Abstract
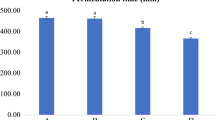
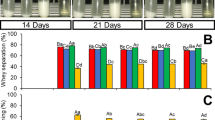
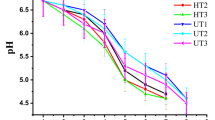
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of high-intensity ultrasound as pre-treatment in the development of fermented whey and oat beverages. Oat malt was produced, incorporated into a whey formulation (35, 50 and 65% v/v of whey) and ultrasonicated (at 40 kHz and 11 W/cm2) for 0, 3 or 10 min, prior to fermentation with L. casei 431. The treatments were identified as 35/65/0, 50/50/0, 65/35/0, 35/65/3, 50/50/3, 65/35/3, 35/65/10, 50/50/10 and 65/35/10, referring to the whey percentage, oat percentage, and the ultrasound time (min), respectively. The beverages 50/50/0 and 50/50/3 registered the highest (P < 0.05) growth with 1.96 and 2.00 log CFU ml, respectively. In general, the final average population of L. casei 431 was 7 to 8.86 log CFU/ml, being this adequate for a probiotic beverage. The highest antioxidant activity was found in the 35/65/3, 35/65/10, 50/50/3 and 50/50/10 beverages without difference (P < 0.05) among them. There was no effect of gender on the acceptance of the probiotic beverages. The best accepted beverage by women was 50/50/3 and both genders disliked the beverage 35/65/10. There was no relationship between the acceptance of the beverages and the consumers’ habit by fermented milk beverages. No difference in the preference between the 50/50/0 and the 50/50/3 beverage was found. It is concluded that the probiotic beverage containing 50% whey and 50% oat and ultrasonicated for 3 min generated the highest levels of L. casei 431 growth, high antioxidant activity and good consumer acceptance and preference.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hilphy AR, Verma DK, Niamah AK, Billoria S, Srivastar P (2016) Principles of ultrasonic technology for treatment of milk and milk products. In: Meghwal M, Goyal MR (eds) Food process engineering: Emerging trends in research and their applications. Apple Academic Press, Palm Bay, FL, pp 178–202
Alrahmany R, Avis TJ, Tsopmo A (2013) Treatment of oat bran with carbohydrases increases soluble phenolic acid content influences antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Food Res Int 52:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.03.037
Alvarado Pérez Y, Muro Urista C, Maciel Cerda A, Álvarez Sánchez J, Riera Rodríguez F (2018) Antihypertensive and antioxidant properties from whey protein hydrolysates produced by encapsulated Bacillus subtilis cells. Int J Pept Res Ther 25:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-018-9714-9
Ashokkumar M (2011) The characterization of acoustic cavitation bubbles: an overview. Ultras Sonochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.11.016
Barukčić I, Jakopović KL, Herceg Z, Karlović S, Božanić R (2015) Influence of high intensity ultrasound on microbial reduction, physico-chemical characteristics and fermentation of sweet whey. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 27:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2014.10.013
Bhat ZF, Kumar S, Bhat HF (2015) Bioactive peptides of animal origin: a review. J Food Sci Technol 52(9):5377–5392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1731-5
Bobková A, Fikselová M, Tóth T, Bobko M (2016) Flavored whey drinks: preparation and evaluation of selected parameters. J Anim Sci Biotechno 2:195–199
Brandelli A, Joner Daroit D, Folmer Correa AP (2015) Whey as a source of peptides with remarkable biological activities. Food Res Int 73:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.016
Bulatović ML, Rakin MB, Mojović LV, Nikolić SB, Vukašinović Sekulić MS, Đukić Vuković P (2012) Selection of Lactobacillus strains for functional whey-based beverage production. J Food Eng 2:705–711. https://doi.org/10.17265/2159-5828/2012.12.006
Bulatović ML, Krunić TZ, Vukašinović-Sekulić MS, Zarić DB, Rakin MB (2014) Quality attributes of a fermented whey-based beverage enriched with milk and a probiotic strain. RSC Adv 98:1–31. https://doi.org/10.2298/hemind141106016r
Castro WF, Cruz AG, Bisinotto MS, Guerreiro LM, Faria JAF, Bolini HMA, Cunha RL, Deliza R (2013) Development of probiotic dairy beverages: rheological properties and application of mathematical models in sensory evaluation. J Dairy Sci 96:16–25. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5590
Castro WF, Cruz AG, Rodrigues D, Ghiselli G, Oliveira CAF, Faria JAF, Godoy HT (2013) Short communication: effects of different whey concentrations on physicochemical characteristics and viable counts of starter bacteria in dairy beverage supplemented with probiotics. J Dairy Sci 96:96–100. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5576
Cheung IWY, Nakayama S, Hsu MNK, Samaranayaka AGP, Li-Chan ESY (2009) Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity of hydrolysates from oat (Avena sativa) proteins by in silico and in vitro analyses. J Agr Food Chem 57:9234–9242. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9018245
Coman MM, Verdenelli MC, Cecchini C, Silvi S, Vasile A, Bahrim GE, Orpianesi C, Cresci A (2013) Effect of buckwheat flour and oat bran on growth and cell viability of the probiotic strains Lactobacillus rhamnosus IMC 501®, Lactobacillus paracasei IMC 502® and their combination SYNBIO®, in synbiotic fermented milk. Int J Food Microbiol 167:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.09.015
Gholamhosseinpour A, Hashemi SMB (2018) Ultrasound pretreatment of fermented milk containing probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum AF1: Carbohydrate metabolism and antioxidant activity. J Food Process Eng 42(1):e12930. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12930
Gokavi S, Zhang L, Huang M, Zhao X, Guo M (2005) Oat-based symbiotic beverage fermented by L. plantarum, L. paracasei ssp. casei, and L. acidophilus. J Food Sci 70:216–223
Granato D, Barba FJ, Kovačević DB, Lorenzo JM, Cruz AG, Putnik P (2020) Functional Foods: Product development, technological trends, efficacy testing and safety. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 11:3.1-3.26. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-032519-051708
Guimarães JT, Balthazar CF, Scudino H, Pimentel TC, Esmerino EA, Ashokkumar M, Freitas MQ, Cruz AG (2019) High-intensity ultrasound: a novel technology for the development of probiotic and prebiotic dairy products. Ultras Sonochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.05.004
Herrera-Ponce AL, Nevárez-Morillón G, Ortega-Rivas E, Pérez-Vega S, Salmerón I (2014) Fermentation adaptability of three probiotic Lactobacillus strains to oat, germinated oat and malted oat substrates. Lett Appl Microbiol 59(4):449–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12302
Hill D, Sugrue I, Tobin C, Hill C, Stanton C, Ross P (2018) The lactobacillus casei group: history and health related applications. Front Microbiol 9:2107. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02107
Jeličić I, Božanić R, Brnčić M, Tripalo B (2012) Influence and comparison of thermal, ultrasonic and thermosonic treatments on microbiological quality and sensory properties of rennet cheese whey. Mljekarstvo 62:165–178
Kamble N, Puranik DB, Salooja MK (2017) Preparation of probiotic guduchi whey beverage. Int J Environ Sci Te 6(4):2258–2270
Kumar MD, Beena AK, Baig MD (2017) Optimization of Lactobacillus casei and inulin levels in the preparation of symbiotic whey beverage using response surface methodology. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(7):558–568. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.067
Lawless TH, Heymann H (2010) Sensory evaluation of food: principles and practice. Springer, New York, NY
Marranzino G, Villena J, Salva S, Alvarez S (2012) Stimulation of macrophages by immunobiotic Lactobacillus strains: influence beyond the intestinal tract. Microbiol Immunol 56:771–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2012.00495.x
Potoroko I, Kalinina I, Botvinnikova V, Krasulya O, Fatkullin R, Bagale U (2018) Ultrasound effects based on simulation of milk processing properties. Ultras Sonochem 48:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.06.019
SAS Institute (2006) SAS/STAT User’s guide. SAS Inst. Inc. Cary, NC
Sawas T, Al Halabi S, Hernaez R, Carey WD, Cho WK (2015) Patients receiving prebiotics and probiotics before liver transplantation develop fewer infections than controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(9):1567–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2015.05.027
Šubarić D, Babić J, Lalić A, Ačkar Đ, Kopjar M (2011) Isolation and characterisation of starch from different barley and oat varieties. Czech J Food Sci 29(4):354–360. https://doi.org/10.17221/297/2010-cjfs
Thaipong K, Boonprakob U, Crosby K, Cisneros-Zevallos L, Byrn DH (2006) Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J Food Compos Anal 19:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2006.01.003
Uluko H, Li H, Cui W, Zhang S, Liu L, Chen J, Sun Y, Su Y, Lv J (2013) Response surface optimization of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition of milk protein concentrate hydrolysates in vitro after ultrasound pretreatment. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 20:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2013.08.012
Yamahata N, Toyotake Y, Kunieda S, Wakayama S (2020) Optimal fermentation conditions and storage period of fermented beverages made from demineralized whey using Kluyveromyces marxians. J Food Sci Nutr 3(1):001–017. https://doi.org/10.26502/jfsnr.2642-11000035
Zhao CC, Kim PH, Eun JB (2019) Influence of high-intensity ultrasound application on the physicochemical properties, isoflavone composition, and antioxidant activity of tofu whey. LWT Food Sci Technol 117:108618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ADA-R and ALH-P designed the study. IS and ES interpreted the results. AH-P collected test data and drafted the manuscript. IAG-G, IS, JCR-F and ADA-R reviewed and edited the manuscript. ADA-R and IS conducted the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from each subject prior to their participation in the sensory studies carried out in the study.
Ethical aproval
The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Bioethics Committee of the Faculty of Animal Science and Ecology of the Autonomous University of Chihuahua, Mexico (Decision No. P/302/2017).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera-Ponce, A.L., Salmeron-Ochoa, I., Rodriguez-Figueroa, J.C. et al. High-intensity ultrasound as pre-treatment in the development of fermented whey and oat beverages: effect on the fermentation, antioxidant activity and consumer acceptance. J Food Sci Technol 59, 796–804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05074-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05074-9