Abstract
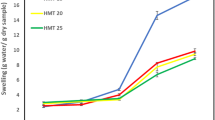
Native buckwheat starch was extracted and modified by heat-moisture treatment (HMT) with different treatment time (15, 30 and 45 min) to investigate its effect on physicochemical, morphological, functional properties, starch profile (rapidly digestible starch, RDS; slowly digestible starch, SDS and resistant starch, RS fractions) and expected glycemic index (eGI). Results revealed that with increasing time duration of HMT from 15 to 45 min, amylose content, pasting temperature and thermostability increased substantially whereas swelling power, solubility and viscosity parameters decreased. The SEM micrographs showed that HMT caused fissures in the granule and surface indentation. HMT-45 (starch treated for 45 min) had the lowest RDS content (29.33%) and the highest SDS (51.30%) and RS (8.21%) levels. The decreased hydrolysis rate, high amylose and RS content of HMT-45 resulted in a significant decrease in estimated glycemic index (eGI) values from 51.49% (Native) to 44.16% (HMT-45) thus indicating its role in prevention of non-insulin- dependent diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale KO, Henle T, Schwarzenbolz U, Doert T (2009) Modification and properties of African yam bean (Sphenostylis stenocarpa Hochst. Ex A. Rich.) Harms starch I: heat moisture treatments and annealing. Food Hydrocoll 23:1947–1957
AOAC (2012) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
BeMiller JN, Huber KC (2015) Physical modification of food starch functionalities. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 6:19–69
Chung HJ, Liu Q, Hoover R (2009) Impact of annealing and heat-moisture treatment on rapidly digestible, slowly digestible and resistant starch levels in native and gelatinized corn, pea and lentil starches. Carbohydr Polym 75:436–447
Englyst HN, Kingman SM, Cummings JH (1992) Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur J Clin Nutr 46:33–50
Goni I, Garcia-Alonso A, Saura-Calixto F (1997) A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr Res 17:427–437
Gunaratne A, Hoover R (2002) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches. Carbohydr Polym 49:425–437
Hoover R (2001) Composition, molecular structure and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches—a review. Carbohydr Polym 45:253–267
Hoover R, Manuel H (1996) Effect of heat- moisture treatment on structure and physicochemical properties of legume starches. Food Res Int 29:731–750
Hormdok R, Noomhorn A (2007) Hydrothermal treatment of rice starch for improvement of rice noodle quality. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:1723–1731
Jenkins D, Wolever T, Buckley G, Lam K, Giudici S, Kalmusky J (1988) Low glycemic index starchy foods in the diabetic diet. Amer J Clin Nutr 48(2):248–254
Jiranuntakul W, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V, Puncha-arnon S, Uttapap D (2011) Microstructural and physicochemical properties of heat-moisture treated waxy and normal starches. J Food Engg 104:246–258
Khunae P, Tran T, Sirivongpaisal P (2007) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on structural and thermal properties of rice starches differing in amylose content. Starch–Starke 59:593–599
Leach HW, Mccowen LD, Sohoch TJ (1959) Structure of the starch granule I. Swelling and solubility pattern of various starches. Cereal Chem 36:534–544
Liu H, Guo X, Li W, Wang X, Lv M, Peng Q, Wang M (2015) Changes in physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of common buckwheat starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing. Carbohydr Polym 132:237–244
Liu H, Guo X, Li Y, Li H, Fan H, Wang M (2016) In vitro digestibility and changes in physicochemical and textural properties of tartary buckwheat starch under high hydrostatic pressure. J Food Engg 189:64–71
Lorenz K, Kulp K (1982) Cereal and root starch modification by heat moisture treatment. I. Physicochemical properties. Starch/Starke 34:50–54
Majzoobi M, Roushan F, Kadivar M, Farahnaky A, Seifzadeh N (2017) Effects of heat-moisture treatment on physicochemical properties of wheat starch. Iran Agric Res 36:1–6
Medcalf DG, Gilles KA (1965) Wheat starch. I. Comparison of physicochemical properties. Cereal Chem 42:558–568
Miyoshi E (2002) Effects of heat-moisture treatment and lipids on gelatinization and retrogradation of maize and potato starches. Cereal Chem 79:72–77
Oh HE, Hemar Y, Anema SG, Wong M, Pinder DN (2008) Effect of high-pressure treatment on normal rice and waxy rice starch-in-water suspensions. Carbohydr Polym 73(2):332–343
Palma-Rodriguez HM, Agama-Acevedo E, Mendez-Montealvo G, Gonzalez-Soto RA, Vernon-Carter EJ, Bello-Pérez LA (2012) Effect of acid treatment on the physicochemical and structural characteristics of starches from different botanical sources. Starch–Starke 64:115–125
Qian J, Rayas-Duarte P, Grant L (1998) Partial characterization of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) starch. Cereal Chem 75:365–373
Qingjie S, Tao W, Liu X, Yunxia Z (2013) The effect of heat moisture treatment on physicochemical properties of early indica rice. Food Chem 141:853–857
Rungarun H, Athapol N (2007) Hydrothermal treatments of rice starch for improvement of rice noodle quality. LWT - Food Sci Technol 40:1723–1731
Rutenberg MW, Solarek D (1984) Starch derivatives: production and uses. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN, Paschall EF (eds) Starch: chemistry and technology. Academic Press, London
Sajilata MG, Singhal RS (2005) Specialty starches for snack foods. Carbohydr Polym 59:131–151
Singh N, Sandhu KS, Kaur M (2004) Characterization of starches separated from Indian chickpea (Cicer arietinum) cultivars. J Food Engg 63:441–449
Snow P, O’Dea K (1981) Factor affecting the rate of hydrolysis of starch in food. Am J Clin Nutr 43:2721–2727
Sowbhagya CM, Bhattacharya KR (1979) Simplified determination of amylose in milled rice. Starch–Starke 31:159–163
Subramanian V, Hoseney RC, Bramel-Cox P (1994) Shear thinning properties of sorghum and corn starches. Cereal Chem 71:272–275
Sun Q, Han Z, Wang L, Xiong L (2014) Physicochemical differences between sorghum starch and sorghum flour modified by heat-moisture treatment. Food Chem 145:756–764
Tester RF, Morrison WR (1990) Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. I. Effects of amylopectin, amylase and lipids. Cereal Chem 67:551–557
Tsakama M, Mwangwela AM, Manani TA, Mahungu NM (2011) Effect of heat moisture treatment on physicochemical and pasting properties of starch extracted from eleven sweet potato varieties. Int J Agric Sci Soil Sci 1:254–260
Zavareze EDR, Dias ARG (2011) Impact of heat-moisture treatment and annealing in starches: a review. Carbohydr Polym 83:317–328
Zhang J, Chen F, Liu F, Wang Z (2010) Study on structural changes of microwave heat-moisture treated resistant Canna edulis Ker starch during digestion in vitro. Food Hydrocoll 24:27–34
Acknowledgements
The author, Charu Goel acknowledge Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, India, for awarding doctoral fellowship under the INSPIRE fellowship programme. The authors sincerely thank Director, DFRL for providing all the necessary facilities for carrying out the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, C., Semwal, A.D., Khan, A. et al. Physical modification of starch: changes in glycemic index, starch fractions, physicochemical and functional properties of heat-moisture treated buckwheat starch. J Food Sci Technol 57, 2941–2948 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04326-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04326-4