Abstract
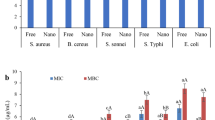
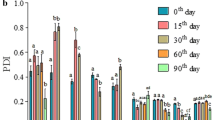
Preparation of oil-in-water nanoemulsions has emerged as a subject of interest for the encapsulation of lipophilic functional ingredients to increase their stability and activity. In this study, black cumin essential oil nanoemulsions (BCO-NE) using different ratios of essential oil with canola and flax seed oils (ripening inhibitors) were formulated and stabilized with octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) modified waxy maize starch. The nanoemulsions exhibited monomodal size distributions with mean droplet diameter below 200 nm and zeta potential above −30, indicating a strong electrostatic repulsion between the dispersed oil droplets. Further, during storage (4 weeks at 25 °C ± 2) emulsions showed shear thinning phenomena and stability towards coalescence. Antimicrobial properties of nanoemulsions were determined by minimum inhibitory concentration and time-kill method against two Gram-positive bacterial (GPB) strains (Bacillus cereus and Listeria monocytogenes). Negatively charged BCO-NE showed prolonged bactericidal activities as compared to pure BCO due to better stability, controlled release and self-assembly with GPB cell membrane followed by destruction of cellular constituents. Our results suggest the application of BCO-NE may be exploited in aqueous food systems for extending the shelf life and other functional properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas S, Mohanad B, Waseem A, Wei WL, Xiaoming Z (2014) Process optimization of ultrasound-assisted curcumin nanoemulsions stabilized by OSA-modified starch. Ultrason Sonochem 21:1265–1274
Abbas S, Eric K, Mohanad B, Khizar H, Xiao H, Hafiz RS, Zhang X (2015) Fabrication of polymeric nanocapsules from curcumin-loaded nanoemulsion templates by self-assembly. Ultrason Sonochem 23:81–92
Adamczak M, Para G, Simon C, Warszyński P (2013) Natural oil nanoemulsions as cores for layer-by-layer encapsulation. J Microencapsul 30(5):479–489
Alam S, Zeenat IK, Gulam M, Manish K, Fakhrul I, Aseem B, Farhan JA (2012) Development and evaluation of thymoquinone-encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for nose-to-brain targeting: a pharmacoscintigraphic study. Int J Nanomed 7:5705–5718
Al-Haj NA, Mariana NS, Norfarrah MA, Hana FZ, Ahmad B, Siddig I, Rasedee A (2010) Characterization of Nigella sativa L. essential oil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Am J Pharmacol and Toxicol 5(1):52–57
Bonilla J, Atares L, Vargas M, Chiralt A (2012) Effect of essential oils and homogenization conditions on properties of chitosan-based films. Food Hydrocolloid 26(1):9–16
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods–a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94(3):223–253
Butt MS, Sultan MT (2010) Nigella sativa: reduces the risk of various maladies. Crit Rev Food Sci 50:654–665
Deepak Suruchi S, Mohd S, Veena G, Mohd S (2011) Entrapment of seed extract of Nigella sativa into thermosensitive (NIPAAm–Co–VP) co-polymeric micelles and its antibacterial activity. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 3(3):246–252
Donsi F, Annunziata M, Vincensi M, Ferrari G (2012) Design of nanoemulsion based delivery systems of natural antimicrobials: effect of the emulsifier. J Biotechnol 159:324–350
Fawzy Ramadan M (2015) Nutritional value and applications of Nigella sativa essential oil: a mini review. J Essent Oil Res 27:271–275
Harzallah HJ, Bochra K, Guido F, Amina B, Touhami M (2011) Chemical composition, antimicrobial potential against cariogenic bacteria and cytotoxic activity of Tunisian Nigella sativa essential oil and thymoquinone. Food Chem 129:1469–1474
Hassanien MFR, Adel MAA, Ahmed MA, Hesham FO (2015) Health-promoting value and food applications of black cumin essential oil: an overview. J Food Sci Technol 52(10):6136–6142
Heurtault B, Saulnier P, Pech B, Proust J-E, Benoit J-P (2003) Physico-chemical stability of colloidal lipid particles. Biomaterials 24(23):4283–4300
Liang R, Xu S, Shoemaker CF, Li Y, Zhong F, Huang Q (2012) Physical and antimicrobial properties of peppermint oil nanoemulsions. J Agric Food Chem 60(30):7548–7555
Majeed H, Fei L, Joseph H, Hafiz RS, Jing Q, Barkat A, Yuan-Yuan B, Jianguo M, Wallace Y, Fang Z (2016) Bactericidal action mechanism of negatively charged food grade clove oil nanoemulsions. Food Chem 197:75–83
Manju S, Balasubramanian M, Sekar V, Sathappan S, Ameeramja J, Perumal E, Baskaralingam V (2016) Antibacterial, antibiofilm and cytotoxic effects of Nigella sativa essential oil coated gold nanoparticles. Microb Pathogenesis 91:129–135
Pasqua RD, Betts G, Hoskins N, Edwards M, Ercolini D, Mauriello G (2007) Membrane toxicity of antimicrobial compounds from essential oils. J Agric Food Chem 55:4863–4870
Periasamy VS, Jegan A, Ali AA (2016) Anticancer activity of an ultrasonic nanoemulsion formulation of Nigella sativa L. essential oil on human breast cancer cells. Ultrason Sonochem 31:449–455
Piras A, Rosa A, Marongiu B, Porcedda S, Falconieri D, Dessì MA, Ozcelik B, Koca U (2013) Chemical composition and in vitro bioactivity of the volatile and fixed oils of Nigella sativa L. extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind Crop Prod 46:317–323
Qian C, Decker EA, Xiao H, McClements DJ (2011) Comparison of biopolymer emulsifier performance in formation and stabilization of orange oil in water emulsions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88:47–55
Salvia-Trujillo L, Alejandra R-G, Robert S-F, Olga M-B (2015) Physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial activity of food-grade emulsions and nanoemulsions incorporating essential oils. Food Hydrocolloid 43:547–556
Shaaban HA, Zainab S, Emr EE, Amal S-H (2015) Analysis and antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa essential oil formulated in microemulsion system. J Oleo Sci 64(2):223–232
Sharif HR, Williams PA, Sharif MK, Khan MA, Majeed H, Safdar W, Shamoon M, Shoaib M, Haider J, Zhong F (2017) Influence of OSA-starch on the physico chemical characteristics of flax seed oil-eugenol nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 66:365–377
Singh S (2014) Composition, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oil and oleoresins obtained from black cumin seeds (Nigella sativa L.). Biomed Res. doi:10.1155/2014/918209
Singh G, Palanisamy M, Sde-H Carola, Cesar C (2005) Chemical constituents and antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials of essential oil and acetone extract of Nigella sativa seeds. J Sci Food Agr 85:2297–2306
Solati Z, Badlishah SB (2015) Antioxidant effect of supercritical CO2 extracted Nigella sativa L. seed extract on deep fried oil quality parameters. J Food Sci Technol 52(6):3475–3484
Venkatachallam SKT, Hajimalang P, Soundar D, Udaya SK (2010) Chemical composition of Nigella sativa L. seed extracts obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide. J Food Sci Technol 47(6):598–605
Verma SK, Shweta R, Kalim J, Mohd A, Indu A, Mohd S (2013) Nanothymoquinone, a novel hepatotargeted delivery system for treating CCl4 mediated hepatotoxicity in rats. J Mater Chem B 1:2956–2966
Zinoviadou KG, Konstantinos PK, Costas GB (2009) Physico-chemical properties of whey protein isolate films containing oregano oil and their antimicrobial action against spoilage flora of fresh beef. Meat Sci 82:338–345
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the support of state key laboratory of food science and technology, school of food science and technology, jiangnan university, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharif, H.R., Abbas, S., Majeed, H. et al. Formulation, characterization and antimicrobial properties of black cumin essential oil nanoemulsions stabilized by OSA starch. J Food Sci Technol 54, 3358–3365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2800-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2800-8