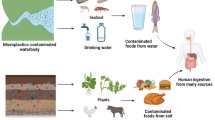
Abstract
Present study was performed using a Box–Behnken Design (BBD) combined with a response surface methodology (RSM). The ultimate goal of this research was to apply BBD for modeling of copper (Cu2+) ions from alcoholic beverages and evaluate health risk assessment of Cu2+ via consumption of alcoholic beverages. The importance of independent paramaters and their interactions were examined using analysis of variance (ANOVA). Natural clay was investigated to remove Cu2+ ions from some alcoholic beverage samples including beer and wine. X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with energy dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis were used for adsorbent characterization. Same analyzes were applied for Cu2+ loaded clay. In addition, experimental studies showed that Freundlich isotherm was better than Langmuir isotherm. Finally, optimized method was applied to alcoholic beverages. Besides target hazard quotients (THQ), estimated daily intake (EDI) values were calculated, to assess a health risk resulting from these alcoholic beverages regular consumption. The EDI values of Cu (µg/day/person) through consumption of investigated drinks were less than the recommended dietary allowance values. Also, the THQ values of Cu2+ were less than 1. According to estimated target hazard, it can be said no long life health concerns of Cu2+ is associated with the consumption of studied drinks. Obtained results were compared with the data from literature and levels set by regulatory authorities, it can be clearly stated that the consumption of mentioned alcoholic beverages do not pose a toxicological risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MZ, Muyibi SA, Toramae J (2007) Statistical optimization of adsorption processes for removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol by activated carbon derived from oil palm empty fruit bunches. J Environ Sci 19:674–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60113-2
Alp H, Ince M, Kaplan Ince O, Onal A (2020) Evaluation the weekly intake of some wild edible indigenous mushrooms collected in different regions in Tunceli, Turkey. Biol Trace Elem Res 195(2):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01814-3
Amuda OS, Ibrahim AO (2006) Industrial wastewater treatment using natural material as adsorbent. Afr J Biotechnol 5(16):1483–1487
Bingöl D (2011) Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions using a central composite design. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:2704–2709
Chowdhury S, Saha PD (2011) Biosorption kinetics, thermodynamics and isosteric heat of sorption of Cu(II) onto Tamarindus indica seed powder. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 88(2):697–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.08.003
de Moraes NV, Carey M, Neville CE, Cruise S, McGuinness B, Kee F, Young IS, Woodside JV, Meharg Andrew A (2019) Water dilutes and alcohol concentrates urinary arsenic species when food is the dominant source of exposure. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00329-5
Djukic A, Jovanovic U, Tuvic T, Andric V, Novakovic JG, Ivanovic N, Matovic L (2013) The potential of ball-milled Serbian natural clay for removal of heavy metal contaminants from wastewaters: Simultaneous sorption of Ni, Cr, Cd and Pb ions. Ceram Int 39:7173–7178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.02.061
Eticha T, Hymete A (2014) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in locally produced beer to the population in Ethiopia. J Bioanal Biomed 6:065–068. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-593X.1000114
Commission E (2006) Commission regulation (EC) No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union 70:12–34
Fakhri A (2015) Investigation of mercury (II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto copper oxide nanoparticles: optimization using response surface methodology. Process Saf Environ Prot 93:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.06.003
Ghalay AE, Snow A, Kamal M (2008) Kinetics of manganese uptake by wetland plants. Am J Environ Sci 5(10):1415–1423
Ihugba UA, Nwoko CO, Tony-Njoku FR, Ojiaku AA, Izunobi L (2018) Heavy metal determination and health risk assessment of oyster mushroom Pleurotus tuberregium (Fr.) inger collected from selected markets in Imo State Nigeria. Am J Environ Prot 6:22–27. https://doi.org/10.12691/env-6-1-4
Ince M (2014) Comparision of low-cost and eco-friendly adsorbent for adsorption of Ni(II). At Spectrosc 35:223–233
Ince M, Kaplan Ince O (2019a). Heavy metal removal techniques using response surface methodology: Water/wastewater treatment [Online First], IntechOpen, https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.88915. https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/heavy-metal-removal-techniques-using-response-surface-methodology-water-wastewater-treatment
Ince M, Kaplan Ince O (2019b) Application of response surface methodological approach to optimize removal of Cr ions from industrial wastewater. At Spectrosc 40(3):91–97
Ince M, Kaplan Ince O, Asam E, Onal A (2017) Using food waste biomass as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment for Cu(II) removal. At Spectrosc 38:142–148
Kaplan Ince O, Ince M, Onal A (2018) Response surface modeling for Pb(II) removal from alcoholic beverages using natural clay: process optimization with Box–Behnken experimental design and determination by electrothermal AAS. At Spectrosc 39(6):242–250
Kaplan Ince O, Ince M, Yonten V, Goksu A (2017) A food waste utilization study for removing lead (II) from drinks. Food Chem 214:637–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.1177
Khajeh M (2012) Application of modified organo-nanoclay as the sorbent for zinc determination by FAAS: an Optimization study of an online pre-concentration system. Biol Trace Elem Res 145:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9169-8
Kishor GR, Krishna D (2013) Response surface modeling and optimization of Cu (II) removal from waste water using custard apple peel powder. Chem Eng 60:16129–16134
Kocaoba S, Orhan Y, Akyüz T (2007) Kinetics and equilibrium studies of heavy metal ions removal by use of natural zeolite. Desalination 214(1–3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.09.023
Kwon JS, Yun ST, Lee JH, Kim SO, Jo HY (2010) Removal of divalent heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions using scoria: kinetics and equilibria of sorption. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.052
Le Man H, Behera SK, Park HS (2010) Optimization of operational parameters for ethanol production from Korean food waste leachate. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326127
Mahvi AH, Naghipour D, Vaezi F, Nazmara S (2005) Teawaste as an adsorbent for heavy metal removal from industrial wastewaters. Am J Appl Sci 2:372
Omar W, Al-Itawi H (2007) Removal of Pb+2 ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on kaolinite clay. Am J Environ Sci 4(7):502–507
Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2000) Removal of toxic metals from solution by leaf, stem and root phytomass of Quercus ilex L. (holly oak). Environ Pollut 110:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00306-1
Rajic N, Stojakovic D, Jovanovic M, Logar NZ, Mazaj M, Kaucic V (2010) Removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions using the natural clinoptilolite and preparation of nano-NiO on the exhausted clinoptilolite. Appl Surf Sci 257:1524–1532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.08.090
Thirugnanasambandham K, Sivakumar V (2015) An eco-friendly approach for copper (II) ion adsorption onto cotton seed cake and its characterization: simulation and validation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 50:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.002
Turan NG, Ozgonenel O (2013) Study of montmorillonite clay for the removal of copper (II) by adsorption: Full factorial design approach and cascade forward neural network. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/342628
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng 156(1):11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.10.029
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd ed., Geneva vol 1, p 334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ince, M., Kaplan Ince, O. & Onal, A. Exposure to copper and risk assessment for human health via consumption of alcoholic beverages. J Food Sci Technol 58, 510–519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04562-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04562-8