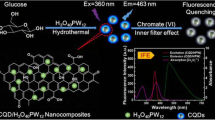
Abstract
Green-synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (N-CQDs), offering an excellent platform for the ultra-sensitive dual detection of tannic acid and Hg2+ ions, were explored in this work. The N-CQDs were synthesized in a straightforward, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly hydrothermal method. These N-CQDs exhibited remarkable and dynamic “on-off-on” luminescent characteristics, demonstrating an exceptional sensitivity and selectivity towards tannic acid and Hg2+ ions. The specific interactions between the N-CQDs and tannic acid, along with the reversible binding with Hg2+ ions, contribute to the distinct dual-detection capabilities. The sensing system covers a linear concentration range of 10–80 µM to tannic acid and 0.1 to 1 nm for Hg2+, showcasing its versatility for different concentration range with a lower detection limit of 25 nM and 3 nM, respectively. Furthermore, the N-CQDs displayed high stability and minimal interference from typical interfering species, making them a desirable tool for environmental monitoring and quality control. Validation through real sample analysis substantiates the accuracy and reliability of the developed sensing approach in practical scenarios. This study not only underscores the promise of green-synthesized N-CQDs as enhanced fluorescence probes but also contributes to the development of efficient and environmentally friendly materials for dual sensing applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data were generated at SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai using the facilities with Project No. 31/03/2014-15/PVSE-R&D, Government of India. Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Abbas AN, Liu B, Chen L, Ma Y, Cong S, Aroonyadet N, Köpf M, Nilges T, Zhou C (2015) Black phosphorus gas sensors. ACS Nano 9(5):5618–5624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b01961
Barvin RKB, Prakash P, Ganesh V, Jeyaprabha B (2019) Highly selective and sensitive sensing of toxic mercury ions utilizing carbon quantum dot-modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Environ Res 13(6):1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00236-2
Behrouzifar F, Shahidi S-A, Chekin F, Hosseini S, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A (2021) Colorimetric assay based on horseradish peroxidase/reduced graphene oxide hybrid for sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide in beverages. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 257:119761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119761
Chen Z, Zhang X, Cao H, Huang Y (2013) Chitosan-capped silver nanoparticles as a highly selective colorimetric probe for visual detection of aromatic ortho-trihydroxy phenols. Analyst 138(8):2343. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an36905f
Cheng C, Shi Y, Li M, Xing M, Wu Q (2017) Carbon quantum dots from carbonized walnut shells: Structural evolution, fluorescence characteristics, and intracellular bioimaging. Mater Sci Eng C 79:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.094
Cui H, Li Q, Meng R, Zhao H, He C (1998) Flow injection analysis of tannic acid with inhibited chemiluminescent detection. Anal Chim Acta 362(2–3):151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00031-2
Delimont NM, Haub MD, Lindshield BL (2017) The impact of tannin consumption on iron bioavailability and status: a narrative review. Curr Dev Nutr 1(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3945/cdn.116.000042
EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) (2014) Scientific opinion on the safety and efficacy of tannic acid when used as feed flavouring for all animal species. EFSA J. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3828
Gaddam RR, Vasudevan D, Narayan R, Raju KVSN (2014) Controllable synthesis of biosourced blue-green fluorescent carbon dots from camphor for the detection of heavy metal ions in water. RSC Adv 4(100):57137–57143. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA10471D
He J, Zhang H, Zou J, Liu Y, Zhuang J, Xiao Y, Lei B (2016) Carbon dots-based fluorescent probe for “off-on” sensing of Hg(II) and I. Biosens Bioelectron 79:531–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.084
Hong KH (2017) Polyvinyl alcohol/tannic acid hydrogel prepared by a freeze-thawing process for wound dressing applications. Polym Bull 74(7):2861–2872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1868-z
Huo X, He Y, Ma S, Jia Y, Yu J, Li Y, Cheng Q (2020) Green synthesis of carbon dots from grapefruit and its fluorescence enhancement. J Nanomater 2020:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8601307
Hutton GAM, Martindale BCM, Reisner E (2017) Carbon dots as photosensitisers for solar-driven catalysis. Chem Soc Rev 46(20):6111–6123. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00235A
Khalilzadeh MA, Sadeghifar H, Venditti R (2019) Natural clinoptilolite/KOH: an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for carboxymethylation of hemicellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(27):11680–11688. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02239
Kharian S, Teymoori N, Khalilzadeh MA (2012) Multi-wall carbon nanotubes and TiO2 as a sensor for electrocatalytic determination of epinephrinein the presence of p-chloranil as a mediator. J Solid State Electrochem 16(2):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1362-3
Kumari L, Baghel M, Panda S, Sakure K, Giri TK, Badwaik H (2021) Chemistry, biological activities, and uses of moringa gum. In: Murthy HN (ed) Gums, resins and latexes of plant origin. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–24
Li G-W, Hong L, Tong M-S, Deng H-H, Xia X-H, Chen W (2015) Determination of tannic acid based on luminol chemiluminescence catalyzed by cupric oxide nanoparticles. Anal Methods 7(5):1924–1928. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY02736A
Li L, Yin D, Xu K, Liu Y, Song D, Wang J, Zhao C, Song X, Li J (2017a) A sandwich immunoassay for brucellosis diagnosis based on immune magnetic beads and quantum dots. J Pharm Biomed Anal 141:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.03.002
Li SM, Zhang K, Wang J, Yan B, Wang CQ, Xiong ZP, Xu H, Du YK (2017b) Enhanced TA determination on 3D fluorescenceower-like ZnO-PT nanocomposites under ultraviolet light illumination. Sens Actuators B 252:717–724
Li Y, Zheng X, Zhang X, Liu S, Pei Q, Zheng M, Xie Z (2017c) Porphyrin-based carbon dots for photodynamic therapy of hepatoma. Adv Healthc Mater 6(1):1600924. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201600924
Liu X, Zhang W, Yang C, Yao Y, Huang L, Li S, Wang J, Ji Y (2019) Rapid and selective fluorometric determination of tannic acid using MoO3-x quantum dots. Microchim Acta 186(4):247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3311-2
Luo H, Zhang S, Li X, Liu X, Xu Q, Liu J, Wang Z (2017) Tannic acid modified Fe3O4 core–shell nanoparticles for adsorption of Pb2+ and Hg2+. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 72:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.026
Martindale BCM, Hutton GAM, Caputo CA, Reisner E (2015) Solar hydrogen production using carbon quantum dots and a molecular nickel catalyst. J Am Chem Soc 137(18):6018–6025. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b01650
Martins NCT, Ângelo J, Girão AV, Trindade T, Andrade L, Mendes A (2016) N-doped carbon quantum dots/TiO2 composite with improved photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B 193:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.016
Radhakrishnan K, Panneerselvam P, Marieeswaran M (2019) A green synthetic route for the surface-passivation of carbon dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescent sensor for the recognition and detection of toxic metal ions from aqueous solution. Anal Methods 11(4):490–506. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY02451K
Raj MA, Revin SB, John SA (2013) Synthesis, characterization and modification of functionalized pyrimidine stabilized gold nanoparticles on ITO electrode for the determination of tannic acid. Bioelectrochemistry 89:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2012.08.003
Raoof JB, Teymoori N, Khalilzadeh MA (2015) ZnO Nanoparticle ionic liquids carbon paste electrode as a voltammetric sensor for determination of sudan I in the presence of vitamin B6 in food samples. Food Anal Methods 8(4):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9962-z
Ravikumar A, Panneerselvam P, Radhakrishnan K, Christus AAB, Sivanesan S (2018) MoS2 nanosheets as an effective fluorescent quencher for successive detection of arsenic ions in aqueous system. Appl Surf Sci 449:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.098
Saini RK, Sivanesan I, Keum Y-S (2016) Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: a review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance. 3 Biotech 6(2):203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0526-3
Salman BI (2023) Utility of eco-friendly microwave-assisted nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a luminescent nano-sensor for the ultra-sensitive analysis of tigecycline in dosage form and biological samples. Chem Pap 77(10):5979–5988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02914-0
Shi Y, Yang L, Zhu J, Yang J, Liu S, Qiao M, Duan R, Hu X (2017) Resonance Rayleigh scattering technique for simple and sensitive analysis of tannic acid with carbon dots. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 173:817–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.10.054
Sistani S, Shekarchizadeh H (2021) Fabrication of fluorescence sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on amine-modified carbon quantum dots for fast and highly sensitive and selective detection of tannic acid in food samples. Anal Chim Acta 1186:339122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339122
Tabrizi M, Shahidi S-A, Chekin F, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A, Raeisi SN (2022) Reduce graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite biosynthesized by sour lemon peel; using as electro-catalyst for fabrication of vanillin electrochemical sensor in food products analysis and anticancer activity. Top Catal 65(5–6):726–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-021-01541-x
Vatandost E, Chekin F, Shahidi Yasaghi SA (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by pepper extracts reduction and its electocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Russ J Electrochem 52(10):960–965. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319351610013X
Vatandost E, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A, Chekin F, Naghizadeh Raeisi S, Shahidi S-A (2020) Green tea extract assisted green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide: application for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of sunset yellow in food products. Food Chem X 6:100085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2020.100085
Vu DL, Ertek B, Červenka L, Dilgin Y (2013) Determination of tannic acid using silica gel modified carbon paste electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 8(7):9278–9286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1452-3981(23)12967-1
Vu DL, Ertek B, Dilgin Y, Červenka L (2015) Voltammetric determination of tannic acid in beverages using pencil graphite electrode. Czech J Food Sci 33(1):72–76. https://doi.org/10.17221/221/2014-CJFS
Wei J, Liu B, Zhang X, Song C (2018) One-pot synthesis of N, S co-doped photoluminescent carbon quantum dots for Hg2+ ion detection. New Carbon Mater 33(4):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(18)60343-9
Xie C, Li H (2010) Determination of tannic acid in industrial wastewater based on chemiluminescence system of KIO4–H2O2–Tween40. Luminescence 25(5):350–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.1152
Xu L, He N, Du J, Deng Y (2008) Determination of tannic acid by adsorptive anodic stripping voltammetry at porous pseudo-carbon paste electrode. Electrochem Commun 10(11):1657–1660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2008.08.044
Yang X, Zhuo Y, Zhu S, Luo Y, Feng Y, Dou Y (2014) Novel and green synthesis of high-fluorescent carbon dots originated from honey for sensing and imaging. Biosens Bioelectron 60:292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.046
Yang H, He L, Pan S, Liu H, Hu X (2019) Nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of tannic acid. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 210:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.029
Yılmaz ÜT, Çalık E, Uzun D, Karipcin F, Yılmaz H (2016) Selective and sensitive determination of tannic acid using a 1-benzoyl-3-(pyrrolidine) thiourea film modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 776:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.06.037
Zhang X, Huang Y (2015) Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of phenols and tannic acid determination with Mn3 O4 nano-octahedrons as an oxidase mimic. Anal Methods 7(20):8640–8646. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY01732G
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the HRTEM, and XRD facilities at SRMIST, which were built with funding from the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) (Project No. 31/03/2014-15/PVSE-R&D), Government of India. The authors also acknowledge the financial support from GRT Institute of Engineering & Technology, Tiruttani for the consumables used for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: K. Periyarselvam; methodology: P. Sivakumar, Kanimozhi S, R. Elavarasi; formal analysis and investigation: K. Periyarselvam, P. Sivakumar; writing—original draft preparation: Kanimozhi S, R. Elavarasi; writing—review and editing: K. Periyarselvam; funding acquisition: K. Periyarselvam; resources: K. Periyarselvam, P. Sivakumar; supervision: K. Periyarselvam.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Periyarselvam, K., Sivakumar, P., Kanimozhi, S. et al. One-pot hydrothermal method of green-synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for ultra-sensitive dual detection of tannic acid and Hg2+ ions. Appl Nanosci 14, 649–662 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03036-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03036-z