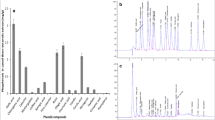
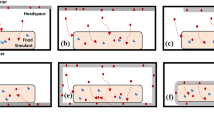
Abstract
The pleothera of micro organisms obtained from contaminated food cultured in a starch broth was effectively tested against antibacterial agents, i.e. nisin, lysozyme and chelating agent EDTA. A variety of combination treatments of these antimicrobial agents and their incorporation in Starch based active packaging film according to their permissibility standards was done. 4 variables of Nisin concentration (ranging from 0 to 750 IU/ml), 3 variables of lysozyme concentration (ranging from 0 to 500 IU/ml) and 3 variables of EDTA concentration from (0 to 20 μM) were chosen. Bacterial inhibition by combination of different levels of different factors without antimicrobial films was evaluated using a liquid incubation method. The samples were assayed for turbidity at interval of 2, 4 and 24 h to check effectiveness of combined effects of antimicrobial agents which proved a transitory bactericidal effect for short incubation times. Zone of Inhibition was observed in the antimicrobial films prepared by agar diffusion method. Statistical analysis of experimental data for their antimicrobial spectrum was carried out by multi regression analysis and ANOVA using Design-Expert software to plot the final equation in terms of coded factors as antimicrobial agents. The experimental data indicated that the model was highly significant. Results were also evaluated graphically using response surface showing interactions between two factors, keeping other factor fixed at values at the center of domain. Synergy was also determined among antibacterial agents using the fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index which was observed to be 0.56 supporting the hypothesis that nisin and EDTA function as partial synergistically. The presented work aimed to screen in quick fashion the combinatorial effect of three antimicrobial agents and evaluating their efficacy in anti microbial film development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appendini P, Hotchkiss JH (2002) Review of antimicrobial packaging food packaging. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 3:113–126
Banin E, Brady KM, Greenberg EP (2006) Chelator induced dispersal and killing Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells in a biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2064–2069
Berenbaum MC (1981) Criteria for analyzing interactions between biologically active agents. Adv Cancer Res 35:269–335
Boussouel N, Mathieu F, Benoit V, Linder M, Revol-Junelles AM, Milliere JB (1999) Response surface methodology an approach to predict the effects of a lactoperoxidase system, Nisin, alone or in combination, on Listeria monocytogenes in skim milk. J Appl Microbiol 86:642–652
Branen JK, Davidson PM (2004) Enhancement of nisin, lysozyme and monolaurin antimicrobial activities by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and lactoferrin. Int J Food Microbiol 90:63–74
Breukink E, van Kraaij C, van Dalen A, Demel RA, Siezen RJ, de Kruijff B, Kuipers OP (1998) The orientation of nisin in membranes. Biochemistry 37:8153–8162
Bruno ME, Kaiser A, Montville TJ (1992) Depletion of proton motive force by nisin in Listeria monocytogenes cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2255–2259
Chauhan K, Trivedi U, Patel KC (2006) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of lactic acid production using date juice. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16(9):1410–1415
Chung D, Papadakis SE, Yam KL (2003) Evaluation of a polymer coating containing triclosan as the antimicrobial layer for packaging materials. Int J Food Sci Technol 38:165–169
Corbo MR, Mastromatteo M, Lucera A, Sinigaglia M (2010) Use of Lysozyme, Nisin, and EDTA combined treatments for maintaining quality of packed ostrich patties. J Food Sci 75:178–186
Cutter CN, Willett JL, Siragusa GR (2001) Improved antimicrobial activity of nisin incorporated polymer film by formulation change and addition of food grade chelator. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:325–328
Ellison RT, Giehl JJ (1991) Killing of gram negative bacteria by lactoferrin and lysozyme. J Clin Investig 88:1080–1091
Eswaranandam S, Hettiarachchy NS, Johnson MG (2004) Antimicrobial activity of citric, lactic, malic, or tartaric acids and nisin-incorporated soy, protein film against Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella gaminara. J Food Sci 69:78–84
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (1988) Nisin preparation: affirmation of GTAS status as a direct human food ingredient. Fed Regist 53:11247–11251
Gram HC (1884) Über die isolierte Färbung der Schizomyceten in Schnitt- und Trockenpräparaten. Fortschr Med 2:185–189
Hansen JN, Chung Y, Liu W (1991) Biosynthesis and mechanism of the action of nisin and subtilin. ESCOM Science Publishers In: Nisin and novel lantibiotics, Leiden., pp. 287–302
Hansen LT, Austin JW, Gill TA (2001) Antibacterial effect of protamine in combination with EDTA and refrigeration. Int J Food Microbiol 66:149–161
Harris LJ, Fleming HP, Klaenhammer TR (1991) Sensitivity and resistance of Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19115, Scott A, and UAL 500 to nisin. J Food Prot 54:836–840
Hettiarachchy NS, Gadang VP, Johnson MG, Owens C (2008) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of whey protein isolate coating incorporated with nisin, grape seed extract, malic acid, and EDTA on a turkey frankfurter system. J Food Sci 73:389–394
Holley RA, Gill AO (2003) Interactive inhibition of meat spoilage and pathogenic bacteria by lyozyme, nisin and EDTA in the presence of nitrite and sodium chloride at 24 °C. Int J Food Microbiol 80:251–259
Hotchkiss JH (1997) Food-packaging interactions influencing quality and safety. Food Addit Contam 14:601–607
Hughey VL, Johnson EA (1987) Antimicrobial activity of lysozyme against bacteria involved in food spoilage and food-borne disease. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2165–2170
Hurst A (1967) Functions of nisin and nisin like basic proteins in the growth cycle of Streptococcus lactis. Nature 214:1232–1234
Jin T, Zhang H (2008) Biodegradable polylactic acid polymer with nisin for use in antimicrobial food packaging. J Food Sci 73:127–134
Kiss IF, Márialigeti K, Zukál E, Makk J (2007) Method for measurement of antibacterial activity of Nisin. Bulletin USAMV-CN. 63 - 64/2007
Ko S, Janes ME, Hettiarachchy NS, Johnson MG (2001) Physical and chemical properties of edible films containing nisin and their action against Listeria monocytogenes. J Food Sci 66:1006–1011
Lee DS, Lee CH, An DS, Lee SC, Park HJ (2004) A coating for use as an antimicrobial and antioxidative packaging material incorporating nisin and alpha-tocopherol. J Food Eng 62:323–329
Monk JD, Beuchat LR, Hathcox AK (1996) Inhibitory effects of sucrose monolaurate, alone and in combination with organic acids, on Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Bacteriol 81:7–18
Monteville TJ, Chen Y (1998) Mechanistic action of pediocin and nisin: recent progress and unresolved questions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 511–519
Muhammad II, Razali F, Liza MS (2005) Study of an active antimicrobial system using a bio-switch concept. Project Report. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (Unpublished)
Murdock CA, Cleveland J, Matthews KR, Chikindas ML (2007) The synergistic effect of nisin and lactoferrin on the inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol 44:255–261
Okereke A, Montville TJ (1992) Nisin dissipates the proton motive force of the obligate anaerobe Clostridium sporogenes PA 3679. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2463–2467
Padgett T, Han IY, Dawson PL (1998) Incorporation of food antimicrobial compounds into biodegradable packaging films. J Food Prot 61:1330–1335
Parente E, Giglio MA, Ricciardi A, Clementi F (1998) The combined effect of nisin, leucocin F10, pH, NaCl and EDTA on the survival of Listeria monocytogenes in broth. Int J Food Microbiol 40:65–75
Payne KD, Oliver SP, Davidson PM (1994) Comparison of EDTA and apo-lactoferrin with lysozyme on the growth of foodborne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. J Food Prot 57:62–65
Proctor VA, Cunningham RE (1988) The chemistry of lysozyme and its use as a food preservative and a pharmaceutical. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 26:359–395
Schillinger U, Geisen R, Holzapfel WH (1996) Potential of antagonistic microorganisms and bacteriocins for the biological preservation of foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 7:158–164
Shelef LA, Seiter J (1993) Enhancement of the activity of novobiocin against Escherichia coli by lactoferrin. J Dairy Sci 82:492–499
Shively JM, Hartsell SE (1964a) Bacteriolysis of the Pseudomonads:I. Agents potentiating lysis. Can J Microbiol 10:905–909
Shively JM, Hartsell SE (1964b) Bacteriolysis of the Pseudomonads: II. Chemical treatments affecting the lytic response. Can J Microbiol 10:911–915
Siragusa GR, Cutter CN, Willett JL (1999) Incorporation of bacteriocin in plastic retains activity and inhibits surface growth of bacteria on meat. Food Microbiol 16:229–235
Stevens KA, Sheldon BW, Klapes NA, Klaenhamme TR (1991) Nisin treatment for inactivation of Salmonella species and other gram- negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3613–3615
Thomas LV, Ingram RE, Bevis HE, Davies A, Milne CF, Delves-Broughton J (2002) Effective use of nisin to control Bacillus and Clostridium spoilage of a pasteurized mashed potato product. J Food Prot 65:1580–1585
Vessoni Penna TC, Moraes DA (2002) The effect of nisin on growth kinetics from activated Bacillus cereus spores in cooked rice and milk. J Food Prot 65:419–422
Winkowski K, Ludescher RT, Montville TJ (1996) Physiochemical characterization of the nisin-membrane interaction with liposomes derived from Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:323–327
Zhang SS, Mustapha A (1999) Reduction of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 numbers on vacuum packaged fresh beef treated with nisin or nisin combined with EDTA. J Food Prot 62:1123–1127
Zhang YC, Yam KL, Chikindas ML (2004) Effective control of Listeria monocytogenes by combination of nisin formulated and slowly released into a broth system. Int J Food Microbiol 90:15–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, S., Bharti, A. Evaluating the antimicrobial activity of Nisin, Lysozyme and Ethylenediaminetetraacetate incorporated in starch based active food packaging film. J Food Sci Technol 52, 3504–3512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1414-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1414-7