Abstract
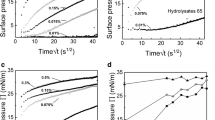
The complexation of corn protein hydrolyzate (CPH) with tannic acid (TA) was utilized to improve the foaming properties of CPH itself, and the air–water interfacial behavior of CPH–TA complex was also investigated. The results showed that the surface hydrophobicity of pure CPH was significantly decreased in bulk solution after the complexation with TA. Compared with pure CPH, the foams stabilized by CPH–TA complex showed higher interfacial thickness between the bubbles, which well explained the better long term stability of the corresponding foams. Therefore, the complexation maintained the good foaming capacity of CPH itself, but considerably increased its foam stability. Moreover, the air–water interfacial behavior study demonstrated that the complexation slightly decreased the interfacial activity of CPH itself, but considerably increased its interfacial viscoelasticity, suggesting more stable of the air–water interface stabilized by CPH–TA complex compared with that stabilized by CPH alone. These findings indicated that foaming properties of the surface active components were closely related with its air–water interfacial behavior. The study suggested that CPH–TA complex could be used as a stabilizer in constructing the peptides-based foams.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agyare KK, Addo K, Xiong YL (2009) Emulsifying and foaming properties of transglutaminase-treated wheat gluten hydrolysate as influenced by pH, temperature and salt. Food Hydrocoll 23(1):72–81
Almajano MP, Gordon MH (2004) Synergistic effect of BSA on antioxidant activities in model food emulsions. J Oil Fat Ind 81(81):275–280
Balange AK, Benjakul S (2009) Effect of oxidised tannic acid on the gel properties of mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) mince and surimi prepared by different washing processes. Food Hydrocoll 23(7):1693–1701
Chen FP, Li BS, Tang CH (2015) Nanocomplexation between curcumin and soy protein isolate: influence on curcumin stability/bioaccessibility and in vitro protein digestibility. J Agric Food Chem 63(13):3559–3569
Lin F, Chen L, Liang R, Zhang Z, Wang J, Cai M et al (2011) Pilot-scale production of low molecular weight peptides from corn wet milling byproducts and the antihypertensive effects in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem 124(3):801–807
Lucassen-Reynders EH (1974) Dynamic surface measurements as a tool to obtain equation-of-state data for soluble monolayers. Adv Chem 21(144):272–285
Manoi K, Rizvi SS (2009) Emulsification mechanisms and characterizations of cold, gel-like emulsions produced from texturized whey protein concentrate. Food Hydrocoll 23(7):1837–1847
Patel AR, Tenhoorn JS, Hazekamp J, Blijdenstein TB, Velikov KP (2013) Colloidal complexation of a macromolecule with a small molecular weight natural polyphenol: implications in modulating polymer functionalities. Soft Matter 9(5):1428–1436
Rodriguez Patino JM, Miñones CJ, Millán LH, Pedroche Jiménez JJ et al (2007) Interfacial and foaming properties of enzyme-induced hydrolysis of sunflower protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll 21(5–6):782–793
Ruízhenestrosa VP, Sánchez CC, Patino JMR (2008) Adsorption and foaming characteristics of soy globulins and tween 20 mixed systems. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(9):2876–2885
Tamm F, Sauer G, Scampicchio M, Drusch S (2012) Pendant drop tensiometry for the evaluation of the foaming properties of milk-derived proteins. Food Hydrocoll 27(2):371–377
Walsh DJ, Russell K, FitzGerald RJ (2008) Stabilisation of sodium caseinate hydrolysate foams. Food Res Int 41(1):43–52
Wan ZL, Wang LY, Wang JM, Yuan Y, Yang XQ (2014a) Synergistic foaming and surface properties of a weakly interacting mixture of soy glycinin and biosurfactant stevioside. J Agric Food Chem 62(28):6834–6843
Wan ZL, Wang LY, Wang JM, Zhou Q, Yuan Y, Yang XQ (2014b) Synergistic interfacial properties of soy protein–stevioside mixtures: relationship to emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll 39(8):127–135
Wang JM, Xia N, Yang XQ, Yin SW, Qi JR, He XT et al (2012) Adsorption and dilatational rheology of heat-treated soy protein at the oil–water interface: relationship to structural properties. J Agric Food Chem 60(12):3302–3310
Wang YH, Wan ZL, Yang XQ, Wang JM, Guo J, Lin Y (2016a) Colloidal complexation of zein hydrolysate with tannic acid: constructing peptides-based nanoemulsions for alga oil delivery. Food Hydrocoll 54:40–48
Wang YH, Yuan Y, Yang XQ, Wang JM, Guo J, Lin Y (2016b) Comparison of the colloidal stability, bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of corn protein hydrolysate and sodium caseinate stabilized curcumin nanoparticles. J Food Sci Technol 53(7):2923–2932
Zayas JF (1997) Foaming properties of proteins. Springer, Berlin
Zou Y, Guo J, Yin SW, Wang JM, Yang XQ (2015) Pickering emulsion gels prepared by hydrogen-bonded zein/tannic acid complex colloidal particles. J Agric Food Chem 63(33):7405–7414
Zou Y, Wan ZL, Guo J, Wang JM, Yin SW, Yang XQ (2017) Tunable assembly of hydrophobic protein nanoparticle at fluid interfaces with tannic acid. Food Hydrocoll 63:364–371
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371744), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong province (2016B090920082), and the Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (182102110450).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YH., Lin, Y. & Yang, XQ. Foaming properties and air–water interfacial behavior of corn protein hydrolyzate–tannic acid complexes. J Food Sci Technol 56, 905–913 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-03553-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-03553-0