Abstract
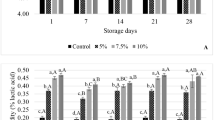
Ready-to-drink (RTD) ice tea is a ready prepared tea, produced from green and black tea originating from same plant Camellia sinensis. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of prebiotics [galacto-oligosaccharide (GOS), fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS), and inulin] or synbiotic ingredients (GOS, FOS, inulin, and Lactobacillus acidophilus) on the sensory properties and consumer acceptability of RTD. The quality of green tea extract (GTE) and black tea extract (BTE) was improved with pretreatment of cellulase and pectinase enzymes. The combined enzymatic extraction amplified total extractives up to 76% in GTE and 72% in BTE. Total polyphenol was found to be enhanced to 24% in GTE and 19% in BTE. GTE was further selected for development of RTD in two different formats; synbiotic RTD and prebiotic RTD premix and analyzed for sensory attributes (colour, aroma, taste, and acceptability). Synbiotic RTD was also evaluated for stability over a period of 28 days at 4 °C. Synbiotic RTD developed an unpleasant flavor and aroma during the shelf life. Premix format of RTD developed using spray drying was reconstituted and found to be functionally and sensorially acceptable.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasalvar C, Pelvan E, Özdemir KS, Kocadağlı T, Mogol BA, Pasli AA, Gökmen V (2013) Compositional, nutritional, and functional characteristics of instant teas produced from low and high quality black teas. J Agric Food Chem 61:7529–7536
Alegre I, Viñas I, Usall J, Anguera M, Abadias M (2011) Microbiological and physicochemical quality of fresh-cut apple enriched with the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Food Micro 28:59–66
Anesini C, Ferraro GE, Filip R (2008) Total polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of commercially available tea (Camellia sinensis) in Argentina. J Agric Food Chem 56:9225–9229
Baik JH, Shin KS, Park Y, Yu KW, Suh HJ, Choi HS (2015) Biotransformation of catechin and extraction of active polysaccharide from green tea leaves via simultaneous treatment with tannase and pectinase. J Sci Food Agric 95:2337–2344
Bakker-Zierikzee AM, Alles MS, Knol J, Kok FJ, Tolboom JJ, Bindels JG (2005) Effects of infant formula containing a mixture of galacto-and fructo-oligosaccharides or viable Bifidobacterium animalis on the intestinal microflora during the first 4 months of life. Br J Nutr 94:783–790
Barberousse H, Kamoun A, Chaabouni M, Giet JM, Roiseux O, Paquot M, Blecker C (2009) Optimization of enzymatic extraction of ferulic acid from wheat bran, using response surface methodology, and characterization of the resulting fractions. J Sci Food Agric 89:1634–1641
Cardona F, Andrés-Lacueva C, Tulipani S, Tinahones FJ, Queipo-Ortuño MI (2013) Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health. J Nutr Biochem 24:1415–1422
Chamorro S, Viveros A, Alvarez I, Vega E, Brenes A (2012) Changes in polyphenol and polysaccharide content of grape seed extract and grape pomace after enzymatic treatment. Food Chem 133:308–314
Chandini SK, Rao LJ, Gowthaman MK, Haware DJ, Subramanian R (2011) Enzymatic treatment to improve the quality of black tea extracts. Food Chem 127:1039–1045
Chen H, Qu Z, Fu L, Dong P, Zhang X (2009) Physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of 3 polysaccharides from green tea oolong tea and black tea. J Food Sci 74:C469–C474
Cruz AG, Cadena RS, Walter EH, Mortazavian AM, Granato D, Faria JA, Bolini H (2010) Sensory analysis: relevance for prebiotic probiotic and synbiotic product development. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 9:358–373
da Silva Pinto M (2013) Tea: a new perspective on health benefits. Food Res Int 53:58–567
Daneshi M, Ehsani MR, Razavi SH, Labbafi M (2013) Effect of refrigerated storage on the probiotic survival and sensory properties of milk/carrot juice mix drink. Electron J Biotechn 16:5
Ferreira-Nunes R, Gratieri T, Gelfuso GM, Cunha-Filho M (2018) Mixture design applied in compatibility studies of catechin and lipid compounds. J Pharm Biomed Anal 149:612–617
Hanlin L, Hrmova M, Harbertson JF, Downey MO (2010) Review: Condensed tannin and grape cell wall interactions and their impact on tannin extractability into wine. Aust J Grape Wine Res 16:173–188
Lacey AL, Pérez-Santín E, López-Caballero ME, Montero P (2014) Survival and metabolic activity of probiotic bacteria in green tea. LWT Food Sci Technol 55:314–322
Lorenzo JM, Munekata PES (2016) Phenolic compounds of green tea: health benefits and technological application in food. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 6(8):709–719
Luckow T, Delahunty C (2004) Consumer acceptance of orange juice containing functional ingredients. Food Res Int 37:805–814
Mortazavian AM, Ehsani MR, Mousavi SM, Rezaei K, Sohrabvandi S, Reinheimer JA (2007) Effect of refrigerated storage temperature on the viability of probiotic microorganisms in yogurt. Int J Dairy Technol 60:123–127
Nadeem HŞ, Torun M, Demir F (2011) Spray drying of the mountain tea Sideritisstricta water extract by using different hydrocolloid carriers. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:1626–1635
Nagpal R, Kaur A (2011) Synbiotic effect of various prebiotics on in vitro activities of probiotic Lactobacilli. Ecol Food Nutr 50:63–68
Palframan R, Gibson GR, Rastall RA (2003) Development of a quantitative tool for the comparison of the prebiotic effect of dietary oligosaccharides. Lett Appl Microbiol 37:281–284
Ridley BL, O’Neill MA, Mohnen D (2001) Pectins: structure biosynthesis and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochemistry 57:929–967
Ruxton CHS (2008) Black tea and health. Nutr Bull 33:91–101
Rycroft CE, Jones MR, Gibson GR, Rastall RA (2001) A comparative in vitro evaluation of the fermentation properties of prebiotic oligosaccharides. J Appl Microbiol 91:878–887
Someswararao C, Srivastav PP (2012) A novel technology for production of instant tea powder from the existing black tea manufacturing process. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 16:143–147
Spiro M, Price WE (1987) Kinetics and equilibria of tea infusion—part 6: the effects of salts and of pH on the concentrations and partition constants of theaflavins and caffeine in Kapchorua Pekoe Fannings. Food Chem 24:51–61
Tuohy KM, Probert HM, Smejkal CW, Gibson GR (2003) Using probiotics and prebiotics to improve gut health. Drug Discov Today 8:692–700
Van Laere KM, Hartemink R, Bosveld M, Schols HA, Voragen AG (2000) Fermentation of plant cell wall derived polysaccharides and their corresponding oligosaccharides by intestinal bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 48:1644–1652
Vodnar DC, Socaciu C (2012) Green tea increases the survival yield of Bifidobacteria in simulated gastrointestinal environment and during refrigerated conditions. Chem Cent J 6:1–8
Wang LF, Kim DM, Lee CY (2000) Effects of heat processing and storage on flavanols and sensory qualities of green tea beverage. J Agric Food Chem 48:4227–4232
Yang CS, Landau JM, Huang MT, Newmark HL (2001) Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Annu Rev Nutr 21:381–406
Yang-Hee H, Jung E, Yooheon P, Kwang-Soon S, Kim T, Kwang-Won Y, Suh H (2013) Enzymatic improvement in the polyphenol extractability and antioxidant activity of green tea extracts. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:22–29
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Institute of Chemical Technology for providing facilities and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that the work described is approved by all authors and the responsible authorities where the work was carried out.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tewari, S., Dubey, K.K. & Singhal, R.S. Evaluation and application of prebiotic and probiotic ingredients for development of ready to drink tea beverage. J Food Sci Technol 55, 1525–1534 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3070-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3070-9