Abstract
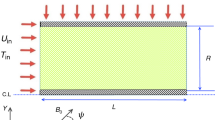
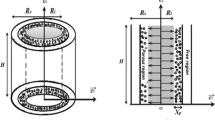
The simultaneous effects of the porous medium, i.e., an aluminium foam, and nanoparticles on heat transfer have not been investigated well. Therefore, a 3D computational fluid dynamics model was used in the present research to examine Al2O3/water-based nanofluid heat transfer using five cylinders with different configurations of porous media. An isothermal boundary condition was provided to all cylinders, and different configurations were compared with each other based on their Nusselt number (Nu) and enhancement parameter (EP) values. According to numerical results, due to the higher turbulency increment, the fully porous cylinder had the maximum improvement in the Nu number and the EP value (about 45% increment) in contrast to the empty cylinder.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fluent 6.3 User’s Guide (2006). Fluent Inc, Centerra Resource Park, 10 Cavendish Court, Lebanon, NH 03766
Aguilar-Madera CG, Valdés-Parada FJ, Goyeau B, Ochoa-Tapia JA (2011) Convective heat transfer in a channel partially filled with a porous medium. Int J Therm Sci 50:1355–1368
Alvariño PF, Jabardo JS, Arce A, Galdo ML (2013) A numerical investigation of laminar flow of a water/alumina nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 59:423–432
Aspen Technology (2002) Hysys V3.2.2003 user guide. Hyprotech Aspen Technology, Inc
Azari A, Derakhshandeh M (2015) An experimental comparison of convective heat transfer and friction factor of Al2O3 nanofluids in a tube with and without butterfly tube inserts. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 52:31–39
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S (2011) Numerical investigation on nanofluids turbulent convection heat transfer inside a circular tube. Int J Therm Sci 50:341–349
Darzi AAR, Farhadi M, Sedighi K (2014) Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer and friction factor of Al2O3/water nanofluid in helically corrugated tube. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 57:188–199
Enwald H, Peirano E, Almstedt A-E (1996) Eulerian two-phase flow theory applied to fluidization. Int J Multiph Flow 22:21–66
Gharibshahi R, Jafari A, Ahmadi H (2019) CFD investigation of enhanced extra-heavy oil recovery using metallic nanoparticles/steam injection in a micromodel with random pore distribution. J Pet Sci Eng 174:374–383
Godson L, Deepak K, Enoch C, Jefferson B, Raja B (2014) Heat transfer characteristics of silver/water nanofluids in a shell and tube heat exchanger. Arch Civ Mech Eng 14:489–496
Gunnasegaran P, Abdullah M, Yusoff M (2014) Effect of Al2O3-H2O nanofluid concentration on heat transfer in a loop heat pipe. Proc Mater Sci 5:137–146
Hajipour M, Dehkordi AM (2014) Mixed-convection flow of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid in a channel partially filled with porous metal foam: experimental and numerical study. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 53:49–56
Hatami M, Sheikholeslami M, Ganji D (2014) Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an asymmetric porous channel with expanding or contracting wall. J Mol Liq 195:230–239
Hejazian M, Moraveji MK, Beheshti A (2014) Comparative study of Euler and mixture models for turbulent flow of Al2O3 nanofluid inside a horizontal tube. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 52:152–158
Jafari A, Tynjälä T, Mousavi S, Sarkomaa P (2008a) Simulation of heat transfer in a ferrofluid using computational fluid dynamics technique. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 29:1197–1202
Jafari A, Zamankhan P, Mousavi S, Pietarinen K (2008b) Modeling and CFD simulation of flow behavior and dispersivity through randomly packed bed reactors. Chem Eng J 144:476–482
Jafari A, Shahmohammadi A, Mousavi SM (2015) CFD Investigation of gravitational sedimentation effect on heat transfer of a nano-ferrofluid. Iran J Chem Chem Eng (IJCCE) 34:87–96
Jafari A, Hasani M, Hosseini M, Gharibshahi R (2019) Application of CFD technique to simulate enhanced oil recovery processes: current status and future opportunities. Pet Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-019-00363-7
Lotfi R, Saboohi Y, Rashidi A (2010) Numerical study of forced convective heat transfer of nanofluids: comparison of different approaches. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 37:74–78
Mahmoudi Y, Maerefat M (2011) Analytical investigation of heat transfer enhancement in a channel partially filled with a porous material under local thermal non-equilibrium condition. Int J Therm Sci 50:2386–2401
Michaelides EES (2014) Nanofluidics. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Mirfendereski S, Abbassi A, Saffar-avval M (2015) Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluid heat transfer in helically coiled tubes at constant wall heat flux. Adv Powder Technol 26:1483–1494
Nazari M, Ashouri M, Kayhani MH, Tamayol A (2015) Experimental study of convective heat transfer of a nanofluid through a pipe filled with metal foam. Int J Therm Sci 88:33–39
Nield D, Kuznetsov A (2014) Forced convection in a parallel-plate channel occupied by a nanofluid or a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 70:430–433
Park SS, Kim NJ (2014) A study on the characteristics of carbon nanofluid for heat transfer enhancement of heat pipe. Renew Energy 65:123–129
Peng H, Ding G, Jiang W, Hu H, Gao Y (2009) Measurement and correlation of frictional pressure drop of refrigerant-based nanofluid flow boiling inside a horizontal smooth tube. Int J Refrig 32:1756–1764
Rana P, Dhanai R, Kumar L (2017) MHD slip flow and heat transfer of Al2O3-water nanofluid over a horizontal shrinking cylinder using Buongiorno’s model: effect of nanolayer and nanoparticle diameter. Adv Powder Technol 28:1727–1738
Rashad A, Chamkha A, Modather M (2013) Mixed convection boundary-layer flow past a horizontal circular cylinder embedded in a porous medium filled with a nanofluid under convective boundary condition. Comput Fluids 86:380–388
Reddy MCS, Rao VV (2014) Experimental investigation of heat transfer coefficient and friction factor of ethylene glycol water based TiO2 nanofluid in double pipe heat exchanger with and without helical coil inserts. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 50:68–76
Saha G, Paul MC (2015) Heat transfer and entropy generation of turbulent forced convection flow of nanofluids in a heated pipe. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 61:26–36
Sajadi A, Kazemi M (2011) Investigation of turbulent convective heat transfer and pressure drop of TiO2/water nanofluid in circular tube. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 38:1474–1478
Sarafraz M, Hormozi F (2015) Intensification of forced convection heat transfer using biological nanofluid in a double-pipe heat exchanger. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 66:279–289
Selimefendigil F, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ (2017) Mixed convection in superposed nanofluid and porous layers in square enclosure with inner rotating cylinder. Int J Mech Sci 124:95–108
Servati AA, Javaherdeh K, Ashorynejad HR (2014) Magnetic field effects on force convection flow of a nanofluid in a channel partially filled with porous media using Lattice Boltzmann Method. Adv Powder Technol 25:666–675
Shahmohammadi A (2014) Application of different CFD multiphase models to investigate effects of baffles and nanoparticles on heat transfer enhancement. Front Chem Sci Eng 8:320–329
Sundar LS, Singh MK, Bidkin I, Sousa AC (2014) Experimental investigations in heat transfer and friction factor of magnetic Ni nanofluid flowing in a tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf 70:224–234
Utomo AT et al (2014) The effect of nanoparticles on laminar heat transfer in a horizontal tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf 69:77–91
Xue Q-Z (2003) Model for effective thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Phys Lett A 307:313–317
Zhang Z, Huo Y, Guo D (2013) A model for nanogrinding based on direct evidence of ground chips of silicon wafers. Sci China Technol Sci 56:2099–2108
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloy Compd 726:514–524
Zhang Z, Shi Z, Du Y, Yu Z, Guo L, Guo D (2018) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:409–415
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467:5–11
Zhao N, Yang J, Li H, Zhang Z, Li S (2016) Numerical investigations of laminar heat transfer and flow performance of Al2O3–water nanofluids in a flat tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf 92:268–282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alihosseini, S., Jafari, A. The effect of porous medium configuration on nanofluid heat transfer. Appl Nanosci 10, 895–906 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01192-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01192-1