation. For this, a 10 % slurry of WS or BS was incubated in 1 N NaOH or 1 N H2SO4 at room temperature for 24 h following which the slurries were washed repeatedly with water to a neutral pH, and then oven dried at 60 °C to a constant weight.
Fungal (biological) pretreatment
Fungal pretreatment was carried out with 15.0 g of WS or BS in 500 ml Erlenmeyer flasks and were moistened with a medium described by Asther et al. (1988) to give a final substrate to moisture ratio of 1:4 (w/v). The moistening medium containing (g/L) KH2PO4 0.2, CaCl2·2H2O 0.0132, MgSO4·7H2O 0.05, FeC6H5O7·NH4OH 0.085, ZnSO4·7H2O 0.0462, MnSO4·7H2O 0.035, CoCl2·6H2O 0.007, CuSO4·5H2O 0.007, l-Aspargine 1.0, NH4NO3 0.5, Thiamine-HCl 0.0025, yeast extract 0.5, Glucose 10, Tween-80 0.1, and pH 5.0. Each flask was inoculated with P. ostreatus HP-1 to a ratio of 65 mg fungal dry mass per gram of BS or WS and incubated at 30 °C for various incubation periods. The flasks without fungal biomass served as a control.
Enzyme assays
The cultures in the flasks harvested at intervals of 4 days, suspended in 30 mL acetate buffer (pH 5.0, 100 mM) and shaken in a rotatory shaker at 150 rpm at 30 °C. After 2 h incubation, the cultures were filtered through muslin cloth, and the cloth squeezed to maximize enzyme extraction. The filtrate was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min and the supernatant was analyzed for laccase, peroxidase, xylanase, and β-Glucosidase activities. Laccase activity (E.C. 1.10.3.2) was determined by monitoring the A420 change related to the rate of oxidation of 2, 2-Azino- Bis-3-ethyl-benzthiozoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS, ε = 36,000 cm−1 M−1) at 30 °C for 3 min (Niku-Paavola et al. 1990). The reaction mixture contained 100 μL of 50 mM ABTS, 800 μL of 100 mM Na-Acetate buffer (pH 5.0), and 100 μL of appropriately diluted enzyme extract. Manganese peroxidase (MnP) activity (E.C. 1.11.1.13) was measured by oxidation of 2, 6-dimethoxy phenol (DMP, ε = 27,500 cm−1 M−1) in the presence of H2O2 and MnSO4 at 469 nm. The reaction mixture contained 1 mM DMP, 0.1 mM H2O2, 1 mM MnSO4, and 100 mM Sodium tartarate buffer (pH 4.5). MnP activity was corrected for manganese-independent peroxidase activity by subtracting the activity obtained at pH 3.25 in the absence of MnSO4 at 469 nm (Martinez et al. 1996). One unit of enzyme activity (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme which leads to the oxidation of 1 μM of substrate/min under the standard assay condition. Xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8) activity was determined according to Bailey et al. (1992) using birch wood xylan (1 % w/v) as a substrate. Filter paper activity (FPase) was determined according to Ghose (1987) using Whatman no. 1 filter paper as a substrate. One unit of enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that liberates 1 μmole of reducing sugar as xylose or glucose per min under the standard assay condition. β-glucosidase activity was determined by measuring p-nitrophenol released from p-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside at 50 °C. The reaction mixture consisting of 2 mM p-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside in 50 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.8) was incubated with enzyme at 50 °C for 30 min in a total volume of 0.5 mL. The reaction was terminated by addition of 1 mL 2 M sodium carbonate. The amount of p-nitrophenol released was determined by measuring absorbance at 410 nm. One unit of β-Glucosidase activity is defined as amount of enzyme required to release 1 μM p-nitrophenol per minute under the standard assay condition.
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Enzymatic hydrolysis of untreated and pretreated WS and BS was performed using in-house produced crude cellulase from mixed culture of Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillusellipticus. The reaction system for saccharification consisted of 100 ml of sodium citrate buffer (0.05 M, pH 5.0) containing 5 g of respective substrate (untreated and pretreated) and a mixture of 6.0 U/g of crude filter paper cellulase (FPase) and 17 U/g of β-glucosidase. The reaction was carried out at 50 °C and 150 rpm for 48 h. The samples were withdrawn at regular interval of 4 h, centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 15 min and the supernatant was analyzed for total reducing sugar released by dinitrosalicylic acid method (Miller 1959).
Ethanol production
The enzymatic hydrolysates obtained were supplemented with (g/L) (NH4)2SO4 0.5, KH2PO4 0.5, yeast extract 2.5, pH 5.5, and inoculated with 2.0 % (v/v) culture of S. cerevisiae NCIM 3570 (O.D. 0.6) and incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. The fermented broth obtained was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm at 4 °C for 10 min and the cell-free supernatant was used for the analysis of ethanol.
Analytical methods
Weight loss of substrate was determined by subtracting the weight of oven dried pretreated substrate at 60 °C to a constant weight from the weight of control (untreated) substrate. The content of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin were determined by methods described by Van Soest (Goering and Van Soest 1970; Van Soest et al. 1991). Total reducing sugars were estimated by the dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA) method (Miller 1959).
Ethanol was estimated by gas chromatography (GC) (Perklin Elmer, Turbometrix 40 headspace sampler) with PE wax column at oven temperature of 85 °C and flame ionization detector (FID) at 200 °C. Nitrogen was used as a carrier gas with a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The ethanol standards were prepared using commercial grade ethanol (Merck, India).
All the experiments were carried out in triplicates and the data represent the mean values of the experiments.
Results and discussion
Chemical pretreatment
Chemical Pretreatment employed different chemicals such as acid and alkali. The purpose of pretreatment of substrates is to disorganize the crystalline structure of micro and macro fibrils to release polymer chains of cellulose and hemicelluloses and modify the pore size to render them accessible to enzymatic attack. Among the various pretreatments, dilute acid and mild alkali pretreatments are effective in targeting hemicelluloses and lignin, respectively (Talebnia et al. 2010). Table 1a depicts the chemical composition of untreated (control) WS and BS. In the present study, mild alkali (1 N NaOH) and dilute acid (1 N H2SO4) pretreatments were evaluated on each lignocellulosic substrate (WS and BS) separately. Table 1b summarizes the compositional changes during chemical pretreatment of WS and BS. Alkali pretreatment caused a substantial higher removal of lignin, cellulose, and dry matter of 46.3, 12.4, and 42 %, respectively, compared to acid pretreatment, i.e., 13.7, 7.2 and 24.9 %, respectively, in WS. However, the removal of hemicelluloses (21.8 %) was more with acid pretreatment as compared with alkali pretreatment (18.8 %). Similar trend of results were also obtained in case of BS with 49.2, 8.5 and 49.5 % of removal of lignin, cellulose and dry matter, respectively, in alkali pretreatment, while 16.2 % removal of hemicellulose was attained using acid pretreatment. According to the previous report (Talebnia et al. 2010), acid pretreatment helped in removing the hemicellulosic fraction and may have decreased the degree of polymerization during pretreatment. Dilute acid treatment is already reported not to remove the lignin completely from the substrate but modify the lignin–carbohydrate linkage (Dashtban et al. 2009). Moreover, the purpose of mild alkali pretreatment is to remove lignin and hence to increase the susceptibility of cellulose to become readily available for enzymes, which permits the yeast to convert the glucose into ethanol. The results thus obtained in the present study are in agreement with Bjerre et al. (1996) who have also reported dilute NaOH pretreatment as an effective method for lignin removal. Similarly in another study, Damisa et al. (2008) reported, pretreatment of substrates with alkali may result in the swelling of the particle causing easy lignin removal and cellulose depolymerization.
Fungal pretreatment
Biological pretreatment uses microorganisms and their enzymatic machinery for selective delignification of the lignocellulosic residues (Adenipekun and Fasidi 2005). The one of the main purpose of the biological pretreatment using white-rot basidiomycetes is to make substrate-carbohydrate digestible as much as possible and reduce environmental hazard (Adenipekun and Fasidi 2005). In the present study, white-rot basidiomycete Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1 was used for fermentation of WS and BS which resulted in decrease in lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose, and dry matter content (Table 2). Higher dry matter loss (DML) in WS (40 %) was obtained as compared with BS (32 %) after 32 days of fermentation which may be attributed to the collective removal of lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose (Gupta et al. 2011). Removal of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose occurred at a slow pace during whole fermentation period. Lignin removal was higher in WS (40 %) compared to BS (29 %) with a decrease in cellulose (10.4 and 7.3 %, respectively) and hemicellulose (12.9 and 14.3 %, respectively) content after 32 days of fermentation. This could be because of difference in cell wall assembly and chemical structure of lignin and lignin–carbohydrate complex present in WS and BS (Shrivastava et al. 2011). Lignin removal over the entire fermentation period obtained in the present study is found to be in the range of previously reported values of lignin degradation (up to 46 %) of plant residue by much studied Phanerochaete flavido-alba (Lopez et al. 2006). An increase in dry matter loss along with lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose removal has also been reported by various authors (Shrivastava et al. 2011; Arora and Sharma 2009). In similar context, Hatakka et al. (2001) reported lignin degradation by Lentinus edodes occurred during secondary metabolism and nitrogen starvation condition which might have been the probable reason for achieving higher lignocellulosic degradation in the later phase of the present experiment. Various researchers have also reported similar degradative capability of P. ostreatus and have shown dry matter loss, hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin removal ranging from 5 to 20 %, 2–20 %, 5–30 % and 2–40 % respectively (Shrivastava et al. 2011; Shabtay et al. 2009; Binod et al. 2010). There are several other reports where Phanerochaete chrysosporium, the most widely studied white-rot fungus for lignin degradation resulted in higher amount of lignin loss but was also found to cause significant loss in carbohydrate fraction (Shrivastava et al. 2011; Taniguchi et al. 2005).
The difference in the degradation pattern of substrate by Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1 could be attributed to the different enzymatic profile observed during growth on WS and BS (Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4). Maximum laccase activity of 14,189 and 8,118.5 U/g, and 562.80 and 344.57 U/g of manganese peroxidase were obtained on 8th day of fermentation with WS and BS, respectively (Figs. 1, 3). Thereafter, no significant increase in the MnP production was observed during entire fermentation period. Initially, in the lag phase the activity increases slowly reaching maximum on the 8th day for laccase but thereafter decreases. In the late phase of cultivation, increase in laccase activity was again observed. The twin peak in laccase production could be attributed to the mycelial autolysis and release of mycelial bound enzyme or it might be due to nitrogen starvation in the second phase of cultivation (Shrivastava et al. 2011; Gupte et al. 2007). Similar pattern of laccase activity in two Pleurotus spp has also been reported by Reddy et al. (2003). Xylanase activities of 10 and 9.45 U/g of substrate were obtained on 8th day of fermentation with WS and BS, respectively (Figs. 2, 4).
The degradation of WS and BS (in terms of dry matter, lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose removal) continued throughout the studied period and substrate degradation was not found to be directly correlated with the production of enzymes (Table 2, Figs. 1, 2) as has been reported by Li et al. (2008) and Mendonca et al. (2008). Recently, Sharma and Arora (2010) and Shrivastava et al. (2011) have also observed that the enzyme production profile cannot be correlated well with the degradation of polymer, which showed that fiber degradation not only depends upon the production of enzymes but also regulated by a variety of physiological factors.
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Pretreatment is a crucial step for any lignocelluloses prior to enzymatic hydrolysis (saccharification). Different pretreatments have been reported in the literature to make substrate more conducive for hydrolysis (Zhao et al. 2010). To evaluate the effect of pretreatment conditions on the digestibility of WS and BS, enzymatic hydrolysis was carried out and results are depicted in Figs. 5 and 6. Maximum reducing sugar of 64 mg/g (3.2 g/L), 184.8 mg/g (9.23 g/L), 173 mg/g (8.65 g/L), and 166 mg/g (8.35 g/L) were obtained with untreated, fungal pretreated, alkali pretreated, and acid pretreated WS, respectively, in 44 h. Whereas, in case of BS it was 107.8 mg/g (5.3 g/L), 136.8 mg/g (6.8 g/L), 306.6 mg/g (15.3 g/L) and 210 mg/g (10.5 g/L) with untreated, fungal pretreated, alkali pretreated, and acid pretreated BS, respectively, in 48 h. Chapla et al. (2010) reported alkali (dilute NaOH) pretreated WS and rice straw yielded 151.6 and 163.06 mg/g of sugar, respectively. Taniguchi et al. (2005) reported the release of 330 mg/g of sugar from rice straw fermented with Pleurotus ostreatus. Moreover, Gupta et al. (2011) have reported release of 402 mg/g sugar from Prosopis Juliflora fermented with Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Monsalve et al. (2006) reported 20 g/L reducing sugar yield after sequential alkali–acid pretreatment of BS.
The results thus obtained clearly indicate that the pretreatment of substrates resulted in an improved enzymatic saccharification compared to untreated substrates. This may be attributed to the increase in available surface area and decrease in degree of polymerization along with the separation of lignin–carbohydrate linkage for easy accessibility of substrates for enzymatic hydrolysis (Sun and Cheng 2002).
Ethanol production
The sugar hydrolysate obtained from saccharification of untreated, pretreated WS and BS was investigated for yeast cell biomass and ethanol production (Table 3). Several evidences have suggested that the separate fermentation by substrate-specific organisms worked better instead of using single culture or co-culture (Cheng et al. 2008). The cellulosic hydrolysates were fermented with S. cerevisiae NCIM 3570 and the highest ethanol production of 3.38 g/L with a yield of 0.54 g/g was obtained with fungal pretreated WS hydrolysate along with 0.91 g/L of yeast cell biomass. Moreover, fermentation of fungal pretreated BS hydrolysate gave 2.0 g/L of ethanol with yield of 0.40 g/g, after 48 h along with 0.85 g/L of yeast cell biomass. Lower ethanol yield was obtained with untreated WS (0.31 g/g) and BS (0.15 g/g) in comparison with that of the treated one. In the present experiment, the ethanol yield (0.40 g/g) obtained from fungal pretreated BS hydrolysate was very much in agreement with the report of Mamma et al. (1995) who reported 0.40 g/g of ethanol yield from sweet sorghum. However, the ethanol yield (0.54 g/g) from fungal pretreated WS hydrolysate was higher than that reported by having an ethanol yield of 0.48 g/g from corncob (Chen et al. 2007). Reddy et al. (2010) reported 3.82 g/L of ethanol from alkali pretreated BS. The above results, thus show that the pretreatment increases ethanol yield.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrates that the pretreatment methods are a remarkable approach for massive utilization of lignocellulosic biomass for higher sugar yield during saccharification and eventually to bioethanol production. The results obtained with the biological pretreatment were better in case of WS and BS with respect to the yield of ethanol which shows the potentiality of our culture Pleurotus ostreatus HP-1 which posses a good ligninolytic and lignin degrading ability which lead to the significant improvement of enzymatic hydrolysis of WS and BS. Thus, the utilization of lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production necessitates the production technology to be cost effective and environmentally sustainable. Process integration (process engineering and strain engineering) for second generation bioethanol will still need to be carried out to circumvent the difficulties of co-fermentation (pentose and hexose) and thus, to improve system efficiency.
References
Adenipekun CO, Fasidi IO (2005) Degradation of selected agricultural wastes by Pleurotus ostreatus (Fries) Singer and Lentinus subnudus (Berk) Nigeria edible mushrooms. Adv Food Sci 27:61–64
Arora DS, Sharma RK (2009) Enhancement in Invitro digestibility of wheat straw obtained from different geographical regions during solid state fermentation by white rot fungi. Bioresour 4:909–920
Asther M, Lesage L, Drapron R, Corrieu G, Odier E (1988) Phospholipid and fatty acid enhancement of Phanerochaete chrysosporium INA-12 in relation to ligninase production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:393–398
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270
Binod P, Sindhu R, Singhania RR, Vikram S, Devi L, Nagalakshmi S, Kurien N, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2010) Bioethanol production from rice straw: an overview. Bioresour Technol 101:4767–4774
Bjerre AB, Olesen AB, Fernqvist T (1996) Pretreatment of wheat straw using combined wet oxidation and alkaline hydrolysis resulting in convertible cellulose and hemicellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:568–577
Chapla D, Divecha J, Madamwar D, Shah A (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial waste for xylanase production by Aspergillus foetidus MTCC 4898 under solid state fermentation and its application in saccharification. Biochem Eng J 49:361–369
Chen M, Xia L, Xue P (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob and ethanol production from cellulosic hydrolysate. Int Biodeter Biodeg 59:85–88
Cheng KK, Cai BY, Zhang JA, Ling HZ, Zhou YJ, Ge JP, Xu JM (2008) Sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate for ethanol production by acid recovery process. Biochem Eng J 38:105–109
Damisa DI, Ameh JB, Umoh VJ (2008) Effect of chemical pretreatment of some lignocellulosic wastes on the recovery of cellulase from Aspergillus niger AH3 mutant. Afr J Biotechnol 7:2444–2450
Dashtban M, Schraft H, Qin W (2009) Fungal bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues; opportunities and perspectives. Int J Biol Sci 5:578–595
Espino XM, Perez FB, Gaviria LA, Vazquez RR, Sima MT, Maldonado JD, Canche BBC (2011) Saccharification with Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus enzymatic extracts of pre treated banana waste. Afr J Biotechnol 10:3824–3834
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Goering HK, Van Soest PJ (1970) Forage fiber analysis agricultural handbook. 379, USDA, Washington DC
Gupta R, Mehta G, Khasa YP, Kuhad RC (2011) Fungal delignification of lignocellulosic biomass improves the saccharification of cellulosics. Biodegradation 22:797–804
Gupte A, Gupte S, Patel H (2007) Ligninolytic enzyme production under solid state fermentation by white-rot fungi. J Sci Ind Res 66:611–614
Hatakka A (2001) Biodegradation of lignin. Biopolymers 1:129–180
Hendriks A, Zeeman G (2009) Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 100:10–18
Kuhar S, Nair LM, Kuhad RC (2008) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic material with fungi capable of higher lignin degradation and lower carbohydrate degradation improves substrate acid hydrolysis and the eventual conversion to ethanol. Can J Microbiol 54:305–313
Li L, Li XZ, Tang WZ, Zhao J, Qu YB (2008) Screening of a fungus capable of powerful and selective delignification of wheat straw. Lett Appl Microbiol 47:415–420
Lopez MJ, Vargas-Garcia MC, Suarez-Estrella F, Moreno J (2006) Biodelignification and humification of horticultural plant residues by fungi. Int Biodeter Biodegr 57:24–30
Mamma D, Christakopoulos P, Koullas D, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Koukios E (1995) An alternative approach to the bioconversion of sweet sorghum carbohydrates to ethanol. Biomass Bioenerg 8:99–103
Martinez MJ, Ruiz-Duenas FJ, Guillen FA, Martinez AT (1996) Purification and catalytic properties of two manganese-peroxidase isoenzymes from Pleurotus eryngii. Eur J Biochem 237:424–432
Mendonca RT, Jara JF, Gonzalez V, Elissetche JP, Freer J (2008) Evaluation of the white rot fungi Ganoderma australe and Ceriporiopsis subvermispora in biotechnological applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1323–1330
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Monsalve J, Medina V, Ruiz A (2006) Producción de etanol a partir de la cáscara de banano y de almidón de Yuca. Dyna 73:21–27
Niku-Paavola ML, Raaska L, Itavaara M (1990) Detection of white-rot fungi by a non-toxic stain. Mycol Res 94:27–31
Reddy GV, Ravindra Babu P, Komaraiah P, Roy KRRM, Kothri IL (2003) Utilization of banana waste for the production of ligninolytic and cellulolytic enzymes by solid substrate fermentation using two Pleurotus species (P. ostreatus and P. sajor-caju). Process Biochem 38:1457–1462
Reddy HKY, Srijana M, Reddy MD, Reddy G (2010) Coculture fermentation of banana agro-waste to ethanol by cellulolytic thermophilic Clostridium thermocellum CT2. Afr J Biotechnol 9:1926–1934
Shabtay A, Hadar Y, Eitam H, Brosh A, Orlov A, Tadmor Y, Izhaki I, Kerem Z (2009) The potential of Pleurotus treated olive mill solid waste as cattle feed. Bioresour Technol 100:6457–6464
Sharma RK, Arora DS (2010) Changes in biochemical constituents of paddy straw during degradation by white rot fungi and its impact on in vitro digestibility. J Appl Microbiol 109:679–686
Shrivastava B, Thakur S, Khasa YP, Gupte A, Puniya AK, Kuhad RC (2011) White rot fungal conversion of wheat straw to energy rich cattle feed. Biodegradation 22:823–831
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Talebnia F, Karakashev D, Angelidaki I (2010) Production of bioethanol from wheat straw: an overview of pretreatment, hydrolysis and fermentation. Bioresour Technol 101:4744–4753
Taniguchi M, Suzuki H, Watanabe D, Sakai K, Hoshino K, Tanaka T (2005) Evaluation of pretreatment with Pleurotus ostreatus for enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw. J Biosci Bioeng 100:637–643
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber and non starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74:3583–3597
Volynets B, Dahman Y (2011) Assessment of pretreatments and enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw as a sugar source for bioprocess industry. Int J Energy Environ 2:427–446
Zhao H, Baker GA, Cowins JV (2010) Fast enzymatic saccharification of switch grass after pretreatment with ionic liquids. Biotechnol Prog 26:127–1
Acknowledgments
Authors are very grateful to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT Sanction no. BT/PR9197/PBD/26/120/2007), Ministry of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for their financial support. Ms. Shilpi Thakur and Mr. Bhuvnesh Shrivastava wish to acknowledge Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for Senior Research Fellowship. Shilpi Thakur also wants to acknowledge Sophisticated Instrumentation Centre for Applied Research and Testing (SICART), Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, India for providing instrumentation facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, S., Shrivastava, B., Ingale, S. et al. Degradation and selective ligninolysis of wheat straw and banana stem for an efficient bioethanol production using fungal and chemical pretreatment. 3 Biotech 3, 365–372 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-012-0102-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-012-0102-4