Abstract
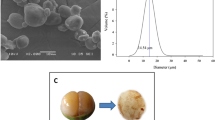
In this paper, starch was extracted from fresh pasta by-product (PS) and its chemical composition and physical and microscopic characteristics were determined. Commercial wheat starch (CS) was used as reference. In general, purity was similar between starches studied. However, others compounds such as protein, lipid and ash were significantly different. PS starch granules had large lenticular-shape (25–33 μm) and small spherical-shape (5–8 μm). The pH and color of PS starch were similar to those reported for CS starch. On the other hand, PS had higher water absorption capacity, viscosity and cooking stability than CS. The gelatinization temperature of PS was similar to that of CS (60 and 61 °C). At high temperature (90 °C) both starches had similar rheological behavior. The results achieved suggest that PS starch has potential for application in food systems requiring high processing temperatures such the manufacture of sugar snap cookie. The effects of PS starch addition on the dough making stage and the final cookie quality were analyzed. Improvements in dough cohesiveness (24 %) and springiness (10 %) were significant relative to those of CS dough. Texture profile analysis confirmed the rheological changes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (1983) Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. AACC-methods 10-50D, 44–19, 54-40A, 56–10, 76–31, eighthth edn. American Association of Cereal Chemists Inc, St. Paul
AACC (1992) Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. 9th ed. Method 76–31, approved September 1992, reviewed October 1994. The American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
AACC (2000) Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th Ed., Methods 46–30, 30–10, 44–19, 08–01, 54–30. The American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Abdul-Hamdi A, Luan YS (2000) Functional properties of dietary fiber prepared from defatted rice bran. Food Chem 68:15–19
Berton B, Scher J, Villieras F, Hardy J (2002) Measurement of hydration capacity of wheat flour: influence of composition and physical characteristics. Powder Technol 128:326–331
Beuchat LR (1977) Functional and electrophoretic characteristics of succinylated peanut flour protein. J Agric Food Chem 25:258–261
Bonet A, Blaszczak W, Rosell CM (2006) Formation of homopolymers and heteropolymers between wheat flour and several protein sources by transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking. Cereal Chem 83:655–662
Burrell MM (2003) Starch: the need for improved quality and quantity—an overview. J Exp Bot 54:451–456
Bushuk W (1966) Distribution of water in dough and bread. Baker’s Dig 40:38–40
Carini E, Vittadini E, Curti E, Antoniazzi F (2009) Effects of different shaping modes on physico-chemical properties and water status of fresh pasta. J Food Eng 93:400–406
Chen JS, Deng ZY, Wu P, Tian JC, Xie QG (2010) Effect of gluten on pasting properties of wheat starch. Agric Sci China 9:1836–1844
Chevallier S, Colonna P, Buleon A, Della Valle G (2000) Physicochemical behaviors of sugars, lipids, and gluten in short dough and biscuit. J Agric Food Chem 48:1322–1326
Copeland L, Blazek J, Salman H, Tang MC (2009) Form and functionality of starch. Food Hydrocoll 23:1527–1534
Dengate HN (1984) Swelling, pasting, and gelling of wheat starch. In: Pomeranz Y (ed) Advances in cereal science and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemists, USA, pp 49–82
Ellouze-Ghorbel R, Zouari ES, Neifar M, Zalila K, Blibech M, Kamoun H, Ellouze CS (2010) Gluten extracted from fresh pasta by-product: physicochemical properties and potential use in bread making. J Texture Stud 41:245–261
Feather MS (1994) The mechanism of non enzymatic browning reactions occurring during cookie and cracker making. In: Faridi H (ed) The science of cookie and cracker production. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 434–453
Friedman RB (1995) Interactions of starches in foods. In: Gaonkar AG (ed) Ingredient interactions: effects on food quality. M Dekker, New York
Fustier P, Castaigne F, Turgeon SL, Biliaderis CG (2007) Semi-sweet biscuit making potential of soft wheat flour patent, middle-cut and clear mill streams made with native and reconstituted flour. J Cereal Sci 46:119–131
Fustier P, Castaigne F, Turgeon SL, Biliaderis CG (2008) Flour constituent interactions and their influence on dough rheology and quality of semi-sweet biscuits: a mixture design approach with reconstituted blends of gluten, water-solubles and starch fractions. J Cereal Sci 48:144–158
Gaines CS, Kassuba A, Finney PL (1992) Instrumental measurement of cookie hardness. 1. Assessment of methods. Cereal Chem 69:115–119
Gazmuri AM, Bouchon P (2009) Analysis of wheat gluten and starch matrices during deep-fat frying. Food Chem 115:999–1005
Jimenez-Hernández J, Meneses-Esparza F, Rosendo-Escobar J, Vivar-Vera MA, Bello-Pérez LA, Garcia-Suárez FJ (2011) Extraction and characterizationof starch from Enterolobium cyclocarpum seeds. CyTA-J Food 9:89–95
Jobling S (2004) Improving starch for food and industrial applications. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:210–218
Kaldy MS, Kereliuk GR, Kozub GC (1993) Influence of gluten components and flour lipids on soft white wheat quality. Cereal Chem 70:77–80
Khabou W, Trigui A, Ghorbel R, Bejar S (1996) L’amidon dans les rameaux d’olivier (Olea europaea) Cv.“Chemlali de sfax”Etude comparative de deux méthodes d’hydrolyse. Olivea 61:57–61
Krogars K, Heinamaki J, Karjalainen M, Rantanen J, Luukkonen P, Yliruusi J (2003) Development and characterization of aqueous amylose-rich maize starch dispersion for film formation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 56:215–221
Labuschagne MT, Elago O, Koen E (2009) The influence of the temperature extremes on some quality and starch characteristics in bread, biscuit and durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 49:184–189
Larsen RA (1964) Hydration as factor in bread quality. Cereal Chem 41:181–187
Lindeboom N, Chang PR, Tyler RT (2004) Analytical, biochemical and physicochemical aspects of starch granule size, with emphasis on small granule starches: a review. Starch-Starke 56:89–99
Manley D (2000) Technologie of biscuits, crakers and cookies. Woodhead Publ. Ltd, Cambridge, p 528
Manohar RS, Rao PH (1997) Effect of sugars on the rheological characteristics of biscuit dough and quality of biscuits. J Sci Food Agric 75:383–390
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for the determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Moorthy S (2001) Tuber crop starches, Tech Bulletin No. 18. CTCRI, Trivandrum
Ozturk S, Kahraman K, Tiftik B, Koksel H (2008) Predicting the cookie quality of flours by using Mixolab. Eur Food Res Technol 227:1549–1554
Pareyt B, Wilderjans E, Goesaert H, Brijs K, Delcour JA (2008) The role of gluten in a sugar-snap cookie system: Amodel approach based on gluten-starch blends. Cereal Sci 48:863–869
Pérez-Pacheco E, Moo-Huchin VM, Estarda-Leon RJ, Ortiz-Fernandez A, May-Hernandez LH, Rios-Soberanis CR, Betancur-Ancona D (2014) Isolation and characterization of starch obtained from Brosimum alicastrum Swaets Seeds. Carbohydr Polym 101:920–927
Perry GH, Dominy NJ, Claw KG, Lee AS, Fiegler H, Redon R et al (2007) Diet and evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation. Nat Genet 39:1256–1260
Rasper VF, De Man JM (1980) Measurement of hydration capacity of wheat flour/starch mixtures. Cereal Chem 57:27–31
Rosell CM, Collar C, Haros M (2007) Assessment of hydrocolloid effects on the thermo-mechanical properties of wheat using the Mixolab. Food Hydrocoll 21:452–462
Rudolph H, Tscheuner HD (1979) Adhesiveness in wheat dough. Backer and Konditor 27:229
Sandhu KS, Singh N, Kaur M (2003) Characteristics of the different corns types and their grain fractions: physicochemical, thermal, morphological, and rheological properties of starches. J Food Eng 64:199–127
Shinde SV, Nelson JE, Huber KC (2003) Soft wheat starch pasting behavior in relation to A- and B-type granule content and composition. Cereal Chem 80:91–98
Shujun W, Jinglin Y, Wenyuan G (2005) Use of X-ray diffractometry (XRD) for identification of Fritillaria according to geographical origin. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 1:207–211
Swinkels JJM (1985) Composition and properties of commercial native starches. Starch-Starke 37:1–5
Van Der Borght A, Goesaert H, Veraverbeke WS, Delcour JA (2005) Fractionation of wheat and wheat flour into starch and gluten: overview of the main processes and the factors involved. J Cereal Sci 41:221–237
Wade P (1988) Biscuits, cookies and crackers: the principles of the craft, vol 1. Elsevier Applied Science, London
Wang FC, Chung DS, Seib PA, Kim YS (2000) Optimum steeping process for wet milling of sorghum. Cereal Chem 77:478–483
Wang F, Wan J, Huang W, Tilley M (2010) Effect of transglutaminase on the rheological and mixolab thermomehanical characteristics of oat dough. Food Chem 121:934–939
Wolfgang B, Detmold W, Hans-Peter G (1999) Potato starch technology. Starch-Starke 51:235–242
Zhou X, Blaik BK, Wang R, Lim ST (2010) Retrogradation of waxy and normal corn starch gels by temperature cycling. J Cereal Sci 51:57–65
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Abdessalem Affes, chairman and managing director of the company “Couscousserie Du Sud” (CDS Sfax, Tunisia), for the facilities provided for sample preparation and rheological measurements. We extend our thanks to Mr. Hamadi Attia, for textural measurements. This work was supported financially by the “Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche Scientifique et de la Technologie-Tunisia” through a grant to “Unité Enzyme et Bioconversion—ENIS”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dorra Driss and Sameh Maktouf have equally participated to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellouzi, S.Z., Driss, D., Maktouf, S. et al. Isolation and characterization of starch from industrial fresh pasta by-product and its potential use in sugar-snap cookie making. J Food Sci Technol 52, 5754–5762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1567-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1567-4