Abstract
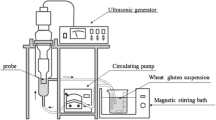
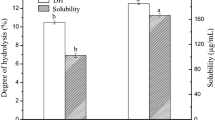
The effects of heating (90 °C/30 min) or ultrasound (200/400/600 W) treatment on antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory (ACEI) activity of hydrolysates from hempseed protein isolates (HPI) were studied. The secondary structure, surface hydrophobicity, intrinsic fluorescence, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of HPI treated by heating or ultrasound were measured. The results showed that hydrolysate from HPI treated with ultrasound at 200 W showed higher hydrolysis degree, proportion of lower molecular mass components (1.0–3.0 kDa), antioxidant and ACEI activity than those from heating or high-power treated. The changes in secondary structure, surface hydrophobicity and intrinsic fluorescence indicated the unfolding of HPI after ultrasound. The SEM results showed that HPI treated with ultrasound at 200 W exhibited decrease in particle size and deformation and further increased in power caused the aggregates of HPI. In conclusion, the ultrasound treatment at low-power was superior to 90 °C/30 min treatment in facilitating enzymatic release of antioxidant and ACEI peptides from HPI.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Nissen J (1979) Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J Agric Food Chem 27:1256
Chen L, Chen JS, Ren JY, Zhao MM (2011) Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein isolates and on the emulsifying properties of hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 59:2600–2609
Cushman DW, Cheung HS (1971) Concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme in tissues of the rat. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Enzymology 250:261–265
Dapčević-Hadnađev T, Hadnađev M, Lazaridou A, Moschakis T, Biliaderis CG (2018) Hempseed meal protein isolates prepared by different isolation techniques. Part II. gelation properties at different ionic strengths. Food Hydrocoll 81:481–489
Decker EA, Welch B (1990) Role of ferritin as a lipid oxidation catalyst in muscle food. J Agric Food Chem 38:674–677
Escudero E, Mora L, Fraser PD, Aristoy MC, Toldrá F (2013) Identification of novel antioxidant peptides generated in Spanish dry-cured ham. Food Chem 138:1282–1288
Feng X, Wu Z, Tong J, Zheng J, Chen L (2017) Effect of combination of high-intensity ultrasound treatment and dextran glycosylation on structural and interfacial properties of buckwheat protein isolates. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:1891–1898
Girgih AT, Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE (2011) In vitro antioxidant properties of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysate fractions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88:381–389
Girgih AT, Alashi AM, He R, Malomo SA, Raj P, Netticadan T, Aluko RE (2014) A novel hemp seed meal protein hydrolysate reduces oxidative stress factors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nutrients 6:5652
Girgih AT, Chao D, Lin L, He R, Jung S, Aluko RE (2015) Enzymatic protein hydrolysates from high pressure-pretreated isolated pea proteins have better antioxidant properties than similar hydrolysates produced from heat pretreatment. Food Chem 188:510–516
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Gülseren I, Güzey D, Bruce BD, Weiss J (2007) Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrason Sonochem 14:173–183
Güzey D, Gülseren İ, Bruce B, Weiss J (2006) Interfacial properties and structural conformation of thermosonicated bovine serum albumin. Food Hydrocoll 20:669–677
Hadnađev M, Dapčević-Hadnađev T, Lazaridou A, Moschakis T, Michaelidou AM, Popović S, Biliaderis CG (2018) Hempseed meal protein isolates prepared by different isolation techniques. Part I: physicochemical properties. Food Hydrocoll 79:526–533
Hartmann R, Meisel H (2007) Food-derived peptides with biological activity: from research to food applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:163–169
House JD, Neufeld J, Leson G (2010) Evaluating the quality of protein from hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) products through the use of the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score method. J Agric Food Chem 58:11801–11807
Hu H, Wu J, Zhu L, Zhang F, Xu X (2013) Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy;protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll 30:647–655
Jamdar SN, Rajalakshmi V, Pednekar MD, Juan F, Yardi V, Arun S (2010) Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ACE inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 121:178–184
Jiang L, Wang J, Li Y, Wang Z, Liang J, Wang R, Chen Y, Ma W, Qi B, Zhang M (2014) Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res Int 62:595–601
Kuda T, Ikemori T (2009) Minerals, polysaccharides and antioxidant properties of aqueous solutions obtained from macroalgal beach-casts in the Noto Peninsula, Ishikawa, Japan. Food Chem 112:575–581
Li B, Chen F, Wang X, Ji B, Wu Y (2007) Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from porcine collagen hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry. Food Chem 102:1135–1143
Li X, Da S, Li C, Xue F, Zang T (2018) Effects of high-intensity ultrasound pretreatment with different levels of power output on the antioxidant properties of alcalase hydrolyzates from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein isolate. Cereal Chem 95:518–526
Liu SC, Lin JT, Wang CK, Chen HY, Yang DJ (2009) Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts from lychee (Litchi chinenesis Sonn.) flowers. Food Chem 114:577–581
Malomo SA, Onuh JO, Girgih AT, Aluko RE (2015) Structural and antihypertensive properties of enzymatic hemp seed protein hydrolysates. Nutrients 7:7616–7632
Misra NN, Martynenko A, Chemat F, Paniwnyk L, Barba FJ, Jambrak AR (2018) Thermodynamics, transport phenomena, and electrochemistry of external field-assisted nonthermal food technologies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:1832–1863
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2012) Tryptophan-containing milk protein-derived dipeptides inhibit xanthine oxidase. Peptides 37:263–272
Pallarès I, Vendrell J, Avilés FX, Ventura S (2004) Amyloid fibril formation by a partially structured intermediate state of alpha-chymotrypsin. J Mol Biol 342:321–331
Ren Y, Liang K, Jin Y, Zhang M, Chen Y, Wu H, Lai F (2016) Identification and characterization of two novel α-glucosidase inhibitory oligopeptides from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed protein. J Funct Foods 26:439–450
Resendiz-Vazquez JA, Ulloa JA, Urías-Silvas JE, Bautista-Rosales PU, Ramírez-Ramírez JC, Rosas-Ulloa P, González-Torres L (2017) Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the technofunctional properties and structure of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed protein isolate. Ultrason Sonochem 37:436–444
Shavandi A, Hu Z, Teh SS, Zhao J, Carne A, Bekhit A, Bekhit EDA (2017) Antioxidant and functional properties of protein hydrolysates obtained from squid pen chitosan extraction effluent. Food Chem 227:194–201
Sun W, Zhou F, Sun DW, Zhao M (2013) Effect of Oxidation on the Emulsifying Properties of Myofibrillar Proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol 6:1703–1712
Sutkar VS, Gogate PR (2009) Design aspects of sonochemical reactors: techniques for understanding cavitational activity distribution and effect of operating parameters. Chem Eng J 155:26–36
Tang CH, Ten Z, Wang XS, Yang XQ (2006) Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein Isolate. J Agric Food Chem 54:8945–8950
Wang XS, Tang CH, Yang XQ, Gao WR (2008) Characterization, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) proteins. Food Chem 107:11–18
Xue F, Wu Z, Tong J, Zheng J, Li C (2017) Effect of combination of high-intensity ultrasound treatment and dextran glycosylation on structural and interfacial properties of buckwheat protein isolates. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:1891–1898
Xue F, Zhu CS, Liu F, Wang SY, Liu HZ, Li C (2018) Effects of high-intensity ultrasound treatment on functional properties of plum (Pruni domesticae semen) seed protein isolate. J Sci Food Agric 98:5690–5699
Yang X, Li Y, Li S, Oladejo AO, Ruan S, Wang Y, Huang S, Ma H (2017) Effects of ultrasound pretreatment with different frequencies and working modes on the enzymolysis and the structure characterization of rice protein. Ultrason Sonochem 38:19–28
Yikling C, Jookheng G, Yauyan L (2009) Assessment of in vitro antioxidant capacity and polyphenolic composition of selected medicinal herbs from Leguminosae family in Peninsular Malaysia. Food Chem 116:13–18
Zisu B, Lee J, Chandrapala J, Bhaskaracharya R, Palmer M, Kentish S, Ashokkumar M (2011) Effect of ultrasound on the physical and functional properties of reconstituted whey protein powders. J Dairy Res 78:226–232
Žuža MG, Milašinović NZ, Jonović MM, Jovanović JR, Kalagasidis Krušić MT, Bugarski BM, Knežević-Jugović ZD (2017) Design and characterization of alcalase—chitosan conjugates as potential biocatalysts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:1713–1723
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC31501529), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150950, BK20171066) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (035062002002A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, J., Xue, F. et al. Effects of heating or ultrasound treatment on the enzymolysis and the structure characterization of hempseed protein isolates. J Food Sci Technol 56, 3337–3346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03815-5
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03815-5