Abstract
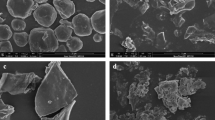
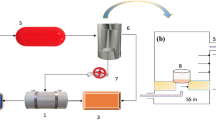
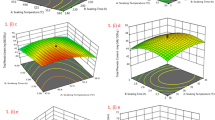
Post-harvest hydrothermal processing of grains are targeted at improving milling performances and nutritional properties. In this study, the effects of two hydrothermal processes, namely steam parboiling and soaking in boiling water for different durations on properties of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum L.) grown in the Indian Himalayan regions were assessed. Both treatments significantly improved milling yield. Changes in grain section morphology were evidenced under scanning electron microscope. Milder processing for 5 and 10 min mostly exerted annealing effect, represented by increased intensities of X-ray diffraction peaks. Starch gelatinization occurred upon prolonged processing for 15 and 20 min. This resulted in decreased crystallinity, increased sedimentation volume, paste thinning during rapid viscosity analysis and lower thermal transition in differential scanning calorimetry. Marginal changes in oil uptake suggested limited protein denaturation. Natural antioxidant compounds were variably denatured. Maillard browning was indicated by CIE L* a* b* colour and antioxidant levels. The starchy flour samples showed partial resistance to enzymatic amylolysis post retrogradation. Soaking in boiling water can be considered as a feasible alternative to conventional steam parboiling for better milling yield of buckwheat. Altered physicochemical and nutritional properties of buckwheat suggested that the hydrothermally modified flours can be used in ready to eat therapeutic food products.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarowicz R (2009) Antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 111(2):109–111
AOAC (2012) Official methods of analysis, 19th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Bhattacharjya B, Dutta H, Patwari K, Mahanta CL (2015) Properties of annealed jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) seed starch. Acta Aliment 44(4):501–510
Bhattacharya KR (2011) Rice quality: a guide to rice properties and analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Christa K, Soral-Śmietana M (2008) Buckwheat grains and buckwheat products–nutritional and prophylactic value of their components—a review. Czech J Food Sci 26(3):153–162
De Pilli T, Derossi A, Talja RA, Jouppila K, Severini C (2012) Starch–lipid complex formation during extrusion-cooking of model system (rice starch and oleic acid) and real food (rice starch and pistachio nut flour). Eur Food Res Technol 234(3):517–525
Dutta H, Mahanta CL (2014) Laboratory process development and physicochemical characterization of a low amylose and hydrothermally treated ready-to-eat rice product requiring no cooking. Food Bioproces Technol 7:212–223
Dutta H, Saikia S, Mahanta CL (2014) A preliminary investigation on bioactive potential of milling fractions of Komal chaul of Assam processed from pigmented Kola chokua paddy. Int J Sci Technol 4(3):1–9
Dutta H, Mahanta CL, Singh V (2015) Changes in the properties of rice varieties with different amylose content on dry heat parboiling. J Cereal Sci 65:227–235
Goñi I, Garcia-Diz L, Mañas E, Saura-Calixto F (1996) Analysis of resistant starch: a method for foods and food products. Food Chem 56(4):445–449
Himmelsbach DS, Manful JT, Coker RD (2008) Changes in rice with variable temperature parboiling: thermal and spectroscopic assessment. Cereal Chem 85(3):384–390
Jacobs H, Eerlingen RC, Spaepen H, Grobet PJ, Delcour JA (1997) Impact of annealing on the susceptibility of wheat, potato and pea starches to hydrolysis with pancreatin. Carbohydr Res 305(2):193–207
Lamberts L, Brijs K, Mohamed R, Verhelst N, Delcour JA (2006) Impact of browning reactions and bran pigments on color of parboiled rice. J Agric Food Chem 54(26):9924–9929
Mahanta CL, Bhattacharya KR (2010) Relationship of starch changes to puffing expansion of parboiled rice. J Food Sci Technol 47(2):182–187
Nithiyanantham S, Siddhurajua P, Francis G (2013) Proximate composition and functional properties of raw and processed Jatropha curcas L. Kernel meal. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci 4(1):183–219
O’Sullivan AC, Perez S (1999) The relationship between internal chain length of amylopectin and crystallinity in starch. Biopolym Orig Res Biomol 50(4):381–390
Pal P, Singh N, Kaur P, Kaur A (2018) Effect of parboiling on phenolic, protein, and pasting properties of rice from different paddy varieties. J Food Sci 83(11):2761–2771
Pandey S, Senthil A, Fatema K (2015) Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the nutritional and functional properties of husked and dehusked buckwheat. J Food Process Technol 6(7):461–467
Pathare PB, Opara UL, Al-Said FAJ (2013) Colour measurement and analysis in fresh and processed foods: a review. Food Bioprocess Technol 6(1):36–60
Patindol J, Newton J, Wang YJ (2008) Functional properties as affected by laboratory-scale parboiling of rough rice and brown rice. J Food Sci 73(8):E370–E377
Putseys JA, Derde LJ, Lamberts L, Ostman E, Bjorck IM, Delcour JA (2009) Functionality of short chain amylose–lipid complexes in starch—water systems and their impact on in vitro starch degradation. J Agric Food Chem 58(3):1939–1945
Qin P, Wu L, Yao Y, Ren G (2013) Changes in phytochemical compositions, antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities during the processing of tartary buckwheat tea. Food Res Int 50(2):562–567
Rockembach CT, El Halal SLM, Mesko MF, Gutkoski LC, Elias MC, de Oliveira M (2019) Morphological and physicochemical properties of rice grains submitted to rapid parboiling by microwave irradiation. LWT Food Sci Technol 103:44–52
Sarangapani C, Thirumdas R, Devi Y, Trimukhe A, Deshmukh RR, Annapure US (2016) Effect of low-pressure plasma on physico–chemical and functional properties of parboiled rice flour. LWT Food Sci Technol 69:482–489
Shin SI, Kim HJ, Ha HJ, Lee SH, Moon TW (2005) Effect of hydrothermal treatment on formation and structural characteristics of slowly digestible non-pasted granular sweet potato starch. Starch Stärke 57(9):421–430
Wang S, Copeland L (2013) Molecular disassembly of starch granules during gelatinization and its effect on starch digestibility: a review. Food Funct 4(11):1564–1580
Wang S, Li C, Copeland L, Niu Q, Wang S (2015) Starch retrogradation: a comprehensive review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 14(5):568–585
Zhang M, Chen H, Li J, Pei Y, Liang Y (2010) Antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat extracts as affected by different thermal processing methods. LWT Food Sci Technol 43(1):181–185
Zobel HF (1964) X-ray analysis of starch granules. Methods Carbohydr Chem 4:109–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, M., Dutta, H., Jaganmohan, R. et al. Effect of steam parboiling and hot soaking treatments on milling yield, physical, physicochemical, bioactive and digestibility properties of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum L.). J Food Sci Technol 56, 3524–3533 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03849-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03849-9