Abstract
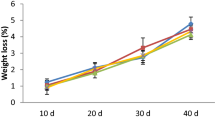
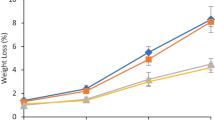
The effect of postharvest dipping treatments with 0.5 mM melatonin (MT) and 1% chitosan (CT) either alone or in combination on quality of pre-climacteric ‘Williams’ bananas during ripening at ambient conditions were investigated. MT or CT treatments delayed ripening by retaining greener peel, higher firmness, titratable acidity (TA), but lower total soluble solids (TSS) and TSS/TA, weight loss, browning and electrolyte leakage than the control. Total phenol (TPC) and flavonoid contents (TFC) in both peel and pulp increased up to 6 days and then decreased and was higher in treated fruit than the control. Vitamin C content decreased up to 3 days, then increased and was higher in treated fruit than control. MT and CT combination exhibited the highest TPC, TFC and vitamin C contents compared to other treatments. Radical scavenging capacity (RSC) of peel and pulp increased up to 6 days, then decreased and was higher in treated fruit than the control. The treated fruit exhibited lower polyphenoloxidase (PPO) and hydrolytic enzymes but higher peroxidase (POD) activities in both peel and pulp than the control. Postharvest treatments with 0.5 mM MT and 1% CT alone or in combination could be used to retain quality of ‘Williams’ bananas during ripening.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aghdam MS, Fard JR (2017) Melatonin treatment attenuates postharvest decay and maintains nutritional quality of strawberry fruits (Fragaria x anannasa cv. Selva) by enhancing GABA shunt activity. Food Chem 221:1650–1657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.123
Ao C, Li A, Elzaawely AA, Xuan TD, Tawata S (2008) Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Ficusmicrocarpa L. fil. extract. Food Control 19:940–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2007.09.007
AOAC (2000) Association of official analytical chemists, official methods of analysis. 17th edition. International, Gaithersburg, MD
Arnao MB, Hernandez-Ruiz J (2018) Melatonin and its relationship to plant hormones. Ann Bot 121:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx114
Awad MA, Al-Qurashi AD, Mohamed SA, El-Shishtawy RM, Ali MA (2017) Postharvest chitosan, gallic acid and chitosan gallate treatments effects on shelf life quality, antioxidant compounds, free radical scavenging capacity and enzymes activities of ‘Sukkari’ bananas. J Food Sci Technol 54:447–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2481-8
Baez-Sañudo M, Siller-Cepeda J, Muy-Rangel D, Basilio Heredia J (2009) Extending the shelf-life of bananas with 1-methylcyclopropene and a chitosan-based edible coating. J Sci Food Agric 98:2343–2349. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3715
CSIRO (1972) Banana ripening guide. Commonwealth scientific industrial research organisation division of fruit research, North Ryde, NSW p. 13
Ding P, Ling YS (2014) Browning assessment methods and polyphenoloxidase in UV-C irradiated Berangan banana fruit. Int Food Res J 21:1667–1674
Duan XW, Joyce DC, Jiang YM (2007) Postharvest biology and handling of banana fruit: review. Fresh Prod 1:140–152
Fernando HRP, Srilaong V, Boonyaritthongchai PN, P, Jitareerat P, (2014) Changes in antioxidant properties and chemical composition during ripening in banana variety ‘Hom Thong’ (AAA group) and ‘Khai’ (AA group). Int Food Res J 21:749–754
Gao H, Zhang ZK, Chai HK, Cheng N, Yang Y, Wang DN, Yang T, Cao W (2016) Melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence and regulates reactive oxygen species metabolism in peach fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 118:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.03.006
Hoff JF, Singleton KI (1977) A method for determination of tannin in foods by means of immobilized enzymes. J Food Sci 42:1566–1569. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1977.tb08427.x
Hu W, Yang H, Tie W, Yan Y, Ding Z, Liu Y, Wu C, Wang J, Reiter RJ, Tan D, Shi H, Xu B, Jin Z (2017) Natural variation in banana varieties highlights the role of melatonin in postharvest ripening and quality. J Agric Food Chem 65:9987–9994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03354
Jaiswal P, Jha SN, Kaur PP, Bhardwaj R, Singh AK, Wadhawan V (2014) Prediction of textural attributes using color values of banana (Musa sapientum) during ripening. J Food Sci Technol 51:1179–1184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0614-2
Jayarajan S, Sharma RR (2021) Melatonin: a blooming biomolecule for postharvest management of perishable fruits and vegetables. Trends Food Sci Technol 116:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.07.034
Jiang YM, Zhang ZQ, Joyce DC, Ketsa S (2002) Postharvest biology and handling of longan fruit (Dimocarpuslongan Lour.). Posthrvest Biol Technol 26:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(02)00047-9
Kerch G (2015) Chitosan films and coatings prevent losses of fresh fruit nutritional quality: a review. Trend Food Sci Technol 46:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.10.010
Li Y, Jia F (2008) A survey on status and countermeasures of banana industry in China. Chin Agric Sci Bull 24:443–447
Li T, Wu Q, Zhu H, Zhou Y, Jiang Y, Gao H, Yun Z (2019) Comparative transcriptomic and metabolic analysis reveals the effect of melatonin on delaying anthracnose incidence upon postharvest banana fruit peel. BMC Plant Biol 19:289. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1855-2
Liu FW (1976) Banana response to low concentrations of ethylene. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 101:222–224
Liu C, Zheng H, Sheng K, Liu W, Zheng L (2018) Effects of melatonin treatment on the postharvest quality of strawberry fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 139:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.01.016
Liu S, Huang H, Huber DJ, Pan Y, Shi X, Zhang Z (2020) Delay of ripening and softening in ‘Guifei’ mango fruit by postharvest application of melatonin. Postharvest Biol Technol 163:111136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111136
Lufu R, Ambaw A, Opara LU (2020) Water loss of fresh fruit: Influencing pre-harvest, harvest and postharvest factors. Sci Hortic 272:109519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109519
Maqbool M, Ali A, Alderson PG, Zahid N, Siddiqui Y (2011) Effect of a novel edible composite coating based on gum Arabic and chitosan on biochemical and physiological responses of banana fruits during cold storage. J Agric Food Chem 59:5474–5482. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf200623m
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for the determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–429. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Miranda MV, Fernandez Lahor HM, Cascone O (1995) Horseradish peroxidase extraction and purification by aqueous two-phase partition. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 53:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02788604
Miranda S, Vilches P, Suazo M, Pavez L, García K, M´endez M, González M, Meisel LA, Defilippi BG, Pozo T, (2020) Melatonin triggers metabolic and gene expression changes leading to improved quality traits of two sweet cherry cultivars during cold storage. Food Chem 319:126360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126360
Shiga TM, Soares CA, Nascimento JRO, Purgatto E, Lajolo FM, Cordenunsi BR (2011) Ripening-associated changes in the amounts of starch and non-starch polysaccharides and their contributions to fruit softening in three banana cultivars. J Sci Food Agric 91:1511–1516. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4342
Singh B, Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Bioactive compounds in banana and their associated health benefits – a review. Food Chem 206:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.033
Suseno N, Savitri E, Sapei L, Padmawijaya KS (2014) Improving shelf-life of Cavendish banana using chitosan edible coating. Procedia Chem 9:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.05.014
Waliszewski KN, Pardio VT, Ovando S (2007) Control of polyphenol oxidase activity in banana slices during osmotic dehydration. Drying Technol 25:375–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373930601120613
Xu T, Chen Y, Kang H (2019) Melatonin is a potential target for improving postharvest preservation of fruits and vegetables. Front Plant Sci 10:1388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01388
Zhang Y, Huber DJ, Hu M, Jiang G, Gao Z, Xu X, Jiang Y, Zhang Z (2018) Delay of postharvest browning in litchi fruit by melatonin via the enhancing of antioxidative processes and oxidation repair. J Agric Food Chem 66:7475–7484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01922
Zhao H, Wang L, Belwal T, Jiang Y, Li D, Xu Y et al (2020) Chitosan based melatonin bilayer coating for maintaining quality of fresh-cut products. Carbohydr Polym 235:115973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115973
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant G: 540-155-1442. The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Funding
The Deanship of Scientific Research, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant G: 540-155-1442.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ADA conceived, carried out the experiments and edited the MS; MAA experimental design, supervised the work and wrote the MS; MIE regular fruit quality measurements and data collections; MDAA, biochemical analysis and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to participate
All Authors listed have contributed significantly to the work and agree to be in the author list.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Qurashi, A.D., Awad, M.A., Elsayed, M.I. et al. Postharvest melatonin and chitosan treatments retain quality of ‘Williams’ bananas during ripening. J Food Sci Technol 61, 84–96 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05819-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05819-8