Abstract
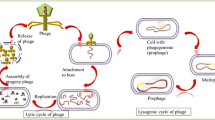
Bacteriophages are viruses that only infect bacterial cells. Phages are categorized based on the type of their life cycle, the lytic cycle cause lysis of the bacterium with the release of multiple phage particles where as in lysogenic phase the phage DNA is incorporated into the bacterial genome. Lysogeny does not result in lysis of the host. Lytic phages have several potential applications in the food industry as biocontrol agents, biopreservatives and as tools for detecting pathogens. They have also been proposed as alternatives to antibiotics in animal health. Two unique features of phage relevant for food safety are that they are harmless to mammalian cells and high host specificity, keeping the natural microbiota undisturbed. However, the recent approval of bacteriophages as food additives has opened the discussion about ‘edible viruses’. This article reviews in detail the application of phages for the control of foodborne pathogens in a process known as “biocontrol”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedon ST (1999) Bacteriophage T4 resistance to lysis-inhibition collapse. Genet Res 74:1–11
Ackermann HW (2007) 5500 phages examined in the electron microscope. Arch Virol 152:227–243
Ackermann HW (2009) Phage classification and characterization. In: Bacteriophages. Humana press, pp 127–140
Ackermann HW, DuBow MS (1987) Viruses of prokaryotes: general properties of bacteriophage. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ackermann HW, Prangishvili D (2012) Prokaryote viruses studied by electron microscopy. Arch Virol 157(10):1843–1849
Atterbury RJ (2009) Bacteriophage biocontrol in animals and meat products. Microb Biotechnol 2:601–612
Bigot B, Lee WJ, McIntyre L et al (2011) Control of Listeria monocytogenes growth in a ready-to-eat poultry product using a bacteriophage. Food Microbiol 28(8):1448–1452
Bigwood T, Hudson JA, Billington C (2009) Influence of host and bacteriophage concentrations on the inactivation of food-borne pathogenic bacteria by two phages. FEMS Microbiol Lett 291:59–64
Borysowski J, Weber-Dabrowska B, Gorski A (2006) Bacteriophage endolysins as a novel class of antibacterial agents. Exp Biol Med 231:366–377
Bruttin A, Brussow H (2005) Human volunteers receiving escherichia coli phage T4 orally: a safety test of phage therapy. Am Soc Microbiol 49:2874–2878
Bueno E, Garcıa P, Martınez B, Rodrıguez A (2012) Phage inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in fresh and hard-type cheeses. Int J Food Microbiol 158(1):23–27
Carlton RM, Noordman WH, Biswas B, de Meester ED, Loessner MJ (2005) Bacteriophage P100 for control of Listeria monocytogenes in foods: genome sequence, bioinformatic analyses, oral toxicity study, and application. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 43(3):301–312
Carvalho CM, Gannon BW, Halfhide DE, Santos SB, Hayes CM, Roe JM, Azeredo J (2010) The in vivo efficacy of two administration routes of a phage cocktail to reduce numbers of campylobacter coli and campylobacter jejuni in chickens. BMC Microbiol 10(1):232
Civerolo EL, Kiel HL (1969) Inhibition of bacterial spot of peach foliage by Xanthomonas pruni bacteriophage. Phytopathology 59:1966–1967
Coffey B, Mills S, Coffey A, McAuliffe O, Ross RP (2010) Phage and their lysins as biocontrol agents for food safety applications. Ann Rev Food Sci Technol 1:449–468
Delbruck M (1940) The growth of bacteriophage and lysis of the host. J Gen Physiol 23:643–660
Delisle AL, Levin RE (1969) Bacteriophages of psychrophilic pseudomonads. I. Host range of phage pools active against fish spoilage and fish-pathogenic pseudomonads. Anton Leeuw 35:307–317
DuPont HL (2007) The growing threat of foodborne bacterial enteropathogens of animal origin. Clin Infect Dis 45:1353–1361
During K, Porsch P, Fladung M, Lorz H (1993) Transgenic potato plants resistant to the phytopathogenic bacterium Erwinia carotovora. Plant J 3:587–598
Dykes GA, Moorhead SM (2002) Combined antimicrobial effect of nisin and a listeriophage against Listeria monocytogenes in broth but not in buffer or on raw beef. Int J Food Microbiol 73(1):71–81
El-Shibiny A, Scott A, Timms A, Metawea Y, Connerton P, Connerton I (2009) Application of a group II campylobacter bacteriophage to reduce strains of Campylobacter jejuni and campylobacter coli colonizing broiler chickens. J Food Prot 72(4):733–740
Fischetti VA (2008) Bacteriophage lysins as effective antibacterials. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:393–400
Fischetti VA (2010) Bacteriophage endolysins: a novel anti-infective to control gram-positive pathogens. Int J Med Microbiol 300:357–362
Gaeng S, Scherer S, Neve H, Loessner MJ (2000) Gene cloning and expression and secretion of Listeria monocytogenes bacteriophage-lytic enzymes in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2951–2958
Gill J, Abedon ST (2003) Bacteriophage ecology and plants. APSnet Feature
Gill J, Sabour PM, Leslie KE, Griffiths MW (2006) Bovine whey proteins inhibit the interaction of staphylococcus aureus and bacteriophage K. J Appl Microbiol 101(2):377–386
Greer GG (1982) Psychrotrophic bacteriophages for beef spoilage pseudomonads. J Food Prot 45:1318–1325
Greer GG (1988) Effects of phage concentration, bacterial density, and temperature on phage control of beef spoilage. J Food Sci 53:1226–1227
Greer GG (2005) Bacteriophage control of foodborne bacteria. J Food Prot 68(5):1102–1111
Guenther S, Loessner MJ (2011) Bacteriophage biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes on soft ripened white mold and red- smear cheeses. Bacteriophage 1(2):94–100
Guenther S, Herzig O, Fieseler L, Klumpp J, Loessner MJ (2012) Biocontrol of salmonella typhimurium in RTE foods with the virulent bacteriophage FO1-E2. Int J Food Microbiol 154(1–2):66–72
Guttman B, Raya R, Kutter E (2005) Basic phage biology. In: Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (eds) Bacteriophages: biology and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 28
Hagens S, Loessner MJ (2010) Bacteriophage for biocontrol of foodborne pathogens: calculations and considerations. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 11(1):58–68
Holck A, Berg J (2009) Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in cooked ham by virulent bacteriophages and protective cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(21):6944–6946
Hooton SPT, Atterbury RJ, Connerton IF (2011) Application of a bacteriophage cocktail to reduce salmonella typhimurium U288 contamination on pig skin. Int J Food Microbiol 151(2):157–163
Ikeda H, Tomizawa J (1965) Transducing fragments in generalized transduction by phage P1. I. Molecular origin of the fragments. J Mol Biol 14:85–109
Kasman LM, Kasman A, Westwater C, Dolan J, Schmidt MG, Norris JS (2002) Overcoming the phage replication threshold: a mathematical model with implications for phage therapy. J Virol 76:5557–5564
Kim W-S, Salm H, Geider K (2004) Expression of bacteriophage fEa1h lysozyme in escherichia coli and its activity in growth inhibition of Erwinia amylovora. Microbiology 150:2707–2714
Kim KP, Klumpp J, Loessner MJ (2007) Enterobacter sakazakii bacteriophages can prevent bacterial growth in reconstituted infant formula. Int J Food Microbiol 115:195–203
Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (2005) Introduction. In: Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (eds) Bacteriophages: biology and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 1
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Alavidze Z (2001) Examination of bacteriophage as a biocontrol method for salmonella on fresh-cut fruit: a model study. J Food Prot 64(8):1116–1121
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Camp MJ et al (2003) Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes on fresh-cut produce by treatment with lytic bacteriophages and a bacteriocin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):4519–4526
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Janisiewicz W, Camp MJ (2004) Optimizing concentration and timing of a phage spray application to reduce Listeria monocytogenes on honeydew melon tissue. J Food Prot 67(8):1682–1686
Martınez B, Obeso JM, Rodrıguez A, Garcıa P (2008) Nisin- bacteriophage crossresistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Food Microbiol 122(3):253–258
Maura D, Debarbieux L (2011) Bacteriophages as twenty-first century antibacterial tools for food and medicine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:851–885
McIntyre L, Hudson JA, Billington C, Withers H (2007) Biocontrol of bacteria: past, present and future strategies. Food N Z 7:25–32
Modi R, Hirvi Y, Hill A, Griffiths MW (2001) Effect of phage on survival of salmonella enteritidis during manufacture and storage of cheddar cheese made from raw and pasteurized milk. J Food Prot 64(7):927–933
Monk AB, Rees CD, Barrow P, Hagens S, Harper DR (2010) Bacteriophage applications: where are we now? Lett Appl Microbiol 51:363–369
Montanez-Izquierdo VY, Salas-Vazquez DI, Rodrıguez-Jerez JJ (2012) Use of epifluorescence microscopy to assess the effectiveness of phage P100 in controlling Listeria monocytogenes biofilms on stainless steel surfaces. Food Control 23:470–477
Murray AG, Jackson GA (1992) Viral dynamics: a model of the effects size, shape, motion and abundance of single-celled planktonic organisms and other particles. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 89:103–116
O’Flaherty S, Coffey A, Meaney WJ, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2005) Inhibition of bacteriophage K proliferation on staphylococcus aureus in raw bovine milk. Lett Appl Microbiol 41(3):274–279
O’Flynn G, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Coffey A (2004) Evaluation of a cocktail of three bacteriophages for biocontrol of Escherichia coli O157: H7.Applied and. Environ Microbiol 70(6):3417–3424
Obeso JM, Martınez B, Rodrıguez A, Garcıa P (2008) Lytic activity of the recom- binant staphylococcal bacteriophage FH5 endolysin active against staphylococcus aureus in milk. Int J Food Microbiol 128:212–218
Patel J, Sharma M, Millner P, Calaway T, Singh M (2011) Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 attached to spinach harvester blade using bacteriophage. Foodborne Pathog Dis 8(4):541–546
Ravensdale M, Blom TJ, Gracia-Garza A, Svircev AM, Smith RJ (2007) Bacteriophages and the control of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. Can J Plant Pathol 29(2):121–130
Rosenquist H, Nielsen NL, Sommer HM, Nørrung B, Christensen BB (2003) Quantitative risk assessment of human campylobacteriosis associated with thermophilic campylobacter species in chickens. Int J Food Microbiol 83(1):87–103
Roy B, Ackermann HW, Pandian S, Picard G, Goulet J (1993) Biological inactivation of adhering Listeria monocytogenes by listeriaphages and a quaternary ammonium compound. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2914–2917
Santander J, Robeson J (2007) Phage-resistance of salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis and pathogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans is mediated by the lipopolysaccharide. Electron J Biotechnol 10:627–632
Sharma M, Patel JR, Conway WS, Ferguson S, Sulakvelidze A (2009) Effectiveness of bacteriophages in reducing Escherichia coli O157:H7 on fresh-cut cantaloupes and lettuce. J Food Prot 72(7):1481–1485
Sheng H, Knecht HJ, Kudva IT, Hovde CJ (2006) Application of bacteriophages to control intestinal Escherichia coli O157:H7 levels in ruminants. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(8):5359–5366
Sillankorva SM, Oliveira H, Azeredo J (2012) Bacteriophages and their role in food safety. Int J Microbiol 2012:1–13
Siringan P, Connerton PL, Payne RJH, Connerton IF (2011) Bacteriophage- mediated dispersal of campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(10):3320–3326
Soni A, Nannapaneni R, Hagens S (2010) Reduction of Listeria monocytogenes on the surface of fresh channel catfish fillets by bacteriophage listex p100. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7(4):427–434
Strauch E, Hammerl J, Hertwig S (2007) Bacteriophages: new tools for safer food? J Verbr Lebensm 2:138–143
Tabla R, Martínez B, Rebollo JE, González J, Ramírez MR, Roa I, Rodríguez A, García P (2012) Bacteriophage performance against staphylococcus aureus in milk is improved by high hydrostatic pressure treatments. Int J Food Microbiol 156(3):209–213
Tarahovsky YS, Ivanitsky GR, Khusainov AA (1994) Lysis of escherichia coli cells induced by bacteriophage T4. FEMS Microbiol Lett 122:195–199
Tomat D, Mercanti Q, Balague C, Quiberoni A (2013) Phage biocontrol of enteropathogenic and Shiga toxin-producing escherichia coli during milk fermentation. Lett Appl Microbiol 57:3–10
Viazis S, Akhtar M, Feirtag J, Diez-Gonzalez F (2011) Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 viability on hard surfaces by treatment with a bacteriophage mixture. Int J Food Microbiol 145(1):37–42
Wagenaar JA, Bergen MAPV, Mueller MA, Wassenaar TM, Carlton RM (2005) Phage therapy reduces Campylobacter jejuni colonization in broilers. Vet Microbiol 109(3–4):275–283
Ye J, Kostrzynska M, Dunfield K, Warriner K (2009) Evaluation of a biocontrol preparation consisting of enterobacter asburiae JX1 and a lytic bacteriophage cocktail to suppress the growth of salmonella javiana associated with tomatoes. J Food Prot 72(11):2284–2292
Ye J, Kostrzynska M, Dunfield K, Warriner K (2010) Control of salmonella on sprouting mung bean and alfalfa seeds by using a biocontrol preparation based on antagonistic bacteria and lytic bacteriophages. J Food Prot 73(1):9–17
Yoong P, Schuch R, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2004) Identification of a broadly active phage lytic enzyme with lethal activity against antibiotic resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. J Bacteriol 186:4808–4812
Zhang H, Wang R, Bao H (2013) Phage inactivation of foodborne Shigella on ready- to-eat spiced chicken. Poult Sci 92:211–217
Zimmer M, Vukov N, Scherer S, Loessner MJ (2002) The murein hydrolase of the bacteriophage j3626 dual lysis system is active against all tested Clostridium perfringens strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5311–5317
Zuber S, Boissin-Delaporte C, Michot L, Iversen C, Diep B, Brussow H et al (2008) Decreasing Enterobacter sakazakii (Cronobacter spp.) food contamination level with bacteriophages: prospects and problems. Microb Biotechnol 1:532–543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazi, M., Annapure, U.S. Bacteriophage biocontrol of foodborne pathogens. J Food Sci Technol 53, 1355–1362 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1996-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1996-8