Abstract
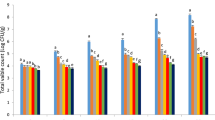
The present study compared the effects of corn starch coatings incorporated with Zataria multiflora essential oil (ZEO) and cinnamaldehyde (CIN) in conventional, nanoemulsion (NZEO) and fortified nanoemulsion (NZEOC) forms, on specific spoilage microorganisms of chicken meat and on the fate of inoculated Listeria monocytogenes during 20 days storage at 4 ± 1 °C. Based on the results of GC–MS analysis of ZEO, carvacrol (36.62%) was the most important compound of essential oil. Samples coated with the starch solution containing nanoemulsions had better antimicrobial activities than conventional forms. Also, NZEOC treatment had the best antimicrobial properties at the end of storage with the following results: Total viable count (7.96 log10 CFU/g), Psychrotrophic count (7.29 log10 CFU/g), Lactic acid bacteria (6.51 log10 CFU/g), Enterobacteriaceae count (6.98 log10 CFU/g), Mold and yeast count (5.16 log10 CFU/g) and inoculated L. monocytogenes (6.51 log10 CFU/g). Furthermore, the addition of CIN–ZEO during nanoemulsion formation (NZEOC) increased the antimicrobial properties of the samples compared to individual addition of NZEO and CIN (NZEO + CIN) to the starch solution. Therefore, corn starch coating containing NZEOC is recommended as a natural preservative to enhance the microbial stability of poultry meat.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahzadeh E, Ojagh SM, Hosseini H, Ghaemi EA, Irajian GH (2018) Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of antibacterial activity of cinnamon essential oil and ZnO nanoparticles against Listeria monocytogenes. J Fish Sci Technol 7:49–55
Basti AA, Misaghi A, Khaschabi D (2007) Growth response and modelling of the effects of Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil, pH and temperature on Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:973–981
Bazargani-Gilani B, Aliakbarlu J, Tajik H (2015) Effect of pomegranate juice dipping and chitosan coating enriched with Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil on the shelf-life of chicken meat during refrigerated storage. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 29:280–287
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94:223–253
Chang Y, McLandsborough L, McClements DJ (2013) Physicochemical properties and antimicrobial efficacy of carvacrol nanoemulsions formed by spontaneous emulsification. J Agric Food Chem 61:8906–8913
Dhara L, Tripathi A (2013) Antimicrobial activity of eugenol and cinnamaldehyde against extended spectrum beta lactamase producing enterobacteriaceae by in vitro and molecular docking analysis. Eur J Integr Med 5:527–536
Donsì F, Ferrari G (2016) Essential oil nanoemulsions as antimicrobial agents in food. J Biotechnol 233:106–120
Gahruie HH, Ziaee E, Eskandari MH, Hosseini SMH (2017) Characterization of basil seed gum-based edible films incorporated with Zataria multiflora essential oil nanoemulsion. Carbohyd Polym 166:93–103
Ghaderi-Ghahfarokhi M, Barzegar M, Sahari M, Gavlighi HA, Gardini F (2017) Chitosan-cinnamon essential oil nano-formulation: application as a novel additive for controlled release and shelf life extension of beef patties. Int J Biol Macromol 102:19–28
Gholami-Shabani MH, Imani A, Chamani M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M, Riazi GH, Chian M et al (2012) Evaluation of the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized with Fusarium Oxysporum and Escherichia coli. New Cell Mol Biotechnol J 6:27–33 (in Persian)
Gill AO, Holley RA (2004) Mechanisms of bactericidal action of cinnamaldehyde against Listeria monocytogenes and of eugenol against L. monocytogenes and Lactobacillus sakei. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5750–5755
Hosseinzadeh H, Ramezani M, Salmani G (2000) Antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and acute toxicity effects of Zataria multiflora Boiss extracts in mice and rats. J Ethnopharmacol 73:379–385
Khanzadi S, Keykhosravy K, Hashemi M, Azizzadeh M (2020) Alginate coarse/nanoemulsions containing Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil as edible coatings and the impact on microbial quality of trout fillet. Aquac Res 51:873–881
Masoomi V, Tajik H, Moradi M, Forough M, Shahabi N (2016) Antimicrobial effects of Zataria multiflora boiss. essential oil nanoemulsion against Escherichia coli O157: H7. J Urmia Univ Med Sci 27:608–617
Mastromatteo M, Lucera A, Sinigaglia M, Corbo MR (2009) Combined effects of thymol, carvacrol and temperature on the quality of non-conventional poultry patties. Meat Sci 83:246–254
Moghimi R, Ghaderi L, Rafati H, Aliahmadi A, McClements DJ (2016) Superior antibacterial activity of nanoemulsion of Thymus daenensis essential oil against E. coli. Food Chem 194:410–415
Mohajeri FA, Misaghi A, Gheisari H, Basti AA, Amiri A, Ghalebi SR, Derakhshan Z, Tafti RD (2018) The effect of Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil on the growth and citrinin production of Penicillium citrinum in culture media and cheese. Food Chem Toxicol 118:691–694
Mohammadi A, Hashemi M, Hosseini SM (2016) Postharvest treatment of nanochitosan-based coating loaded with Zataria multiflora essential oil improves antioxidant activity and extends shelf-life of cucumber. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 33:580–588
Molavi H., Sedaghat N. 2013. Biodegradable films based on starch 2nd National Conference on Food Sci Technol, Islamic Azad University, Quchan Branch, 28–30 (in Persian).
Nasseri M, Arouiee H, Golmohammadzadeh S, Jaafari M, Neamati H (2017) Effect of solid lipid nanoparticle containing essential oil of Zataria multiflora on the inhibitory growth of Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus flavus. J Appl Res Plant Prot 5:161–174
Nasseri M, Golmohammadzadeh S, Arouiee H, Jaafari MR, Neamati H (2016) Antifungal activity of Zataria multiflora essential oil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in-vitro condition. Iran J Basic Med Sci 19:1231–1237
Noori S, Zeynali F, Almasi H (2018) Antimicrobial and antioxidant efficiency of nanoemulsion-based edible coating containing ginger (Zingiber officinale) essential oil and its effect on safety and quality attributes of chicken breast fillets. Food Control 84:312–320
OECD/Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2016) “Meat” in OECD-FAO agricultural outlook 2016–2025. OECD Publishing Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/agr_outlook-2016-10-en
OuYang O, Duan X, Li L, Tao N (2019) Cinnamaldehyde exerts its antifungal activity by disrupting the cell wall integrity of geotrichum citri-aurantii. Front Microbiol 10:55
Pabast M, Shariatifar N, Beikzadeh S, Jahed G (2018) Effects of chitosan coatings incorporating with free or nano-encapsulated satureja plant essential oil on quality characteristics of lamb meat. Food Control 91:185–192
Pei, R.s., Zhou, F., Ji, B.p., Xu, J., (2009) Evaluation of combined antibacterial effects of eugenol, cinnamaldehyde, thymol, and carvacrol against E. coli with an improved method. J Food Sci 74:M379–M383
Raeisi M, Tabaraei A, Hashemi M, Behnampour N (2016) Effect of sodium alginate coating incorporated with nisin, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, and rosemary essential oils on microbial quality of chicken meat and fate of Listeria monocytogenes during refrigeration. Int J Food Microbiol 238:139–145
Ramachandraiah K, Han SG, Chin KB (2015) Nanotechnology in meat processing and packaging: potential applications—a review. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 28:290
Ramos M, Jiménez A, Garrigós M (2016) Carvacrol-based films: usage and potential in antimicrobial packaging, Antimicrobial food packaging. Elsevier Ltd, Academic Press, UK; USA, pp 329–338
Sánchez-González L, Vargas M, González-Martínez C, Chiralt A, Cháfer M (2011) Use of essential oils in bioactive edible coatings: a review. Food Eng Rev 3:1–16
Sandri I, Zacaria J, Fracaro F, Delamare A, Echeverrigaray S (2007) Antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Brazilian species of the genus cunila against foodborne pathogens and spoiling bacteria. Food Chem 103:823–828
Sani MA, Ehsani A, Hashemi M (2017) Whey protein isolate/cellulose nanofibre/TiO2 nanoparticle/rosemary essential oil nanocomposite film: Its effect on microbial and sensory quality of lamb meat and growth of common foodborne pathogenic bacteria during refrigeration. Int J Food Microbiol 251:8–14
Shahabi N, Tajik H, Moradi M, Forough M, Ezati P (2017) Physical, antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties of Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil nanoemulsion. Int J Food Sci Technol 52:1645–1652
Shahnia M, Khaksar R (2013) Antimicrobial effects and determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) methods of essential oils against pathogenic bacteria. Iran J Nutr Sci Food Technol 7:949–955 (in Persian)
Sharififar F, Moshafi M, Mansouri S, Khodashenas M, Khoshnoodi M (2007) In vitro evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of the essential oil and methanol extract of endemic Zataria multiflora Boiss. Food Control 18:800–805
Sheen S, Huang CY, Ramos R, Chien SY, Scullen OJ, Sommers C (2018) Lethality prediction for Escherichia coli O157: H7 and uropathogenic E. coli in ground chicken treated with high pressure processing and trans-cinnamaldehyde. J Food Sci 83:740–749
Ye H, Shen S, Xu J, Lin S, Yuan Y, Jones GS (2013) Synergistic interactions of cinnamaldehyde in combination with carvacrol against food-borne bacteria. Food Control 34:619–623
Zarei M, Ramezani Z, Ein-Tavasoly S, Chadorbaf M (2015) Coating effects of orange and pomegranate peel extracts combined with chitosan nanoparticles on the quality of refrigerated silver carp fillets. J Food Process Preserv 39:2180–2187
Ziaee E, Razmjooei M, Shad E, Eskandari MH (2018) Antibacterial mechanisms of Zataria multiflora Boiss. essential oil against Lactobacillus curvatus. LWT-Food Sci Technol 87:406–412
Acknowledgement
This paper was extracted from the MSc thesis of Zahra Abbasi and financially supported by the School of Public Health, Zanjan University of Medical Science, Zanjan, Iran (project code: A-12-964-5). The Ethics Committee of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences has approved this project (code of ethics: ZUMS.REC.1395.297)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, Z., Aminzare, M., Hassanzad Azar, H. et al. Effect of corn starch coating incorporated with nanoemulsion of Zataria multiflora essential oil fortified with cinnamaldehyde on microbial quality of fresh chicken meat and fate of inoculated Listeria monocytogenes. J Food Sci Technol 58, 2677–2687 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04774-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04774-y