Abstract
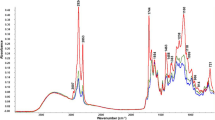
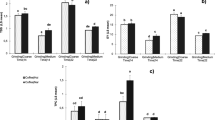
The aim of this research was to evaluate the effect of terebinth (Pistacia terebinthus L.) coffee addition (0.5, 1 and 2 %) on the chemical and physical properties, colour values, organic acid profiles, mineral contents and sensory characteristics of ice creams. The total solids, fat, titratable acidity, viscosity, first dripping time and complete melting time values, a * and b * colour properties, citric, lactic, acetic and butyric acid levels and Ca, Cu, Mg, Fe, K, Zn and Na concentrations of ice creams showed an increase with the increment of terebinth coffee amount, while protein, pH, L *, propionic acid and orotic acid values decreased. However, Al and malic acid were not detected in any of the samples. The overall acceptability scores of the sensory properties showed that the addition of 1 % terebinth coffee to the ice cream was more appreciated by the panellists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1991) R.E.D FACTS, Propionic acid, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Pesticides and toxic substances 738: 91–106
Ayar A, Sert D, Akin N (2009) The trace metal levels in milk and dairy products consumed in middle Anatolia-Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 152:1–12
Baytop T (1994) Dictionary of Turkish plant names. Turkish Linguistic Council Publication No. 578. Turkish Linguistic Council, Ankara
Bodyfelt FW, Tobias J, Trout GM (1988) The sensory evaluation of dairy products. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, p 166
Bonsignore L, Cottiglia F, Loy G (1998) Antibacterial activity of Pistacia lentiscus L. aerial parts. Fitoterapia 69:537–538
Caggiano R, Sabia S, D’Emilio M, Macchiato M, Anastasio A, Ragosta M, Paino S (2005) Metal levels in fodder, milk, dairy products, and tissues sampled in ovine farms of Southern Italy. Environ Res 99:48–57
Çakmakçı S, Topdaş EF, Kalın P, Han H, Şekerci P, Köse LP, Gülçin İ (2015) Antioxidant capacity and functionality of oleaster (Elaeagnus angustifolia L.) flour and crust in a new kind of fruity ice cream. Int J Food Sci Technol 50:472–481
De La Fuente MA, Montes F, Guerrero G, Juarez M (2003) Total and soluble contents of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and zinc in yoghurts. Food Chem 80:573–578
Deeb Azza MM, Gomaa GM (2011) Detection of aluminium in some dairy products at Kafr-El-Sheikh, Egypt. Global Veterinaria 6(19):1–5
Demirci M, Gündüz HH (1994) Dairy technology hand book. Hasad Publ, Istanbul, p 66
Dervisoglu M (2006) Influence of hazelnut flour and skin addition on the physical, chemical and sensory properties of vanilla ice cream. Int J Food Sci Technol 41:657–661
El–Samahy SK, Youssef KM, Moussa–Ayoub TE (2009) Producing ice cream with concentrated cactus pear pulp: a preliminary study. J Prof Assoc Cactus Develop 11:1–12
Fernandez-Garcia E, McGregor JU (1994) Determination of organic acids during the fermentation and cold storage of yogurt. J Dairy Sci 11:2934–2939
Frost MB, Heymann H, Bredie WLP, Dijksterhuis GB, Martens M (2005) Sensory measurement of dynamic flavour intensity in ice cream with different fat levels and flavourings. Food Qual Prefer 16:305–314
Granger C, Leger A, Barey P, Langendorff V, Cansel M (2005) Influence of formulation on the structural networks in ice cream. Int Dairy J 15:255–262
Guven M, Karaca OB (2002) The effects of varying sugar content and fruit concentration on the physical properties of vanilla and fruit ice-cream-type frozen yogurts. Int J Dairy Technol 55(1):27–31
Hambidge KM, Krebs NF (2007) Zinc deficiency: a special challenge. J Nutr 137(4):1101–5
Hwang JY, Shyu YS, Hsu CK (2009) Grape wine lees improves the rheological and adds antioxidant properties to ice cream. LWT - Food Sci Technol 42:312–318
Jimenez-Florez R, Klipfel NJ, Tobias J (1993) Ice cream and frozen desserts. In Dairy Science and Technology Handbook Hui Y. H. (Ed.), Product manufacturing. VCH Publishers, New York 2:57–159
Kavaz A, Bakirci I (2014) Influence of inulin and demineralised whey powder addition on the organic acid profiles of probiotic yoghurts. Int J Dairy Technol 67(4):577–583
Kosmider A, Drozdzynska A, Blaszka K, Leja K, Czaczyk K (2010) Propionic acid production by Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. Shermanii using crude glycerol and whey lactose industrial wastes. Pol J Environ Stud 19(6):1249–1253
Koxholt MMR, Eisenmann B, Hinrichst J (2001) Effect of the fat globule sizes on the meltdown of ice cream. J Dairy Sci 84:31–37
Matthäus B, Özcan MM (2006) Quantitation of fatty acids, sterols, and tocopherols in turpentine (Pistacia terebinthus) growing wild in Turkey. J Agr Food Chem 54:7667–7671
Molkentin J, Precht D (1998) Comparison of gas chromatographic methods for analysis of butyric acid in milk fat and fats containing milk fat. Eur Food Res Technol 206:213–216
Murtaza MA, Huma N, Mueen-Ud-Din G, Shabbir MA, Mahmood S (2004) Effect of fat replacement by fig addition on ice cream quality. Int J Agricult Biol 6:68–70
Okonkwo P, Kinsella J (1969) Orotic acid in food milk powders. Am J Clin Nutr 22:532
Özcan M (2004) Characteristics of fruit and oil of terebinth (Pistacia terebinthus L) growing wild in Turkey. J Sci Food Agric 84:517–520
Rodriguez Rodriguez EM, Sanz Alaejos M, Diaz Romeo C (2002) Mineral content in goats’ milks. J Food Qual 25:343–358
Sofjan R, Hartel RW (2004) Effects of overrun on structural and physical characteristics of ice-cream. Int Dairy J 14(3):255–262
Sniffen CJ, Ballard CS, Carter MP, Contach KW, Danna HM, Grant RJ, Mandepvu P, Suekawa M, Martin SA (2006) Effects of malic acid on microbial efficiency and metabolism in continuous culture of rumen contents and on performance of mid-lactation dairy cows. Anim Feed Sci Tech 127:13–31
Szefer P, Nriagu J (2007) Mineral components in foods. CRC Press, New York
Tarakcı Z (2010) Influence of kiwi marmalade on the rheology characteristics, color values and sensorial acceptability of fruit yogurt. Kafkas Universitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi 16(2):173–178
Temiz H, Yeşilsu AF (2010) Effect of pekmez addition on the physical, chemical, and sensory properties of ice cream. Czech J Food Sci 28(6):538–546
Tormo M, Izco JM (2004) Alternative reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography method to analyse organic acids in dairy products. J Chromatogr A 1033:305–310
Tunick MH (1987) Calcium in dairy products. J Dairy Sci 70(11):2429–2438
Vega C, Goff HD (2005) Phase separation in soft-serve ice cream mixes: rheology and microstructure. Int Dairy J 12:249–254
Viljakainen S, Visti A, Laakso S (2002) Concentrations of organic acids and soluble sugars in juices from Nordic berries. Acta Agr Scand Sec B 52:101–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• The influence of terebinth coffee addition on ice cream quality.
• The physico-chemical characteristics, colour values of ice creams
• The changing on the organic acid profiles of ice creams with the addition of terebinth coffee
• Mineral composition of terebinth coffee added ice creams.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yüksel, A.K., Şat, I.G. & Yüksel, M. The effect of terebinth (Pistacia terebinthus L.) coffee addition on the chemical and physical characteristics, colour values, organic acid profiles, mineral compositions and sensory properties of ice creams. J Food Sci Technol 52, 8023–8031 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1904-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1904-2