Abstract
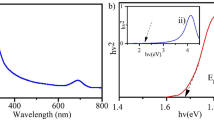
Photocatalytic and magnetic stability of two-dimensional nanomaterials is enhanced by metal doping, which is an environmentally friendly technique used in various industries. There is an urgent need to discover new antimicrobial compounds or extracts to address the crucial problem of increasing microbial resistance against current antibiotics. Similarliy, the whole world is facing water crisis and a possible cost-effective solution is photocatalysis. In this study, an economical and convenient co-precipitation method was adopted to synthesize copper (Cu) loaded graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and magnesium oxide (MgO) composites. Various concentrations (2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10%) of Cu were doped into a fixed amount of g-C3N4/MgO nanostructures for efficient photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities. Results showed that 2.5% Cu loaded samples exhibited best possible results for the photocatalytic activity and 10% loaded Cu nanocomposites displayed enhanced antimicrobial performance. Improved crystallinity and increase in crystal size upon doping were confirmed with X-ray differaction (XRD) analysis, which was corroborated with Selected Area Electron Diffraction (SAED) results. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) revealed that MgO spectra consisted of stretching vibrations of Mg-O bond and other functional groups with minor changes in the vibrational modes upon doping. An high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) fitted with Gatan ® digital software indicated hexagonal phase formation in as-prepared samples and nanorods upon doping, with confirmed d-spacing values. The UV–visible spectroscopy (UV–Vis) analysis exhibited a slight redshift in absorption intensity leading to decreased bandgap (Eg) for Cu-loaded g-C3N4/MgO. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were acquired to investigate the recombination of electron–hole pairs. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was employed to evaluate the elemental and surface composition with binding energy alterations of Cu-loaded g-C3N4/MgO nanorods. The thermal stability and behavior of synthesized samples were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry thermoanalytical (DSC) analysis. Photocatalytic activity (PCA) of as-prepared samples were evaluated against methylene blue and ciprofloxacin (MB&CF) dye in acidic, neutral and basic medium. Furthermore, the efficient antimicrobial potential was evaluated against Escherichia Coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) bacteria.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 January 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03025-2
References
Abdelhamid HN, Mathew AP (2022) Cellulose–metal organic frameworks (CelloMOFs) hybrid materials and their multifaceted Applications: A review. Coord Chem Rev 451:214263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCR.2021.214263
Abebe B, Murthy HCA, Amare E (2020a) Enhancing the photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO Defects, heterojunction, and optimization. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100336. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENMM.2020a.100336
Abebe B, Zereffa EA, Murthy HCA (2020b) Synthesis of Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Aided ZnO/Mn2O3 Nanocomposites for Acid Orange-8 Dye Degradation: Mechanism and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Omega 6:954–964. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.0C05597
Arbuj SS, Hawaldar RR, Mulik UP, Wani BN, Amalnerkar DP, Waghmode SB (2010) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 towards methylene blue degradation. Mater Sci Eng B 168:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEB.2009.11.010
Babushkina EA, Belokopytova LV, Grachev AM, Meko DM, Vaganov EA (2017) Variation of the hydrological regime of Bele-Shira closed basin in Southern Siberia and its reflection in the radial growth of Larix sibirica. Reg Environ Chang. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10113-017-1137-1
Bekena FT, Kuo DH (2020) 10 nm sized visible light TiO2 photocatalyst in the presence of MgO for degradation of methylene blue. Mater Sci Semicond Process 116:105152. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSSP.2020.105152
Bettinelli M, Dallacasa V, Falcomer D, Fornasiero P, Gombac V, Montini T, Romanò L, Speghini A (2007) Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 doped with boron and vanadium. J Hazard Mater 146:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.04.053
Bindhu MR, Umadevi M, Kavin Micheal M, Arasu MV, Abdullah Al-Dhabi N (2016) Structural, morphological and optical properties of MgO nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Mater Lett 166:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2015.12.020
Cai J, Xu W, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Liu G, Ding W, Wang G, Wang H, Luo Y (2019) Robust construction of flexible bacterial cellulose@Ni(OH)2 paper: Toward high capacitance and sensitive H2O2 detection. Eng Sci. 5: 21–29 https://doi.org/10.30919/ES8D669
Chan MH, Liu RS, Hsiao M (2019) Graphitic carbon nitride-based nanocomposites and their biological applications: a review. Nanoscale 11:14993–15003. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR04568F
Cioffi N, Ditaranto N, Torsi L, Picca RA, Sabbatini L, Valentini A, Novello L, Tantillo G, Bleve-Zacheo T, Zambonin PG (2004) Analytical characterization of bioactive fluoropolymer ultra-thin coatings modified by copper nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00216-004-2761-4
De Francisco I, Lennikov VV, Bea JA, Vegas A, Carda JB, De La Fuente GF (2011) In-situ laser synthesis of rare earth aluminate coatings in the system Ln-Al-O (Ln = Y, Gd). Solid State Sci 13:1813–1819. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.solidstatesciences.2011.07.013
Devaraja PB, Nagabhushana H, Sharma SC, Naik R, Prashantha SC, Nagaswarupa HP, Anantharaju KS, Premkumar HB, Jnaneshwara DM (2016) Spectroscopic and photoluminescence properties of MgO:Cr3+ nanosheets for WLEDs. Displays 41:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DISPLA.2015.10.006
Du J, Wei J, Wang M, Tang X, Zhang Y, Zang Z (2017) Enhanced performance of light-controlled conductive switching in hybrid cuprous oxide/reduced graphene oxide (Cu2O/rGO) nanocomposites. Opt. Lett. 42(5):911–914. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.42.000911
Georgouvelas D, Abdelhamid HN, Li J, Edlund U, Mathew AP (2021) All-cellulose functional membranes for water treatment: Adsorption of metal ions and catalytic decolorization of dyes. Carbohydr Polym 264:118044. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2021.118044
Gillet E, Ealet B (1992) Characterization of sapphire surfaces by electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Surf Sci 273:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(92)90079-L
Goh XY (2018) Synthesis of TiO2/G-C3N4 Composite for Sonocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye (Doctoral dissertation, UTAR)
Gu S, Xie J, Li CM (2014) Hierarchically porous graphitic carbon nitride: large-scale facile synthesis and its application toward photocatalytic dye degradation. RSC Adv 4:59436–59439. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA10958A
Herzhaft B, Kakadjian S, Moan M (2005) Measurement and modeling of the flow behavior of aqueous foams using a recirculating pipe rheometer. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 263:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2005.01.012
Hou C, Yang W, Xie X, Sun X, Wang J, Naik N, Pan D, Mai X, Guo Z, Dang F, Du W (2021) Agaric-like anodes of porous carbon decorated with MoO2 nanoparticles for stable ultralong cycling lifespan and high-rate lithium/sodium storage. J Colloid Interface Sci 596:396–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2021.03.149
Huang CW, Wu MC (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by UV-assistant TiO2 and natural sericite composites. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 95(10):2715–2722. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6392
Huang L, Li D, Lin Y, Evans DG, Duan X (2005) Influence of nano-MgO particle size on bactericidal action againstBacillus subtilis var. niger. Chinese Sci Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897474
Ikram M, Ali S, Murray R, Hussain A, Islah-u-din Shah SI (2015) Influence of fullerene derivative replacement with TiO2 nanoparticles in organic bulk heterojunction solar cells. Curr Appl Phys 15:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CAP.2014.10.026
Isono R, Yoshimura T, Esumi K (2005) Preparation of Au/TiO2 nanocomposites and their catalytic activity for DPPH radical scavenging reaction. J Colloid Interface Sci 288(1):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.02.078
Javed R, Usman M, Tabassum S, Zia M (2016) Effect of capping agents: structural, optical and biological properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Surface Sci 386:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.042
Javed R, Ahmed M, ul Haq I, Nisa S, Zia M. (2017) PVP and PEG doped CuO nanoparticles are more biologically active: Antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and cytotoxic perspective. Mater Sci Eng 79:108–115 10. 1016/j. msec. 2017. 05. 006
Kakade PM, Kachere AR, Mandlik NT, Rondiya SR, Jadkar SR, Bhosale SV (2020) Graphene oxide assisted synthesis of magnesium oxide nanorods. ES Mater Manuf https://doi.org/10.30919/ESMM5F1044
Kang Miao K, Lin Luo X, Wang W, Le Guo J, FaN GUOS, Jiu Cao F, Qiao HuY, Mei Chang P, Dong Feng G (2019) One-step synthesis of Cu–SBA-15 under neutral condition and its oxidation catalytic performance. Micropor Mesopor Mater 289:109640. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2019.109640
Kassem AA, Abdelhamid HN, Fouad DM, Ibrahim SA (2020) Hydrogenation reduction of dyes using metal-organic framework-derived CuO@C. Micropor Mesopor Mater 305:110340. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2020.110340
Kaviyarasu K, Manikandan E, Kennedy J, Maaza M (2015) A comparative study on the morphological features of highly ordered MgO:AgO nanocube arrays prepared via a hydrothermal method. RSC Adv 5:82421–82428. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15132E
Kazeminezhad I, Sadollahkhani A (2016) Influence of pH on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-016-4284-0
Khan SA, Arshad Z, Shahid S, Arshad I, Rizwan K, Sher M, Fatima U (2019) Synthesis of TiO2/Graphene oxide nanocomposites for their enhanced photocatalytic activity against methylene blue dye and ciprofloxacin. Compos Part B Eng 175:107120. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2019.107120
Kharlamov A, Bondarenko M, Kharlamova G, Gubareni N (2016) Features of the synthesis of carbon nitride oxide (g-C3N4)O at urea pyrolysis. Diam Relat Mater 66:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIAMOND.2016.03.012
Kong HJ, Won DH, Kim J, Woo SI (2016) Sulfur-doped g-C3N4/BiVO4 composite photocatalyst for water oxidation under visible light. Chem Mater 28:1318–1324. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.CHEMMATER.5B04178/SUPPL_FILE/CM5B04178_SI_001.PDF
Krishnamoorthy K, Moon JY, Hyun HB, Cho SK, Kim SJ (2012) Mechanistic investigation on the toxicity of MgO nanoparticles toward cancer cells. J Mater Chem 22:24610–24617. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM35087D
Kumari L, Li WZ, Vannoy CH, Leblanc RM, Wang DZ (2009) Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of Mg(OH)2 micro-/nanostructure and its conversion to MgO. Ceram Int 35:3355–3364. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2009.05.035
Lam SM, Sin JC, Abdullah AZ, Mohamed AR (2012) Degradation of wastewaters containing organic dyes photocatalysed by zinc oxide: a review. New Pub Balaban 41:131–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.664698
Lee JS, Jang J (2014) Hetero-structured semiconductor nanomaterials for photocatalytic applications. J Ind Eng Chem 20:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JIEC.2013.11.050
Liao L, Zhang Z, Meng F, Liu D, Wu B, Li Y, Xie W (2021) A novel slurry for chemical mechanical polishing of single crystal diamond. Appl Surf Sci 564:150431. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2021.150431
Lin J, Nguyen NYT, Zhang C, Ha A, Liu HH (2020) Antimicrobial Properties of MgO Nanostructures on Magnesium Substrates. ACS Omega 5:24613–24627. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.0C03151
Liu Z, Lu Z, Bosman M, Li N, Frankcombe TJ, Jia G, Tricoli A, Liu Y, Du Y, Yin Z (2018) Photoactivity and stability Co-enhancement: when localized plasmons meet oxygen vacancies in MgO. Small 14:1803233. https://doi.org/10.1002/SMLL.201803233
Mantilaka MMMGPG, De Silva RT, Ratnayake SP, Amaratunga G, de Silva KMN (2018) Photocatalytic activity of electrospun MgO nanofibres: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Mater Res Bull 99:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATERRESBULL.2017.10.047
Manzoor M, Rafiq·A, Ikram·M, Nafees·M, Ali ·S, (2018) Structural, optical, and magnetic study of Ni-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. Int Nano Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40089-018-0225-7
Mao S, Bao R, Fang D, Yi J (2019) Fabrication of sliver/graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic efficiency through ultrasonic spray atomization. J Colloid Interface Sci 538:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2018.11.078
Mao S, Liu C, Xia M, Wang F, Ju X (2021) Construction of a Z-scheme 1D/2D FeV3O8/g-C3N4 composite for ibuprofen degradation: mechanism insight, theoretical calculation and degradation pathway. Catal Sci Technol 11:3466–3480. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CY00025J
Miller RE, Shenoy VB (2000) Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/11/3/301
Morsella M, d’Alessandro N, Lanterna AE, Scaiano JC (2016) Improving the sunscreen properties of TiO2 through an understanding of its catalytic properties. Acs Omega 1(3):464–469. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.6b00177
Nasser Abdelhamid H, Mathew AP (2021) Cellulose-zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (CelloZIFs) for multifunctional environmental remediation: Adsorption and catalytic degradation. Chem Eng J 426:131733. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2021.131733
Nejati K, Rezvani Z, Massoumi B (2007) Syntheses and investigation of thermal properties of copper complexes with azo-containing Schiff-base dyes. Dye Pigment 75:653–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2006.07.019
Nisticò R (2017) Magnetic materials and water treatments for a sustainable future. Res Chem Intermed. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11164-017-3029-X
Nor Fadilah C, Norlida K, Nurhanna B, Kelimah E (2019) Effect of Cu Doped in MgO on nanostructures and their band gap energies. Solid State Phenom 290:323–328. https://doi.org/10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/SSP.290.323
Paradiso D, Larese JZ (2020) Solvent free deposition of Cu on nanocubes of MgO. J Phys Chem C 124:14564–14572. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JPCC.0C01790
Patnaik S, Swain G, Parida KM (2018) Highly efficient charge transfer through a double Z-scheme mechanism by a Cu-promoted MoO3/g-C3N4 hybrid nanocomposite with superior electrochemical and photocatalytic performance. Nanoscale 10:5950–5964. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR09049H
Podder S, Chanda D, Mukhopadhyay AK, De A, Das B, Samanta A, Hardy JG, Ghosh CK (2018) Effect of morphology and concentration on crossover between antioxidant and pro-oxidant activity of MgO nanostructures. Inorgan Chem 57(20):12727–12739. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01938
Poulston S, Parlett PM, Stone P, Bowker M (1996) Surface oxidation and reduction of CuO and Cu2O studied using XPS and XAES. Surf Interface Anal 24:811–820. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9918(199611)24:12%3c811::AID-SIA191%3e3.0.CO;2-Z
Prince MJA (2017) Optical analysis of Cu doped Mg nanoparticles using co-precipitation method. Int J Res Appl Sci Eng. Technol https://doi.org/10.22214/IJRASET.2017.10261
Pugazhendhi A, Prabhu R, Muruganantham K, Shanmuganathan R, Natarajan S (2019) Anticancer, antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities of green synthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgONPs) using aqueous extract of Sargassum wightii. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 190:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOBIOL.2018.11.014
Qi K, Li Y, Xie Y, Liu SY, Zheng K, Chen Z, Wang R (2019) Ag loading enhanced photocatalytic activity of g-C 3 N 4 porous nanosheets for decomposition of organic pollutants. Front Chem 7:91. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2019.00091/BIBTEX
Qiao F, Wang J, Ai S, Li L (2015) As a new peroxidase mimetics: The synthesis of selenium doped graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets and applications on colorimetric detection of H2O2 and xanthine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 216:418–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2015.04.074
Rajendran V, Deepa B, Mekala R (2018) Studies on structural, morphological, optical and antibacterial activity of Pure and Cu-doped MgO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater Today Proc 5:8796–8803. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2017.12.308
Rodriguez JA, Jirsak T, Chaturvedi S (1999) Reaction of H2S with MgO(100) and Cu/MgO(100) surfaces: Band-gap size and chemical reactivity. J Chem Phys 111:8077. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.480141
Rtimi S, Pulgarin C, Bensimon M, Kiwi J (2016) New evidence for Cu-decorated binary-oxides mediating bacterial inactivation/mineralization in aerobic media. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 144:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2016.03.072
Sahidin Winatapura D, Hasnah Dewi S, Ari Adi W (2016) Synthesis, characterization, And Photocatalytic Activity Of Fe3O4 @ZnO nanocomposite. Int J Technol 3: 408–416 https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v7i3.2952
Selvakumar N, Vettivel SC (2013) Thermal, electrical and wear behavior of sintered Cu–W nanocomposite. Mater Des 46:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2012.09.055
Uddin MT, Nicolas Y, Olivier C, Toupance T, Servant L, Müller MM, Kleebe HJ, Ziegler J, Jaegermann W (2012) Nanostructured SnO 2-ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts showing enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of organic dyes. Inorg Chem 51:7764–7773. https://doi.org/10.1021/IC300794J/SUPPL_FILE/IC300794J_SI_001.PDF
Uyak V, Toroz I (2007) Investigation of bromide ion effects on disinfection by-products formation and speciation in an Istanbul water supply. J Hazard Mater 149:445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.04.017
Vickers NJ (2017) Animal communication: when i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 27:R713–R715. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CUB.2017.05.064
Wu D, Bai Y, Wang W, Xia H, Tan F, Zhang S, Su B, Wang X, Qiao X, Wong PK (2019) Highly pure MgO2 nanoparticles as robust solid oxidant for enhanced Fenton-like degradation of organic contaminants. J Hazard Mater 374:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2019.04.058
Xie W, Zhang Z, Liao L, Liu J, Su H, Wang S, Guo D (2020) Green chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafers using a novel slurry. Nanoscale 12:22518–22526. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR04705H
Yang Y, Mao B, Gong G, Li D, Liu Y, Cao W, Xing L, Zeng J, Shi W, Yuan S (2019) In-situ growth of Zn–AgIn5S8 quantum dots on g-C3N4 towards 0D/2D heterostructured photocatalysts with enhanced hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:15882–15891. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2019.01.102
Yockell-Lelièvre H, Lussier F, Masson JF (2015) Influence of the particle shape and density of self-assembled gold nanoparticle sensors on LSPR and SERS. J Phys Chem C 119:28577–28585. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JPCC.5B09570/SUPPL_FILE/JP5B09570_SI_001.PDF
Yousefi S, Ghasemi B, Tajally M, Asghari A (2017) Optical properties of MgO and Mg(OH)2 nanostructures synthesized by a chemical precipitation method using impure brine. J Alloys Compd 711:521–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2017.04.036
Yu X, Zhang J, Zhang J, Niu J, Zhao J, Wei Y, Yao B (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using Zn-doped Cu2O particles: Analysis of degradation pathways and intermediates. Chem Eng J 374:316–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2019.05.177
Zhang Y, Sturge MD, Kash K, Van Der Gaag BP, Gozdz AS, Florez LT, Harbison JP (1995) Temperature dependence of luminescence efficiency, exciton transfer, and exciton localization in GaAs/<span class. Phys Rev B 51:13303. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.51.13303
Zhang Z, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2015) Changes in surface layer of silicon wafers from diamond scratching. CIRP Ann 64:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIRP.2015.04.005
Zhang Q, Liu S, Zhang Y, Zhu A, Li J, Du X (2016) Enhancement of the photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4 via treatment in dilute NaOH aqueous solution. Mater Lett 171:79–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2016.02.043
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloys Compd 726:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2017.08.024
Zhang G, Song A, Duan Y, Zheng S (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/zeolite composite for abatement of pollutants. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 255:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2017.07.028
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467–468:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2018.10.133
Zhang Z, Liao L, Wang X, Xie W, Guo D (2020a) Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy. Appl Surf Sci 506:144670. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2019.144670
Zhang X, Yuan X, Jiang L, Zhang J, Yu H, Wang H, Zeng G (2020b) Powerful combination of 2D g-C3N4 and 2D nanomaterials for photocatalysis: Recent advances. Chem Eng J 390:124475. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2020.124475
Zhang Z, Liu J, Hu W, Zhang L, Xie W, Liao L (2021) Chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire wafers using a developed slurry. J Manuf Process 62:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMAPRO.2021.01.004
Zhao Z, Dai H, Du Y, Deng J, Zhang L, Shi F (2011) Solvo- or hydrothermal fabrication and excellent carbon dioxide adsorption behaviors of magnesium oxides with multiple morphologies and porous structures. Mater Chem Phys 128:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2011.02.073
Zhao Z, Ma H, Feng M, Li Z, Cao D, Guo Z (2019) In situ preparation of WO3/g-C3N4 composite and its enhanced photocatalytic ability, a comparative study on the preparation methods of chemical composite and mechanical mixing. Eng Sci 7: 52–58 https://doi.org/10.30919/ES8D689
Zhou J, Ji X, Zhou X, Guo J, Sun J, Liu Y (2018) Three-dimensional g-C3N4/MgO composites as a high-performance adsorbent for removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Seper Sci Technol 54: 2817–2829 https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1553983
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Higher Education Commission, HEC through start research grant project # 21-1669/SRGP/R&D/HEC/2017 Pakistan for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This manuscript has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03025-2
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akbar, M.U., Ikram, M., Imran, M. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Cu-loaded C3N4-MgO nanorods for promising antibacterial and dye degradation. Appl Nanosci 12, 2443–2458 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02494-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02494-7