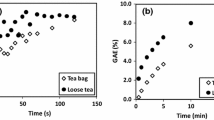
Abstract
The infusion kinetics of tea bags containing black tea or green tea has been studied in detail in the past. However, the tea bag papers have never been characterized and evaluated earlier to understand their contribution towards tea bag infusion. In the present work, papers used for making tea bags were characterized for thickness, wettability, surface topography, pore size, porosity and permeance to understand their influence on infusion kinetics of tea bags. Scanning electron microscopy studies highlighted the pore structure and porous nature of tea bag papers. The porosity of tea bag paper was quantified using image processing and permeance was determined experimentally. Besides, a relationship between porosity and permeance of tea bag papers has been perceived. A general trend of increase in permeance with increasing porosity was observed. Woven nylon paper showed the highest permeance (23.9 × 10−5 m/s) when compared with other tea bag papers. Furthermore, an initial infusion rate was determined using initial infusion data of tea bag infusion for different tea bag papers. The influence of permeance on the initial infusion rate of tea bag papers has also been investigated.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\overline{{P}_{M}}\) :
-
Permeance (m/s)
- \(\overline{A}\) :
-
Average pore area (m2)
- A:
-
Area of the tea bag paper (m2)
- a:
-
Cross-sectional area of the sample (m2)
- \(\hbox{C}_{1}^{\prime }\) :
-
Concentrations of solute at feed and paper interface (kg/m3)
- \(\hbox{C}_{2}^{\prime }\) :
-
Concentrations of solute at paper and permeate interface (kg/m3)
- C0 :
-
Concentration of solute (kg/m3) at time t = 0
- C1 :
-
Feed phase concentration of the diffusing solute (kg/m3)
- C2 :
-
Permeate phase concentration of solute (kg/m3)
- DM :
-
Tea bag diffusivity (m2/s)
- D:
-
Average pore size
- F:
-
Force (N)
- g:
-
Gravitational constant (m/s2)
- h:
-
Immersion depth (m)
- P:
-
Wetted perimeter of the sample (m)
- k1 :
-
Mass transfer coefficient in feed liquid phase (m/s)
- k2 :
-
Mass transfer coefficient in permeate liquid phase (m/s)
- l M :
-
Thickness of TB paper (m)
- NA :
-
Flux of solute gallic acid (kg/m2 s)
- V:
-
Volume of feed and permeate (m3)
- θ:
-
Contact angle (°)
- γ:
-
Surface tension (N/m)
- ρ :
-
Density of fluid (kg/m3)
References
Astill C, Birch MR, Dacombe C, Humphrey PG, Martin PT (2001) Factors affecting the caffeine and polyphenol contents of black and green tea infusions. J Agric Food Chem 49:5340–5347. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010759+
Dhekne PP, Patwardhan AW (2020) Mathematical modeling of tea bag infusion kinetics. J Food Eng 274:109847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.109847
El-newehy MH, Al-deyab SS, Kenawy E, Abdel-megeed A (2011) Nanospider technology for the production of nylon-6 nanofibers for biomedical applications. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/626589
Farakte RA, Yadav G, Joshi B, Patwadhan AW, Singh G (2016) Role of particle size in tea infusion process. Int J Food Eng 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2015-0213
Harbowy ME, Balentine DA (1997) Tea chemistry. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16(5):415–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689709701956
Jaganyi D, Mdletshe S (2000) Kinetics of tea infusion. Part 2: the effect of tea-bag material on the rate and temperature dependence of caffeine extraction from black Assam tea. Food Chem 70:163–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00262-9
Jaganyi D, Ndlovu T (2001) Kinetics of tea infusion. Part 3: the effect of tea bag size and shape on the rate of caffeine extraction from Ceylon orange pekoe tea. Food Chem 75:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00186-8
Joshi BS, Farakte RA, Yadav GU, Patwardhan AW, Singh G (2016) Swelling kinetics of tea in hot water. J Food Sci Technol 53:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2023-9
Kwiatkowski P, Giedrys-kalemba S, Mizielińska M, Bartkowiak A (2016) Modification of PLA foil surface by ethylcellulose and essential oils. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 07:440–444. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2016.5.5.440-444
Ma S, Morrow NR (1996) Relationships between porosity and permeability for porous rocks. In: International symposium of the society of core analysts, pp 8–10
Mofokeng JP, Luyt AS, Tábi T, Kovács J (2012) Comparison of injection moulded, natural fibre-reinforced composites with PP and PLA as matrices. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 25:927–948. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705711423291
Oldani M, Schock G (1989) Characterization of ultrafiltration membranes by infrared spectroscopy, ESCA, and contact angle measurements. J Membr Sci 43:243–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)85101-7
Price WE, Spiro M (1985) Kinetics and equilibria of tea infusion: theaflavin and caffeine concentrations and partition constants in several whole teas and sieved fractions. J Sci Food Agric 36:1303–1308. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740361215
Price WE, Spitzer JC (1993) The temperature dependence of the rate of extraction of soluble constituents of black tea. Food Chem 46:133–136
Son J, Gardner DJ (2007) Dimensional stability measurements of thin wood veneers using the Wilhelmy plate technique. Wood Fiber Sci 36(1):98–106
Spiro M, Jaganyi D (2000) Kinetics and equilibria of tea infusion, Part 15. Transport of caffeine across a teabag membrane in a modified rotating diffusion cell. Food Chem 69:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00251-4
Spiro M, Jaganyi D, Broom MC (1992) Kinetics and equilibria of tea infusion: Part 9. The rates and temperature coefficients of caffeine extraction from green Chun Mee and black Assam Bukial teas. Food Chem 45:333–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-8146(92)90033-X
Suteerapataranon S, Butsoongnern J, Punturat P, Jorpalit W, Thanomsilp C (2009) Caffeine in Chiang Rai tea infusions: effects of tea variety, type, leaf form, and infusion conditions. Food Chem 114:1335–1338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.013
UK Tea & Infusions Association (2010) The history of the tea bag. UK Tea & Infusions Association, London
Yadav GU, Joshi BS, Patwardhan AW, Singh G (2017) Swelling and infusion of tea in tea bags. J Food Sci Technol 54:2474–2484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2690-9
Yeng LC, Wahit MU, Othman N (2015) Thermal and flexural properties of regenerated cellulose (RC)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) biocomposites. J Teknol 75:107–112. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v75.5338
Yuan Y, Lee TR (2013) Contact angle and wetting properties. In: Bracco G, Holst B (eds) Surface science techniques. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–34
Acknowledgements
One of the authors Pallavee P. Dhekne would like to thank the Pidilite Industries Ltd. for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, D.K., Dhekne, P.P. & Patwardhan, A.W. Characterization and evaluation of tea bag papers. J Food Sci Technol 57, 3060–3070 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04339-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04339-z