Abstract
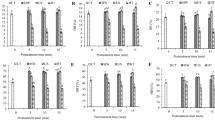
In the study, the effects of nitrate and/or nitrite (150 mg/kg KNO3, 300 mg/kg KNO3, 150 mg/kg NaNO2, and 150 mg/kg KNO3 + 150 mg/kg NaNO2) on proteolytic changes (free amino acid composition, SDS-PAGE) in pastırma were investigated. Pastırma samples were also analyzed in terms of some qualitative (pH, aw, TBARS, residual nitrite, salt) properties. The lowest total free amino acid content (1818.3 mg/ 100 g DM) was observed in the combination of 150 mg/kg KNO3 + 150 mg/kg NaNO2, while the highest content (2847.49 mg/ 100 g DM) was observed in 150 mg/kg KNO3. Although the pastırma groups generally exhibited similar SDS-PAGE profiles, differences were detected at some band intensities. The lowest TBARS value (22.24 μmol MDA/kg) was observed in 150 mg/kg KNO3 + 150 mg/kg NaNO2. As a result, the use of 150 mg/kg KNO3 in the pastırma curing process causes more intense proteolysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkose A, Unal N, Yalınkılıç B, Kaban G, Kaya M (2017) Volatile compounds and some physico-chemical properties of pastirma produced with different nitrate levels. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 30:1168–1174
Aksu MI, Erdemir E, Çakıcı N (2016) Changes in the physico-chemical and microbial quality during the production of pastirma cured with different levels of sodium nitrite. Korean J Food Sci Animal Resour 36:617–625
Aktaş N, Aksu MI, Kaya M (2005) Changes in myofibrillar proteins during processing of pastirma (Turkish dry meat product) produced with commercial starter cultures. Food Chem 90:649–654
Anonymous (2018) Turkish Food Codex Communique on Meat and Meat Products 2018/52: Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Livestock
Antoine FR, Wei CI, Littell RC, Marshall MR (1999) HPLC method for analysis of free amino acids in fish using o-phthaldialdehyde precolumn derivatization. J Agric Food Chem 47:5100–5107
Beltran E, Pla R, Yuste J, Mor-Mur M (2003) Lipid oxidation of pressurized and cooked chicken: role of sodium chloride and mechanical processing on TBARS and hexanal values. Meat Sci 64:19–25
Berardo A, Claeys E, Vossen E, Leroy F, De Smet S (2015) Protein oxidation affects proteolysis in a meat model system. Meat Sci 106:78–84
Bosse M, Gibis M, Schmidt H, Weiss J (2016) Nitrate reductase activity of Staphylococcus carnosus affecting the color formation in cured raw ham. Food Res Int 85:113–120
Ceylan S, Aksu Mİ (2011) Free amino acids profile and quantities of ‘sırt’, ‘bohça’ and ‘sekerpare’ pastırma, dry-cured meat products. J Sci Food Agric 91:956–962
Cordoba JJ, Antequera Rojas T, Garcia Gonzalez C, Ventanas Barroso J, Lopez Bote C, Asensio MA (1994) Evolution of free amino acids and amines during ripening of Iberian cured ham. J Agric Food Chem 42:2296–2301
Deniz E, Mora L, Aristoy MC, Candoğan K, Toldra F (2016) Free amino acids and bioactive peptides profile of Pastırma during its processing. Food Res Int 89:194–201
Erdemir E, Aksu Mİ (2017) Changes in the composition of free amino acid during production of pastirma cured with different levels of sodium nitrite. J Food Process Preserv 41:e12801
Gallego M, Mora L, Escudero E, Toldra F (2018) Bioactive peptides and free amino acids profiles in different types of European dry-fermented sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 276:71–78
Gandemer G (2002) Lipids in muscles and adipose tissues, changes during processing and sensory properties of meat products. Meat Sci 62:309–321
Garrido R, Dominguez R, Lorenzo JM, Franco I, Carballo J (2012) Effect of the length of salting time on the proteolytic changes in dry-cured Lacon during ripening and on the sensory characteristics of the final product. Food Control 25:789–796
Gökalp HY, Kaya M, Zorba Ö (1999a) Engineering of meat products processing (3rd ed) no: 320. Atatürk University, Faculty of Agriculture, Erzurum, Turkey
Gökalp HY, Kaya M, Tülek Y, Zorba Ö (1999b) Guide for quality control and laboratory application of meat and meat products (3rd ed) no: 751. Atatürk University, Faculty of Agriculture, Erzurum, Turkey
Harkouss R, Astruc T, Lebert A, Gatellier P, Loison O, Safa H, Portanguen S, Parafita E, Mirade PS (2015) Quantitative study of the relationships among proteolysis, lipid oxidation, structure and texture throughout the dry-cured ham process. Food Chem 166:522–530
Hazar FY, Kaban G, Kaya M (2017) The effects of different processing conditions on biogenic amine formation and some qualitative properties in pastırma. J Food Sci Technol-Mysore 54:3892–3898
Honikel KO (2008) The use and control of nitrate and nitrite for the processing of meat products. Meat Sci 78:68–76
Huang Y, Li H, Huang T, Li F, Sun J (2014) Lipolysis and lipid oxidation during processing of chinese traditional smoke-cured bacon. Food Chem 149:31–39
Hughes M, Kerry J, Arendt E, Kenneally P, McSweeney P, O'Neill E (2002) Characterization of proteolysis during the ripening of semi-dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci 62:205–216
Jin G, He L, Zhang J, Yu X, Wang J, Huang F (2012) Effects of temperature and NaCl percentage on lipid oxidation in pork muscle and exploration of the controlling method using response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chem 131:817–825
Jurado A, Garcia C, Timon ML, Carrapiso AI (2007) Effect of ripening time and rearing system on amino acid-related flavour compounds of Iberian ham. Meat Sci 75:585–594
Kaban G (2009) Changes in the composition of volatile compounds and in microbiological and physicochemical parameters during pastırma processing. Meat Sci 82:17–23
Kaban G (2013) Sucuk and pastırma: microbiological changes and formation of volatile compounds. Meat Sci 95:912–918
Khan MI, Jo C, Tariq MR (2015) Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors-a systematic review. Meat Sci 110:278–284
Kızılkaya E (2012) Proteolytic changes during reduced sodium pastırma processing. Master thesis, Graduate school of natural and applied sciences. Department of Food Engineering. Ankara, Turkey
Larrea V, Hernando I, Quiles A, Lluch M, Perez-Munuera I (2006) Changes in proteins during Teruel dry-cured ham processing. Meat Sci 74:586–593
Leistner L (1988) Hurden–Technologie bei Fleischerzeugnissen und anderen Lebensmitteln. Lebensmittelqualitat Wissenchaft und Technik, R. Stufe (Hrsg), Wissenschaftliche Arbeitstagung” 25 Jahre Institut fur Forschung und Entwicklung der Maizena Ges. MbH’,s 323–340 in Heilbornn, 2. bis 4 Marz
Lemon DW (1975) An iimproved TBA test for rancidity new series circular. No:51. Halifax-Laboratory, Halifax, Nova Scotia
Marino R, Albenzio M, Malva A, Caroprese M, Santillo A, Sevi A (2014) Changes in meat quality traits and sarcoplasmic proteins during aging in three different cattle breeds. Meat Sci 98:178–186
Mora L, Gallego M, Toldra F (2018) New approaches based on comparative proteomics for the assessment of food quality. Curr Opin Food Sci 22:22–27
Oz E, Kaya M (2019) The proteolytic changes in two different types of pastırma during the production. J Food Process Preserv 43:e14042
Paleari MA, Morretti VM, Beretta G, Mentasti T, Bersani C (2003) Cured products from different animal species. Meat Sci 63:485–489
Sanchez Mainar M, Leroy F (2015) Process-driven bacterial community dynamics are key to cured meat colour formation by coagulase-negative staphylococci via nitrate reductase or nitric oxide synthase activities. Int J Food Microbiol 212:60–66
Sebranek JG, Bacus JN (2007) Cured meat products without direct addition of nitrate or nitrite: what are the issues? Meat Sci 77:136–147
Soyer A, Uğuz Ş, Dalmış Ü (2011) Proteolytic changes during processing in Turkish dry-cured meat product (pastırma) with different salt levels. J Food Qual 34:212–219
Tamura M, Miyoshi T, Mori N, Kinomura K, Kawaguchi M, Ishibashi N, Okai H (1990) Studies on flavored peptides. 8. Mechanism for the bitter tasting potency of peptides using O-aminoacyl sugars as model compounds. Agric Biol Chem 54:1401–1409
Tauchmann F (1987) Methoden der Chemischen Analytik von Fleisch und Fleischwaren. Bundensanstalt für Fleischforschung, Kulmbach, 80 s
Toldra F (2006) The role of muscle enzymes in dry-cured meat products with different drying conditions. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:164–168
Toldra F (2010) Handbook of meat processing, 1st edn. Wiley-Blackwell Publication
Toldra F, Etherington DJ (1988) Examination of cathepsins B, D, H and L activities in dry cured hams. Meat Sci 23:1–7
Toldra F, Cervero MC, Part C (1993) Porcine aminopeptidase activity as affected by curing agents. J Food Sci 58:724–726
Toldra F, Flores M, Sanz Y (1997) Dry-cured ham flavour: enzymatic generation and process influence. Food Chem 59:523–530
Uğuz Ş, Soyer A, Dalmış Ü (2011) Effects of different salt contents on some quality characteristics during processing of dry-cured Turkish pastırma. J Food Qual 34:204–211
Villaverde A, Ventanas J, Estévez M (2014) Nitrite promotes protein carbonylation and Strecker aldehyde formation in experimental fermented sausages: are both events connected? Meat Sci 98:665–672
Virgili R, Schivazappa C (2002) Muscle traits for long matured dried meats. Meat Sci 62:331–343
Waade C, Stahnke LH (1997) Dried sausages fermented with Staphylococcus xylosus at different temperatures and with different ingredient levels. IV. Amino acid profile. Meat Sci 46:101–114
Wu H, Zhang Y, Long M, Tang J, Yu X, Wang J, Zhang J (2014) Proteolysis and sensory properties of dry-cured bacon as affected by the partial substitution of sodium chloride with potassium chloride. Meat Sci 96:1325–1331
Zhou CY, Wang Y, Pan DD, Cao JX, Chen YJ, Liu Y, Sun YY, Ou CR (2017) The changes in the proteolysis activity and the accumulation of free amino acids during chinese traditional dry-cured loins processing. Food Sci Biotechnol 26(3):679–687
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Atatürk University research center with Project No: 286 2015/405. This research presented in part at the International Congress on Engineering and Life Science, Kastamonu, Turkey, April 26–29, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by Atatürk University research center with Project No: 286 2015/405.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oz, E., Kabil, E. & Kaya, M. The effects of curing agents on the proteolysis and lipid oxidation of pastırma produced by the traditional method. J Food Sci Technol 58, 2806–2814 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04889-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04889-2