Abstract
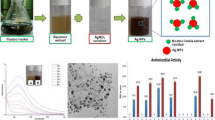
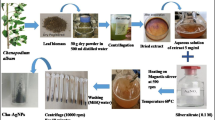
The antibiotics have been used since ages for treating pathogenic bacteria and fungus. However, biofilm formation and multi-drug resistance has compelled the scientific community to come up with an alternative antimicrobial agent that acts against pathogens without triggering microbial resistance. Our work has attempted to study the antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Catharanthus roseus leaves. The leaves were extracted and subjected to nanoparticle synthesis. The UV–Vis spectral analysis showed the peak at 392.4 nm. Scanning electron microscope showed well dispersed and spherical nanoparticles ranging from 20 to 30 nm. The Atomic Force Microscope further confirmed uniform distribution and size less than 100 nm. Fourier Transform Infra-Red indicated the presence of phenols, alcohols, alkenes and other functional groups. Zeta Potential revealed negative charge and Dynamic Light Scattering showed 0.290 polydispersity index. The antibacterial properties were seen best against Vibrio vulnificus ATCC 27562, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 and Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae ATCC 4352 with zone of inhibition of 21, 21 and 19 mm, respectively while 33 mm inhibition zone was seen in case of Candida albicans ATCC 10231. The nanoparticle and ampicillin synergistically act against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 strain and E. coli ATCC 25922 showing 15, 11 mm zone of inhibition, respectively. The hemo-compatibility and antibiofilm property make the silver nanoparticles safe for future In vivo studies. Further Methyl orange degradation proved that the nanoparticles have scope for future environment remediation and Bio-informatics tools helped to study drug-ability scope of secondary metabolites of C. roseus.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data of the study are included in this published article.
References
Abou-Zeid RE, Awwad NS, Nabil S, Salama A, Youssef MA (2019) Oxidized alginate/gelatin decorated silver nanoparticles as new nanocomposite for dye adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 141:1280–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.076
Ahmad S, Tauseef I, Haleem KS, Khan K, Shahzad M, Ali M, Sultan F (2020) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Catharanthus roseus and their antimicrobial activity. Appl Nanosci 10:4459–4464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01221-z
Alshaikh NA, Perveen K, Bahkali AH (2023) Effect of silver nanoparticles alone and in combination with fluconazole on Candida albicans. J King Saud Univ Sci 35:102399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102399
Ananda AP, Krishnamurthy NB, Savitha KR, Nagendra BS (2019) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Priva cordifolia leaf extract (PC@AgNPs) a potent antioxidant, antibacterial and catalytic activity. SN Appl Sci 1:800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0818-4
Asghar MA, Yousuf RI, Shoaib MH, Asghar MA (2020) Antibacterial, anticoagulant and cytotoxic evaluation of biocompatible nanocomposite of chitosan loaded green synthesized bioinspired silver nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 160:934–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.197
AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800596w
Bala Subramaniyan S, Senthilnathan R, Arunachalam J, Anbazhagan V (2020) Revealing the significance of the glycan binding property of Butea monosperma seed lectin for enhancing the antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Bioconjug Chem 31:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00821
Behravan M, Hossein Panahi A, Naghizadeh A, Ziaee M, Mahdavi R, Mirzapour A (2019) Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol 124:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.101
Chouhan S, Guleria S (2020) Green synthesis of AgNPs using Cannabis sativa leaf extract: characterization, antibacterial, anti-yeast and α-amylase inhibitory activity. Mater Sci Energy Technol 3:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2020.05.004
Costa GA, Rossatto FCP, Medeiros AW, Correa AP, Brandelli A, Frazzon AP, Motta AD (2018) Evaluation antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of the antimicrobial peptide P34 against Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. An Acad Bras Cienc 90:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201820160131
Dakshayani SS, Marulasiddeshwara MB, Sharath SK, Golla R, Devaraja SR, Hosamani R (2019) Antimicrobial, anticoagulant and antiplatelet activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Selaginella (Sanjeevini) plant extract. Int J Biol Macromol 131:787–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.222
Dhabalia D, Ukkund SJ, Syed UT, Uddin W, Kabir MA (2020) Antifungal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from Candida albicans on the strain lacking the CNP41 gene. Mater Res Express 7:125401. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abcc83
Dobrucka R, Szymanski M, Przekop R (2019) The study of toxicity effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Veronica officinalis extract. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:8517–8526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02441-0
Edison TNJI, Lee YR, Sethuraman MG (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Terminalia cuneata and its catalytic action in reduction of direct yellow-12 dye. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 161:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.02.044
Fouda MMG, El-Aassar MR, El Fawal GF, Hafez EE, Masry SH, Abdel-Megeed A (2015) k-Carrageenan/poly vinyl pyrollidone/polyethylene glycol/silver nanoparticles film for biomedical application. Int J Biol Macromol 74:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.11.040
Ganachari SV, Bhat R, Deshpande R, Venkataraman A (2012) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using fungi Penicillium diversum and their antimicrobial activity studies. Bionanoscience 2:316–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-012-0046-5
García-Sánchez A, Miranda-Díaz AG, Cardona-Muñoz EG (2020) The role of oxidative stress in physiopathology and pharmacological treatment with pro- and antioxidant properties in chronic diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2082145
Govindappa M, Tejashree S, Thanuja V, Hemashekhar B, Srinivas C, Nasif O, Pugazhendhi A, Raghavendra VB (2021) Pomegranate fruit fleshy pericarp mediated silver nanoparticles possessing antimicrobial, antibiofilm formation, antioxidant, biocompatibility and anticancer activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 61:102289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102289
Gupta P, Goel A, Singh KR, Meher MK, Gulati K, Poluri KM (2021) Dissecting the anti-biofilm potency of kappa-carrageenan capped silver nanoparticles against Candida species. Int J Biol Macromol 172:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.035
Guzman M, Dille J, Godet S (2012) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 8:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.05.007
Jadhav K, Deore S, Dhamecha D, Hr R, Jagwani S, Jalalpure S, Bohara R (2018) Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: characterization, biocompatibility studies, and anticancer activity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00707
Jin R, Cao Y, Mirkin CA, Kelly KL, Schatz GC, Zheng JG (2001) Photoinduced conversion of silver nanospheres to nanoprisms. Science 294:1901–1903. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066541
Kumar KP, Paul W, Sharma CP (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with Zingiber officinale extract and study of its blood compatibility. Bionanoscience 2:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-012-0044-7
Kumar M, Dandapat S, Ranjan R, Kumar A, Sinha MP (2018) Plant mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Punica granatum aqueous leaf extract. J Microbiol Exp. https://doi.org/10.15406/jmen.2018.06.00211
Kumar S, Singh B, Singh R (2022) Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don: a review of its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology and toxicities. J Ethnopharmacol 284:114647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114647
Lai YR, Lai JT, Wang SS, Kuo YC, Lin TH (2022) Silver nanoparticle-deposited whey protein isolate amyloid fibrils as catalysts for the reduction of methylene blue. Int J Biol Macromol 213:1098–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.016
Levac D, Flores PC, De Luca V (2022) Molecular and biochemical characterization of Catharanthus roseus perivine-N-methyltransferase. Phytochemistry 201:113266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113266
Li Y, Qin T, Ingle T, Yan J, He W, Yin JJ, Chen T (2017) Differential genotoxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles and silver ions. Arch Toxicol 91:509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1730-y
Maruthupandy M, Rajivgandhi G, Muneeswaran T, Song JM, Manoharan N (2018) Biologically synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nanoantibiotics against ESBLs producing gram negative bacteria. Microb Pathog 121:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.05.041
Mendes-Gouvêa CC, do Amaral JG, Fernandes RA, Fernandes GL, Gorup LF, Camargo ER, Delbem AC, Barbosa DB (2018) Sodium trimetaphosphate and hexametaphosphate impregnated with silver nanoparticles: characteristics and antimicrobial efficacy. Biofouling 34:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1437146
Meng Y, Zhang H, Hu N, Zhang B, Qiu Z, Hu J, Zheng G, Zhang L, Xu X (2021) Construction of silver nanoparticles by the triple helical polysaccharide from black fungus and the antibacterial activities. Int J Biol Macromol 182:1170–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.130
Mohanta YK, Biswas K, Jena SK, Hashem A, Abd-Allah EF, Mohanta TK (2020) Anti-biofilm and antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized by the reducing activity of phytoconstituents present in the Indian medicinal plants. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01143
Mondal B, Banerjee S, Samanta SK, Senapati S, Tripathy T (2021) Highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensing of trace Zn 2+ ions, by grafted Tricholoma mushroom polysaccharide/Ag composite nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6171
Nie P, Zhao Y, Xu H (2023) Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 253:114636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114636
Nishanthi R, Malathi S, Palani P (2019) Green synthesis and characterization of bioinspired silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles and evaluation of their synergistic antibacterial activity after combining with different classes of antibiotics. Mater Sci Eng C 96:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.050
Nogueira SS, de Araujo-Nobre AR, Mafud AC, Guimarães MA, Alves MMM, Plácido A, Carvalho FAA, Arcanjo DDR, Mascarenhas Y, Costa FG, Albuquerque P (2019) Silver nanoparticle stabilized by hydrolyzed collagen and natural polymers: synthesis, characterization and antibacterial-antifungal evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol 135:808–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.214
Pai AR, Pillai AM, Jayapraksh A, John A (2016) A comparative study of plant mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from fresh leaf extracts of Gracina Gummi-Gutta L., Cynodon Dactylon L. and Bauhinia Acuminata and their antimicrobial activity studies. Nano Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.5101/nbe.v8i4.p288-296
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1712–1720. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Panáček A, Prucek R, Hrbáč J, Nevečná TJ, Steffkova J, Zboril R, Kvítek L (2014) Polyacrylate-assisted size control of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic activity. Chem Mater 26:1332–1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm400635z
Patra JK, Baek K-H (2017) Antibacterial activity and synergistic antibacterial potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against foodborne pathogenic bacteria along with its anticandidal and antioxidant effects. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00167
Polte J, Tuaev X, Wuithschick M, Fischer A, Thuenemann AF, Rademann K, Kraehnert R, Emmerling F (2012) Formation mechanism of colloidal silver nanoparticles: analogies and differences to the growth of gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6:5791–5802. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn301724z
Priyadarshini S, Sulava S, Bhol R, Jena S (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta Indica and Ocimum Sanctum leaf extract. Curr Sci 117:1300. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v117/i8/1300-1307
Qu Y, Safonova O, De Luca V (2019) Completion of the canonical pathway for assembly of anticancer drugs vincristine/vinblastine in Catharanthus roseus. Plant J 97:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14111
Rohaizad A, Shahabuddin S, Shahid MM, Rashid NM, Hir ZA, Ramly MM, Awang K, Siong CW, Aspanut Z (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus dried bark extract deposited on graphene oxide for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103955
Roy P, Das B, Mohanty A, Mohapatra S (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and its antimicrobial study. Appl Nanosci 7:843–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0621-8
Satheeshkumar E, Yang J, Srinivasadesikan V, Lin M-C (2017) Simultaneous production and surface functionalization of silver nanoparticles for label-free colorimetric detection of copper ion. Anal Sci 33:1115–1121. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.33.1115
Schumacher A, Vranken T, Malhotra A, Arts JJ, Habibovic P (2018) In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods: agar dilution to 3D tissue-engineered models. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37:187–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3089-2
Seekonda S, Rani R (2022) Eco-friendly synthesis, characterization, catalytic, antibacterial, antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities of Embelia robusta seeds extract stabilized AgNPs. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 7:100480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2022.100480
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012
Swain SS, Paidesetty SK, Padhy RN (2017) Antibacterial, antifungal and antimycobacterial compounds from cyanobacteria. Biomed Pharmacother 90:760–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.030
Tripathi RM, Kumar N, Shrivastav A, Singh P, Shrivastav BR (2013) Catalytic activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized by Ficus panda leaf extract. J Mol Catal B Enzym 96:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.06.018
Varadavenkatesan T, Pai S, Vinayagam R, Selvaraj R (2021) Characterization of silver nano-spheres synthesized using the extract of Arachis hypogaea nuts and their catalytic potential to degrade dyes. Mater Chem Phys 272:125017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125017
Vijayan S, Divya K, Varghese S, Jisha MS (2020) Antifungal efficacy of chitosan-stabilized biogenic silver nanoparticles against pathogenic Candida spp. Isolated from human. Bionanoscience 10:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-020-00781-7
Vorobyev SA, Novikova GV, Demina AV, Shidlovskiy IP, Volochaev MN (2022) Synthesis and synergistic effect of antibacterial composites based on concentrated hydrosols of silver nanoparticles combined with cephalosporins antibiotics. Inorg Chem Commun 144:109862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109862
Wang G, Jin W, Qasim AM, Gao A, Peng X, Li W, Feng H, Chu PK (2017) Antibacterial effects of titanium embedded with silver nanoparticles based on electron-transfer-induced reactive oxygen species. Biomaterials 124:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.028
Zavascki AP, Magagnin CM, Wink PL, de Oliveira VP, Nunes AG, Krummer TG, Aquino VR, Barth AL (2020) Performance of polymyxin B Etest in a setting of high prevalence of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 22:40–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.006
Zhang X-F, Liu Z-G, Shen W, Gurunathan S (2016) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 17:1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091534
Acknowledgements
This work is based on post-doctoral research of Dr Sonali Priyadarshini. The first author is highly grateful to Dr (Mrs) Sanghamitra Pati, Director & Supervisor, ICMR-RMRC, Bhubaneswar, India for providing all the necessary laboratory facilities, guidance and ICMR fundings. All credit for bio-informatics ideas goes to Dr Atul Nag, Associate Professor, Kalinga Institute of Social Sciences (KISS University), Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
Funding
This work acknowledges the ‘ICMR-Post Doctoral Fellowship Scheme’ awarded to Dr. Sonali Priyadarshini (No.3/1/3/PDF-(21)/HRD-2019–3) by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Department of Health Research, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SP: conceptualization, writing-original draft preparation, data curation and methodology, formal analysis and investigation. SP: supervision, resources, funding acquisition, data validation, visualization, writing—review and editing and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Priyadarshini, S., Pati, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus and its antibacterial properties. Appl Nanosci 13, 6281–6298 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02900-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02900-8