Abstract
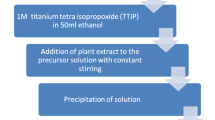
Starch-based biofilms with embedded nanoparticles (NPs) are used to wrap food in biodegradable packaging system that has high antibacterial action against a variety of microorganisms. In this study, ZnO NPs were synthesised using both a green synthesis approach utilising Azadirachta indica (Neem) and a chemical synthesis approach using the sol–gel technique. The structural and morphological properties of all synthesized NPs were characterized through XRD, UV–VIS, UV-DRS, FTIR, and FESEM analysis. Further, these NPs were employed in the development of starch-based biodegradable films. A meticulous comparative analysis was performed to evaluate the functional properties of the nanocomposites, encompassing crucial parameters such as film thickness, moisture content, swelling index, opacity, solubility, water vapor permeability, and tensile strength. In comparison to films embedded with chemically synthesised NPs (F1), nanocomposite with green synthesised NPs (F2) showed 15.27% greater inhibition against Escherichia coli growth and 22.05% stronger inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus bacterial strains. Based on the biodegradability analysis, the nanocomposite film-F2 showed a 53.33% faster degradation rate compared to the film-F1. The developed films were utilized to assess the quality of both wrapped and unwrapped grapes, leading to the generalization of the research for the development of starch-based antibacterial and environmentally friendly food packaging material.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be available on request. A statement has also been added to the manuscript.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Akbar N, Aslam Z, Siddiqui R et al (2021) Zinc oxide nanoparticles conjugated with clinically-approved medicines as potential antibacterial molecules. AMB Exp. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-021-01261-1
Alias SS, Ismail AB, Mohamad AA (2010) Effect of pH on ZnO nanoparticle properties synthesized by sol–gel centrifugation. J Alloys Compd 499:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.03.174
Babaee M, Jonoobi M, Hamzeh Y, Ashori A (2015) Biodegradability and mechanical properties of reinforced starch nanocomposites using cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 132:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.043
Cao N, Fu Y, He J (2007) Mechanical properties of gelatin films cross-linked, respectively, by ferulic acid and tannin acid. Food Hydrocoll 21:575–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2006.07.001
Chiumarelli M, Hubinger MD (2012) Stability, solubility, mechanical and barrier properties of cassava starch—Carnauba wax edible coatings to preserve fresh-cut apples. Food Hydrocoll 28:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.12.006
Delavari MM, Stiharu I (2022) Preparing and characterizing novel biodegradable starch/PVA-based films with nano-sized zinc-oxide particles for wound-dressing applications. Appl Sci (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12084001
Dey A, Dhumal CV, Sengupta P et al (2021) Challenges and possible solutions to mitigate the problems of single-use plastics used for packaging food items: a review. J Food Sci Technol 58:3251–3269
Din MI, Siddique N, Hussain Z, Khalid R (2022) Facile synthesis of biodegradable corn starch-based plastic composite film reinforced with zinc oxide nanoparticles for packaging applications. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2022.2081190
Echeverría I, Eisenberg P, Mauri AN (2014) Nanocomposites fi lms based on soy proteins and montmorillonite processed by casting. J Memb Sci 449:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.08.006
Ghanbarzadeh B, Almasi H, Entezami AA (2011) Improving the barrier and mechanical properties of corn starch-based edible films: effect of citric acid and carboxymethyl cellulose. Ind Crops Prod 33:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.10.016
Ghasemlou M, Khodaiyan F, Oromiehie A (2011) Physical, mechanical, barrier, and thermal properties of polyol-plasticized biodegradable edible film made from Kefiran. Carbohydr Polym 84:477–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.010
Homthawornchoo W, Kaewprachu P, Pinijsuwan S et al (2022) Enhancing the UV-light barrier, thermal stability, tensile strength, and antimicrobial properties of rice starch-gelatin composite films through the incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Polymers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122505
Hu X, Jia X, Zhi C et al (2019) Improving the properties of starch-based antimicrobial composite films using ZnO-chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 210:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.043
Indumathi MP, Sarojini KS, Rajarajeswari GR (2019) International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Antimicrobial and biodegradable chitosan/cellulose acetate phthalate/ZnO nano composite films with optimal oxygen permeability and hydrophobicity for extending the shelf life of black grape fruits. Int J Biol Macromol 132:1112–1120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.171
Ju A, Baek SK, Kim S, Bin SK (2019) Development of an antioxidative packaging film based on Khorasan wheat starch containing moringa leaf extract. Food Sci Biotechnol 28:1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-00546-9
Kim HY, Jane J, Lamsal B (2017) Hydroxypropylation improves film properties of high amylose corn starch. Ind Crops Prod 95:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.10.025
Kumar P, Mahajan P, Kaur R, Gautam S (2020a) Nanotechnology and its challenges in the food sector: a review. Mater Today Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100332
Kumar S, Boro JC, Ray D et al (2019) Bionanocomposite films of agar incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles as an active packaging material for shelf life extension of green grape. Heliyon 5:e01867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01867
Kumar S, Mukherjee A, Dutta J (2020b) Chitosan based nanocomposite films and coatings: emerging antimicrobial food packaging alternatives. Trends Food Sci Technol 97:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.002
Leng F, Wang C, Sun L et al (2022) Effects of different treatments on physicochemical characteristics of ‘Kyoho’ grapes during storage at low temperature. Horticulturae. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020094
Lian R, Cao J, Jiang X, Rogachev AV (2021) Physicochemical, antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of starch/chitosan films incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater Today Commun 27:102265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102265
López C, Medina K, Ambrosio RD et al (2021) PLLA and cassava thermoplastic starch blends: crystalinity, mechanical properties, and UV degradation have arisen a growing interest in this material for various. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02368-y
Mahuwala AA, Hemant V, Meharwade SD et al (2020) Synthesis and characterisation of starch/agar nanocomposite films for food packaging application. In: IET nanobiotechnology. Institution of Engineering and Technology, pp 809–814
Ma J, Zhu W, Tian Y, Wang Z (2016) Preparation of zinc oxide-starch nanocomposite and its application on coating. Nanoscale Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1404-y
Mocanu A, Isopencu G, Busuioc C et al (2019) Bacterial cellulose films with ZnO nanoparticles and propolis extracts: synergistic antimicrobial effect. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54118-w
Napierała DM, Stangierski J (2007) Tensile properties of wheat starch film with the addition of sorbitol and albumin. Acta Agrophys 9:123–133
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—An antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/9/3/035004
Peighambardoust SJ, Peighambardoust SH, MohammadzadehPournasir N, Pakdel P (2019) Properties of active starch-based films incorporating a combination of Ag ZnO and CuO nanoparticles for potential use in food packaging applications. Food Packag Shelf Life. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100420
Pestana CJ, Moura DS, Capelo-Neto J et al (2021) Potentially poisonous plastic particles: microplastics as a vector for cyanobacterial toxins microcystin-LR and microcystin-LF. Environ Sci Technol 55:15940–15949. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c05796
Sathianathan RV, Sundararajan A et al (2023) Intelligent food packaging and shelf-life improvement of chapattis using hybrid nanoparticle-based biopolymer electrospin coating. ACS Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsfoodscitech.3c00012
Seligra PG, Medina Jaramillo C, Famá L, Goyanes S (2016) Biodegradable and non-retrogradable eco-films based on starch-glycerol with citric acid as crosslinking agent. Carbohydr Polym 138:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.041
Shaikh S, Yaqoob M, Aggarwal P (2021) An overview of biodegradable packaging in food industry. Curr Res Food Sci 4:503–520
Shankar S, Teng X, Li G, Rhim J (2015) Food hydrocolloids preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of gelatin/ZnO nanocomposite fi lms. Food Hydrocoll 45:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.12.001
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A et al (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nanomicro Lett 7:219–242
Slavutsky AM, Bertuzzi MA (2016) Improvement of water barrier properties of starch films by lipid nanolamination. Food Packag Shelf Life 7:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2016.01.004
Tamimi N, MohammadiNafchi A, Hashemi-Moghaddam H, Baghaie H (2021) The effects of nano-zinc oxide morphology on functional and antibacterial properties of tapioca starch bionanocomposite. Food Sci Nutr 9:4497–4508. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2426
Tang S, Wang Z, Li W et al (2019) Ecofriendly and biodegradable soybean protein isolate films incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles for food packaging. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2:2202–2207. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.9b00170
Verma A, Mehata MS (2016) Controllable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Neem leaves and their antimicrobial activity. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.11.001
Vijayakumar S, Divya M, Vaseeharan B et al (2021) Biogenic preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles from natural polysaccharide Azadirachta indica L. (neem gum) and its clinical implications. J Clust Sci 32:983–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01863-y
Wang K, Wang W, Ye R et al (2017) Mechanical properties and solubility in water of corn starch-collagen composite films: effect of starch type and concentrations. Food Chem 216:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.048
Wu Y, Gu Y, Tong L et al (2019) Electrochemical synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and preparation of pea starch/ZnO composite for active food packaging application. Int J Electrochem Sci 14:10745–10753. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.12.38
Xu S, Wang ZL (2011) One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res 4:1013–1098
Yates J, Deeney M, Rolker HB et al (2021) A systematic scoping review of environmental, food security and health impacts of food system plastics. Nat Food 2:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00221-z
Zare M, Namratha K, Ilyas S et al (2022) Emerging trends for ZnO nanoparticles and their applications in food packaging. ACS Food Sci Technol
Zare M, Namratha K, Thakur MS, Byrappa K (2019) Biocompatibility assessment and photocatalytic activity of bio-hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Thymus vulgaris leaf extract. Mater Res Bull 109:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.09.025
Zheng R, Xiong X, Li X et al (2022) Changes in polyphenolic compounds of Hutai No. 8 grapes during low-temperature storage and their shelf-life prediction by identifying biomarkers. J Agric Food Chem 70:15818–15829. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06573
Funding
The research is supported by TEQIP-III (MHRD, Govt. of India) grants for Dr. SSB UICET, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Credit author statement: SG conceptualized, investigated, formal analysis, and did funding acquisition, project administration and supervision, DB wrote the original draft, literature investigation, discussion and revision, PK also wrote the original draft, methodology, investigation, experiment and discussion, and RK supported and discussed the antibacterial experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Coflict of interest
The authors a firm that they are free of any known financial conflicts of interest or close personal ties that may have looked to have acted the research presented in this study.
Ethics approval
Not applicable, original research article.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The research article contains original data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Gautam, S., Bansal, D. et al. Starch-based antibacterial food packaging with ZnO nanoparticle. J Food Sci Technol 61, 178–191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05834-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05834-9