Abstract
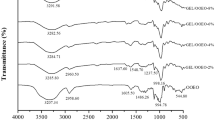
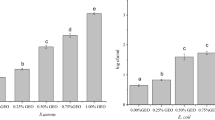
The use of natural polymers, such as gelatin and other proteins, has increased in an attempt to replace part of the consumption of petroleum-based packaging. This study evaluated the influence of green tea extract and lemon nanoemulsion on mechanical, thermal and permeability properties of gelatin matrix. The results showed that green tea increased the gelatin tensile strength (TS) from 86 ± 7 MPa to 101 ± 5 MPa, on the other hand, the nanoemulsion decreases to 78 ± 8 MPa. The incorporation of green tea and nanoemulsion enhanced the water vapor permeability of gelatin film; this could be due to the interacting with the hydrophobic domains of gelatin. This was indicated by melting point (Tm) in differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and degradation temperatures in the thermogravimetric analysis (TG), respectively. Changes in FTIR spectra of gelatin film were observed when the green tea and nanoemulsion were incorporated. Therefore, this study showed a new characterization and formulation of gelatin films incorporated by green tea extract and lemon nanoemulsion and their potential for edible film.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo-Fani A, Salvia-Trujillo L, Rojas-Graü MA, Martín-Belloso (2015) Edible films from essential-oil-loaded nanoemulsions: physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial properties. Food Hydrocoll 47:168–177
Ahmad M, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Agustini TW (2012) Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin film from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket incorporated with essential oils. Food Hydrocoll 28:189–199
Alparslan Y, Yapici HH, Metin C, Baygar T, Baygar AGT (2016) Quality assessment of shrimps preserved with orange leaf essential oil incorporated gelatin. LWT Food Sci Technol 72:457–466
Altiok D, Altiok E, Tihminlioglu F (2010) Physical, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan films incorporated with thyme oil for potential wound healing applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 21:2227–2236
Arrondo JLR, Muga A, Castresana J, Goñi FM (1993) Quantitative studies of the structure of proteins in solution by Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 59:23–56
ASTM—American Society for Testing and Materials (1980) Standard test method for water vapor transmission of materials. In: Annual Book of American Standard Testing Methods. Philadelphia, American Society for Testing and Materials, p E96-80
ASTM—American Society for Testing and Materials (1997) Standard test method for tensile properties of thin plastic sheeting. In: Annual Book of American Standard Testing Methods. Philadelphia, American Society for Testing and Materials, pp D882–D897
Atarés L, Bonilla J, Chiralt A (2010) Characterization of sodium caseinate-based edible films incorporated with cinnamon or ginger essential oils. J Food Eng 100:678–687
Barros CB, Yabiku HY, Pinto AJD (1986) Óleos essenciais cítricos especificações. Fundação Cargill, Campinas
Bigi A, Cojazzi G, Panzavolta S, Rubini K, Roveri N (2001) Mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin at different degrees of glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Biomater 22:763–768
Chen X, Jia Y, Feng L, Sun S, An L (2009) Numerical simulation of coil–helix transition processes of gelatin. Polymer 50:2181–2189
Cozmuta AM, Turila A, Apjok R, Ciocian A, Cozmuta LM, Peter A, Nicula C, Galic N, Benkovic T (2015) Preparation and characterization of improved gelatin films incorporating hemp and sage oils. Food Hydrocoll 49:144–155
Donsí F, Ferrari G (2016) Essential oil nanoemulsions as antimicrobial agents in food. J Biotechnol 233:106–120
Duhoranimana E, Karangwa E, Lai L, Xu X, Yu J, Xia S, Zhang X, Muhoza B, Habinshuti I (2017) Effect of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose on complex coacervates formation with gelatin: Coacervates characterization, stabilization and formation mechanism. Food Hydrocoll 69:111–120
Giménez B, Moreno S, López-Caballero ME, Montero P, Gómez-Guillén MC (2013) Antioxidant properties of green tea extract incorporated to fish gelatin films after simulated gastrointestinal enzymatic digestion. LWT - Food Sci Technol 53:445–451
Gómez-Estaca J, López de Lacey A, López-Caballero M, Gómez-Guillén MC, Montero P (2010) Biodegradable gelatin chitosan films incorporated with essential oils as antimicrobial agents for fish preservation. Food Microbiol 27:889–896
Gómez-Guillén MC, Ihl M, Bifani V, Silva A, Montero P (2007) Edible films made from tuna-fish gelatin with antioxidant extracts of two different murta ecotypes leaves (Ugni molinae Turcz). Food Hydrocoll 21:1133–1143
Gómez-Guillén MC, Pérez-Mateos M, Gómez-Estaca J, López-Caballero E, Giménez B, Montero P (2009) Fish gelatin: a renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends in Food Sci Technol 20:3–16
Gontard N, Duchez C, Cuq JL, Guilbert S (1994) Edible composite films of wheat gluten and lipids: water vapour permeability and other physical properties. Int J Food Sci Technol 29:39–50
Guerrero P, Nur Hanani ZA, Kerry JP, de la Caba K (2011) Characterization of soy protein-based films prepared with acids and oils by compression. J Food Eng 107:41–49
Hong YH, Lim GO, Song KB (2009) Physical properties of Gelidium corneum–gelatin blend films containing grapefruit seed extract or green tea extract and its application in the packaging of Pork Loins. J Food Sci 74:6–10
Hoque MS, Benjakul S, Prodpran T (2011a) Properties of film from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin gelatin incorporated with cinnamon, clove and star anise extracts. Food Hydrocoll 25:1085–1097
Hoque MS, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Songtipya P (2011b) Properties of blend film based on cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin gelatin and mungbean protein isolate. Int J Biol Macromol 49:663–673
Jayaramudu T, Varaprasad K, Kim HC, Kafy A, Kim JW, Kim J (2017) Calcinated tea and cellulose composite films and its dielectric and lead adsorption properties. Carbohyd Polym 171:183–192
Kavoosi G, Rahmatollahi A, Dadfar SMM, Purfard A (2014) Effects of essential oil on the water binding capacity, physico-mechanical properties, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of gelatin films. LWT Food Sci Technol 57:556–561
Kumari M, Mahajan H, Joshi R, Gupta M (2017) Development and structural characterization of edible films for improving fruit quality. Food Packag Shelf Life 12:42–50
Liu F, Chiou BS, Avena-Bustillos RJ, Zhang Y, Li Y, McHugh TH, Zhong F (2017) Study of combined effects of glycerol and transglutaminase on properties of gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll 65:1–9
McHugh TH, Avena-Bustillos FL, Krochta JM (1993) Hydrophilic edible films: modified procedure for water vapor permeability and explanation of thickness effects. J Food Sci 58:899–903
Muriel-Galet V, Cran MJ, Bigger SW, Hernández-Muñoz P, Gavara R (2015) Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer films based on the release of oregano essential oil and green tea extract components. J Food Eng 149:9–16
Nunes JC, Melo PTS, Aouada FA, de Moura MR (2018) Influência da nanoemulsão de óleo essencial de limão em filmes à base de gelatina. Quim Nova 41:1006–1010
Nur Hanani ZA, Roos YH, Kerry JP (2014) Use and application of gelatin as potential biodegradable packaging materials for food products. Int J Biol Macromol 71:94–102
Otoni CG, de Moura MR, Aouada FA, Camilloto GP, Cruz RS, Lorevice MV, Soares NF, Mattoso LHC (2014) Antimicrobial and physical-mechanical properties of pectin/papaya puree/cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion edible composite films. Food Hydrocoll 41:188–194
Peng Y, Wu Y, Li Y (2013) Development of tea extracts and chitosan composite films for active packaging materials. Int J Biol Macromol 59:282–289
Rojas-Graü MA, Avena-Bustillos RJ, Olsen C, Friedman M, Henika PR, Martín-Belloso O, Pan Z, McHugh TH (2007) Effects of plant essential oils and oil compounds on mechanical, barrier and antimicrobial properties of alginate–apple puree edible films. J Food Eng 81:634–641
Sahraee S, Milani JM, Ghanbarzadeh B, Hamishehkar H (2017) Physicochemical and antifungal properties of bio-nanocomposite film based on gelatin-chitin nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 97:373–381
Silvertein RM, Webster FX, Kiemle DJ (2006) Identificação Espectrométrica de Compostos Orgânicos. LTC, Rio de Janeiro
Siripatrawan U, Harte BR (2010) Physical properties and antioxidant activity of an active film from chitosan incorporated with green tea extract. Food Hydrocoll 24:770–775
Steyaert I, Rahier H, Vlierberghe SV, Olijve J, de Clerck K (2016) Gelatin nanofibers: analysis of triple helix dissociation temperature and cold-water. Food Hydrocoll 57:200–208
Tongnuanchan P, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Nilsuwan K (2015) Emulsion film based on fish skin gelatin and palm oil: physical, structural and thermal properties. Food Hydrocoll 48:248–259
Vanin FM, Hirano MH, Carvalho RA, Moraes ICF, Bittante AMQB, Sobral PJA (2014) Development of active gelatin-based nanocomposite films produced in an automatic spreader. Food Res Int 63:16–24
Wrona M, Cran MJ, Nerín C, Bigger SW (2017) Development and characterisation of HPMC films containing PLA nanoparticles loaded with green tea extract for food packaging applications. Carbohydr Polym 156:108–117
Wu J, Chen S, Ge S, Miao J, Li J, Zhang Q (2013) Preparation, properties and antioxidant activity of an active film from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) skin gelatin incorporated with green tea extract. Food Hydrocoll 32:42–51
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. 2019. Grant 2019/06170-1 and 2013/07296-2 CEPID, São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP). The authors are thankful to Embrapa Instrumentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunes, J.C., Melo, P.T.S., Lorevice, M.V. et al. Effect of green tea extract on gelatin-based films incorporated with lemon essential oil. J Food Sci Technol 58, 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04469-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04469-4