Abstract
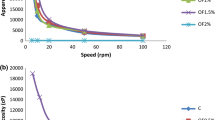
Fermented whey-based beverages were elaborated using commercial probiotics cultures (CHR HANSEN): BCT-1®, ABT-4®, ABC where A: Lactobacillus acidophilus, B: Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis, C: Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei and T: Streptococccus thermophiles. Three treatments were prepared with these probiotics cultures and a treatment without cultures added as a control. All beverage were maintained at 4 °C and evaluated during their shelf life at 0, 7, 14 and 21 days. The variables analyzed were peptide concentration, proteolysis, ACE-inhibitory activity and, peptide and aromatic amino acid profiles. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to assess the relationship between these variables. All whey-based fermented beverages added with probiotics presented ACE inhibitory activity (22–100%). However, whey-based beverage without probiotics added had the highest ACE inhibitory activity (100%), and it was maintained during its shelf life. Fermented beverage with ABT-4® culture had an ACE inhibitory activity from 80 to 100% during its shelf life. Thus can be attributed to the release of peptides during processing. Meanwhile, significative correlations were observed between variables varying this depending on the treatment, both, in magnitude and in direct or inverse direction (0.684–0.986). The ACE inhibitory activity was correlated to proteolysis and peptide and aromatic amino acids profiles. And, the IC50 was observed in the range of 0.01–0.055 mg/mL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JE, Park SY, Atwa A, Gibbs BF, Lee BH (2009) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from whey fermented by Lactobacillus species. J Food Biochem 33:589–602
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochem 72:248–254
Castro WF, Cunha TM, Ogliari PJ, Teófilo RF, Ferreira MMC, Prudencio ES (2009) Influence of different content of cheese whey and oligofructose on the properties of fermented lactic beverages: study using response surface methodology. LWT-Food Sci Technol 42:993–997
Chandan RC, Kilara A (2013) Manufacturing Yogurt and Fermented Milks, Second Edition. John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter DH, Catignani GL (1983) Department of food science spectrophotometric assay using O-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J Dairy Sci 66:1219–1227
Costa EL, Rocha JA, Netto F (2007) Effect of heat and enzymatic treatment on the antihypertensive activity of whey protein hydrolysates. Int Dairy J 17:632–640
Devries M, Phillips SM (2015) Supplemental protein in support of muscle mass and health: advantage whey. J Food Sci 80:A8–A15
Donkor ON, Henriksson A, Singh TK, Vasiljevic T, Shah NP (2007) ACE-inhibitory activity of probiotic yoghurt. Int Dairy J 17:1321–1331
Dullius A, Goettert MI, Volken de Souza CF (2018) Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods – Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J Funct Foods 42:58–74
Dziuba M, Dziuba B, Iwaniak A (2009) Milk proteins as precursors of bioactive peptides. Acta Scientiarium Polunorum Technología Alimententaria 8:71–90
FitzGerald RJ, Murray BA, Walsh DJ (2004) The emerging role of dairy proteins and bioactive: peptides in nutrition and health. J Nutr 134:980S–988S
Ghassem M, Arihara K, Babji AS, Said M, Ibrahim S (2011) Purification and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from Haruan (Channa striatus) myofibrillar protein hydrolysate using HPLC–ESI-TOF MS/MS. Food Chem 129:1770–1777
Hajirostamloo B (2010) Bioactive component in milk and dairy product. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 72:162c166
Khalesi S, Bellissimo N, Vandelanotte C, Williams S, Stanley D, Irwin C (2019) A review of probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: helpful or hype? Eur J Clin Nutr 73:24–37
Martínez AO, Martínez VME (2006) Proteínas y péptidos en nutrición enteral. Nutrición Hospitalaria 21:1–14
Miguel M, Manso M, Aleixandre A, Alonso MJ, Salaices M, López-Fandiño R (2007) Vascular effects, angiotensin i-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity, and antihypertensive properties of peptides derived from egg white. J Agricul Food Chem 55:10615–10621
Minervini F, Bilancia MA, Siragusa S, Gobbetti M, Caponio F (2009) Fermented goats’ milk produced with selected multiple starters as a potentially functional food. Food Microbiol 26:559–564
Ngarize S, Herman H, Adams A, Howell N (2004) Comparison of changes in the secondary structure of unheated, heated, and high-pressure-treated β-lactoglobulin and ovalbumin proteins using Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy and self-deconvolution. J Agric Food Chem 52:6470–6477
Nielsen MS, Martinussen T, Flambard B, Sorensen KI, Otte J (2009) Peptide profiles and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of fermented milk products: Effect of bacterial strain, fermentation pH, and storage time. Int Dairy J 19:155–165
Otte J, Lenhard T, Flambard B, Sorensen KI (2011) Influence of fermentation temperature and autolysis on ACE-inhibitory activity and peptide profiles of milk fermented by selected strains of Lactobacillus helveticus and Lactococcus lactis. Int Dairy J 21:229–238
Pandey M, Kapila S, Kapila R, Trivedi R, Karvande A (2018) Evaluation of the osteoprotective potential of whey derived-antioxidative (YVEEL) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory (YLLF) bioactive peptides in ovariectomized rats. Food Function 9:4791–4801
Park YW (2009) Bioactive Components in Milk and Dairy Products. Athenas Georgia USA Wiley-Blackwell p 396
Patidar SK, Prajapati JB (1998) Standardisation and evaluation of lassi prepared using Lactobacillus acidophilus and Streptococcus thermophilus. J Food Sci Technol 35:428–431
Plaisancié P, Claustre J, Estienne M, Henry G, Boutrou R, Paquet A, Léoni I (2013) A novel bioactive peptide from yoghurts modulates expression of the gel-forming MUC2 mucin as well as population of goblet cells and paneth cells along the small intestine. J Nutr Biochem 24:213–221
Pritchard SR, Phillips M, Kailasapathy K (2010) Identification of bioactive peptides in commercial Cheddar cheese. Food Res Int 43:1545–1548
Puchalska P, García MC, Marina ML (2014) Identification of native angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in commercial soybean based infant formulas using HPLC-Q-ToF-MS. Food Chem 157:62–69
Quirós A, Hernández-Ledesma B, Ramos M, Amigo L, Recio I (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of peptides derived from caprine kefir. J Dairy Sci 88:3480–3487
Qureshi TM, Vegarud GE, Abrahamsen RK, Skeie S (2013) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity of the Norwegian autochthonous cheeses Gamalost and Norvegia after in vitro human gastrointestinal digestion. J Dairy Sci 96:838–853
Regazzo D, Dalt LT, Lombardi A, Andrighetto C, Negro A, Gabai G (2010) Fermented milks from Enterococcus faecalis TH563 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus LA2 manifest different degrees of ACE-inhibitory and immunomodulatory activities. Dairy Sci Technol 90:469–476
Ribeiro J, Tamanini R, Oliveira ALM, Alfieri A, Beloti V (2018) Genetic diversity of thermoduric spoilage microorganisms of milk from Brazilian dairy farms. J Dairy Sci 101:6927–6936
Rodríguez-Figueroa JC, González-Córdova AF, Torres-Llanez MJ, García HS, Vallejo-Córdoba B (2012) Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides produced in fermented milk by specific wild Lactococcus lactis strains. J Dairy Sci 95:5536–5543
Salvador A, Fiszman SM (2004) Textural and sensory characteristic of whole and skimmed flavoured set – type yogurt during long storage. J Dairy Sci 87:4033–4404
Shahidi F, Zhong Y (2008) Bioactive peptides. J AOAC Int 91:914–931
Sanlidere HA, Oner Z (2011) Determination of antioxidant activity of bioactive peptide fractions obtained from yogurt. J Dairy Sci 94:5305–5314
SAS Statistical Analysis System (2006) Version 9.1.3 for Windows SAS Institute Inc. Cary NC
Serra M, Trujillo AJ, Guamis B, Ferragut V (2009) Proteolysis of yogurts made from ultra-high-pressure homogenized milk during cold storage. J Dairy Sci 92:71–78
Smit G, Smit B, Engels W (2005) Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:591–610
Tu M, Wang C, Chen C, Zhang R, Liu H, Lu W, Jiang L, Du M (2018) Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem 256:98–104
Vermeirssen V, Van Camp J, Decroos K, Van Wijmelbeke L, Verstraete W (2003) The impact of fermentation and in vitro digestion on the formation of angiotensin-i-converting enzyme inhibitory activity from pea and whey protein. J Dairy Sci 86:429–438
Walsh C, Meade J, McGill K, Fanning S (2012) The biodiversity of thermoduric bacteria isolated from whey. J Food Safety 32:255–261
Acknowledgements
The author Gabriela Rodríguez-Hernández gratefully acknowledges the National Council of Science and Technology of México (CONACYT) for the award of the D. Ph studentship that made possible to conduct this work. And, author America Chávez-Martinez is grateful to the Program for the Professional Development of Teachers of Mexico (PRODEP) for the financing of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Ethic statement
This research did not include any human subjects and animal experiments.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Hernández, G., Rentería-Monterrubio, A., Gutiérrez-Méndez, N. et al. Effect of probiotic cultures on the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activity of whey-based fermented beverages. J Food Sci Technol 57, 3731–3738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04405-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04405-6