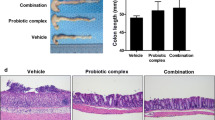
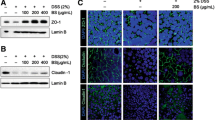
Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease, a typical chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, make up a growing share of the global disease burden. This study firstly evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of corn protein hydrolysate (CPH) using a cell model of tumor cell necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced inflammation and a mouse model of colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate. CPH digests significantly inhibited the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase, and reduced the secretion of interleukin-8 in TNF-α-induced inflammation in Caco-2 cells. In mice, CPH digests significantly improved the body weight loss, clinical scores, shortening of the colon and histological symptoms, and decreased the myeloperoxidase activity, and down regulated the expression of TNF-α, and interleukin-6 in the colon. The above results indicate that the CPH can potentially be used as a health food/nutraceutical for the treatment/management of intestinal inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakrabarti S, Jahandideh F, Wu J (2014) Food-derived bioactive peptides on inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/608979
Chen Y, Patel A, Meier PP, Fantuzzi G (2018) Digested early preterm human milk suppresses tumor necrosis factor–induced inflammation and cytotoxicity in intestinal epithelial cells. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 66(6):1. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001932
Daig R, Andus T, Aschenbrenner E, Falk W, SchöLmerich J, Gross V (1996) Increased interleukin 8 expression in the colon mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 38(2):216–222. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.38.2.216
Fernández-Tomé S, Sanchón J, Recio I, Hernández-Ledesma B (2017) Transepithelial transport of lunasin and derived peptides: inhibitory effects on the gastrointestinal cancer cells viability. J Food Compos Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2017.01.011
Gismera CS, Aladrén BS (2008) Inflammatory bowel diseases: a disease(s) of modern times? Is incidence still increasing? World J Gastroenterol 14(36):5491–5498. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5491
Guo H, Sun J, He H, Yu G-C, Du J (2009) Antihepatotoxic effect of corn peptides against Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 47(10):2431–2435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.06.041
Huang H-L, Liu C-T, Chou M-C, Ko C-H, Wang C-K (2015) Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit extracts improve colon microflora and exert anti-inflammatory activities in Caco-2 cells. J Med Food 18(6):663–676. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2014.3213
Kim JM, Whang JH, Kim KM, Koh JH, Suh HJ (2004) Preparation of corn gluten hydrolysate with angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory activity and its solubility and moisture sorption. Process Biochem 39(8):989–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00205-X
Kühl AA, Erben U, Kredel LI, Siegmund B (2015) Diversity of intestinal macrophages in inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Immunol 6:613. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00613
Lee M, Kovacs-Nolan J, Archbold T, Fan MZ, Juneja LR, Okubo T, Mine Y (2009) Therapeutic potential of hen egg white peptides for the treatment of intestinal inflammation. J Funct Foods 1(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2009.01.005
Liang QF, Ren XF, Ma HL, Li SY, Xu KK, Oladejo AO (2017) Effect of low-frequency ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of corn protein hydrolysates. J Food Qual. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2784146
Liang Q, Chalamaiah M, Ren X, Ma H, Wu J (2018) Identification of new anti-inflammatory peptides from zein hydrolysate after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and transport in caco-2 cells. J Agric Food Chem 66(5):1114. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04562
Majumder K, Mine Y, Wu J (2016) The potential of food protein-derived anti-inflammatory peptides against various chronic inflammatory diseases. J Sci Food Agric 96(7):2303–2311. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7600
Mantovani A, Muzio M, Garlanda C, Sozzani S, Allavena P (2001) Macrophage control of inflammation: negative pathways of regulation of inflammatory cytokines. Wiley, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470868678.ch8
Etchevers JM, Aceituno M, Sans M (2008) Are we giving azathioprine too late? The case for early immunomodulation in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 14(36):5512. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5512
Meram C, Wu J (2017) Anti-inflammatory effects of egg yolk livetins (alpha, beta, and gamma-livetin) fraction and its enzymatic hydrolysates in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Res Int 100(Pt 1):449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.032
Mine Y, Zhang H (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of poly-l-lysine in intestinal mucosal system mediated by calcium-sensing receptor activation. J Agric Food Chem 63(48):10437–10447. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03812
Mochizuki M, Shigemura H, Hasegawa N (2010) Anti-inflammatory effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of corn gluten in an experimental model of colitis. J Pharm Pharmacol 62(3):389–392. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.62.03.0015
Olamilosoye KP, Akomolafe RO, Akinsomisoye OS, Adefisayo MA, Alabi QK (2018) The aqueous extract of Ocimum gratissimum leaves ameliorates acetic acid-induced colitis via improving antioxidant status and hematological parameters in male Wistar rats. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2018.05.006
Puneet Kaur R, Kavinder S, Nirmal S, Amteshwar Singh J (2014) A review on chemical-induced inflammatory bowel disease models in rodents. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Off J Korean Physiol Soc Korean Soc Pharmacol 18(4):279. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.4.279
Rao CV (2004) Nitric oxide signalling in colon cancer chemoprevention. Mutat ResFundam Mol Mech Mutagenesis 555(1):107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.05.022
Ren X, Liang Q, Zhang X, Hou T, Li S, Ma H (2018) Stability and antioxidant activities of corn protein hydrolysates under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Cereal Chem 95(6):760–769. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10092
Rodriguez-Ramiro I, Ramos S, Lopez-Oliva E, Agis-Torres A, Bravo L, Goya L, Martin MA (2013) Cocoa polyphenols prevent inflammation in the colon of azoxymethane-treated rats and in TNF-alpha-stimulated Caco-2 cells. Br J Nutr 110(2):206–215. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512004862
Salaga M, Binienda A, Draczkowski P, Kosson P, Kordek R, Jozwiak K, Fichna J (2018) Novel peptide inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (Tyr-Pro-D-Ala-NH2) with anti-inflammatory activity in the mouse models of colitis. Peptides 108:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.08.011
Sartor RB (1994) Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: Pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology 106(2):533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(94)90614-9
Sedmak JJ, Grossberg SE (1977) A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem 79(1):544–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6
Shi Y, Rupa P, Jiang B, Mine Y (2014) Hydrolysate from eggshell membrane ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice. Int J Mol Sci 15(12):22728–22742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222728
Singer II, Kawka DW, Schloemann S, Tessner T, Riehl T, Stenson WF (1998) Cyclooxygenase 2 is induced in colonic epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 115(2):297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70196-9
Sobczak M, Fabisiak A, Murawska N, Wesołowska E, Wierzbicka P, Wlazłowski M, Wójcikowska M, Zatorski H, Zwolińska M, Fichna J (2014) Current overview of extrinsic and intrinsic factors in etiology and progression of inflammatory bowel diseases. Pharmacol Rep 66(5):766–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.04.005
Stanojevića S, Blagojevića V, Ćuruvijaa I, Veljovićb K, Bajićb SS, Kotur-Stevuljevićc J, Bogdanovićd A, Petrovića R, Vujnovića I, Kovačević-Jovanoviće V (2018) Oral treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus 64 during the early postnatal period improves the health of adult rats with TNBS-induced colitis. J Funct Foods 48:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.07.014
Tsatsanis C, Androulidaki A, Venihaki M, Margioris AN (2006) Signalling networks regulating cyclooxygenase-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38(10):1654–1661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.03.021
United States Pharmacopeial Convention Council of Experts (2007) Simulated gastric and intestinal fluids. In: TS Board of Trustees (Ed.) United States pharmacopeial convention and national formulary, United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc, Rockville, p 2728
Wada S, Sato K, Ohta R, Wada E, Bou Y, Fujiwara M, Kiyono T, Park EY, Aoi W, Takagi T, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T (2013) Ingestion of low dose pyroglutamyl leucine improves dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and intestinal microbiota in mice. J Agric Food Chem 61(37):8807–8813. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf402515a
Yamaguchi M, Nishikiori F, Ito M, Furukawa Y (1997a) The effects of corn peptide ingestion on facilitating alcohol metabolism in healthy men. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61(9):1474–1481. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.61.1474
Yamaguchi M, Takeuchi M, Ebihara K (1997b) Inhibitory effect of peptide prepared from corn gluten meal on 7, 12-dimethylbenz [a] anthracene-induced mammary tumor progression in rats. Nutr Res 17(7):1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0271-5317(97)00083-3
Young D, Ibuki M, Nakamori T, Fan M, Mine Y (2012) Soy-derived di- and tripeptides alleviate colon and ileum inflammation in pigs with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J Nutr. 142(2):363–368. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.149104
Zhao Y, Yao Y, Xu M, Wang S, Wang X, Tu Y (2017) Simulated gastrointestinal digest from preserved egg white exerts anti-inflammatory effects on Caco-2 cells and a mouse model of DSS-induced colitis. J Funct Foods 35:655–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.06.028
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their appreciation for the support obtained from Grant of the Project of National 863 Plan of China (2013AA102203), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801552), Jiangsu Province Key Research and Development Program (BE2018368), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Special Funding Project (2018T110459) and Jiangsu Province Postdoctoral Science Foundation Special Funding Project (2019K114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Q., Ren, X., Chalamaiah, M. et al. Simulated gastrointestinal digests of corn protein hydrolysate alleviate inflammation in caco-2 cells and a mouse model of colitis. J Food Sci Technol 57, 2079–2088 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04242-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04242-7