Abstract
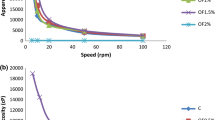
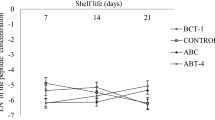
In this study, the effects of fat (0.5 %, 3.2 % and 5.0 %), inulin (0.0 and 1.0 %) and starter culture (0.0 %, 0.5 %, 1.0 % and 1.5 %) on the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory activity of probiotic yogurt containing non-viable bacteria were assessed. Proteolytic activities of bacteria were also investigated. Yogurts were prepared either using a sole yogurt commercial culture including Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subs. bulgaricus or bifidobacterium animalis BB-12 and Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 in addition to yogurt culture. Relative degrees of proteolysis were found to be considerably higher in yogurt samples than UHT milk as the control. Both regular and probiotic yogurts showed considerable ACE-inhibitory activities. Results showed that degree of proteolysis was not influenced by different fat contents, while was increased by high concentration of starter culture (1.5 % w/w) and reduced by inulin (1 % w/w). ACE-inhibitory activities of yogurt were also negatively affected by the presence of inulin and high levels of fat (5 % w/w). Moreover, yogurt containing probiotic bacteria showed higher inhibitory against ACE in comparison to the yogurt prepared with non-probiotic strains.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akın M, Akın M, Kırmacı Z (2007) Effects of inulin and sugar levels on the viability of yogurt and probiotic bacteria and the physical and sensory characteristics in probiotic ice-cream. Food Chem 104:93–99
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter GH, Catignani GL (1983) Spectrophotometric Assay using o-Phthaldialdehyde for Determination of Proteolysis in Milk and Isolated Milk Proteins. J Dairy Sci 66:1219–1227
Cruz A, Castro W, Faria J, Bolini H, Celeghini R, Raices R, Oliveira C, Freitas M, Conte Júnior C, Mársico E (2013) Stability of probiotic yogurt added with glucose oxidase in plastic materials with different permeability oxygen rates during the refrigerated storage. Food Res Int 51:723–728
Dave R, Shah N (1998) Ingredient supplementation effects on viability of probiotic bacteria in yogurt. J Dairy Sci 81:2804–2816
Donkor O, Henriksson A, Vasiljevic T, Shah NP (2005) Probiotic strains as starter cultures improve angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity in soy yogurt. J Food Sci 70:M375–M381
Donkor ON, Henriksson A, Singh T, Vasiljevic T, Shah NP (2007) ACE-inhibitory activity of probiotic yoghurt. Int Dairy J 17:1321–1331
Ejtahed H, Mohtadi-Nia J, Homayouni-Rad A, Niafar M, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Mofid V, Akbarian-Moghari A (2011) Effect of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Dairy Sci 94:3288–3294
Fitzgerald RJ, Murray BA (2006) Bioactive peptides and lactic fermentations. Int J Dairy Technol 59:118–125
Fuglsang A, Rattray FP, Nilsson D, Nyborg NCB (2003) Lactic acid bacteria: inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme in vitro and in vivo. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83:27–34
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. J Applied Bact 66:365
Guven M, Yasar K, Karaca O, Hayaloglu A (2005) The effect of inulin as a fat replacer on the quality of set-type low-fat yogurt manufacture. Int J Dairy Technol 58:180–184
Klaver FAM, Kingma F, Weerkamp A (1993) Growth and survival of bifidobacteria in milk. Nederlands Melk en Zuiveltijdschrif 47:151–164
Kunz AN, Noel JM, Fairchok MP (2004) Two cases of Lactobacillus bacteremia during probiotic treatment of short gut syndrome. J pediatr Gastr Nutr 38:457–458
Laragh JH (1979) L’hypertension. La Recherche 10:1068–1076
Leclerc PL, Gauthier SF, Bachelard H, Santure M, Roy D (2002) Antihypertensive activity of casein-enriched milk fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus. Int Dairy J 12:995–1004.
Mackay AD, Taylor MB, Kibbler CC, Hamilton-miller JMT (2008) Lactobacillus endocarditis caused by a probiotic organism. Clin Microb Infect 5:290–292
Moslehishad M, Ehsani MR, Salami M, Mirdamadi S, Ezzatpanah H, Niasari-Naslaji A, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2013) The comparative assessment of ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities of peptide fractions obtained from fermented camel and bovine milk by Lactobacillus rhamnosus PTCC 1637. Int Dairy J 29:82–87
Özer D, Akin S, Özer B (2005) Effect of inulin and lactulose on survival of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 and Bifidobacterium bifidum BB-02 in acidophilus-bifidus yoghurt. Food Sci Technol Int 11:19–24
Pihlanto-Leppala A (2001) Bioactive peptides from bovine whey proteins: opioid and ACE-inhibitory peptides. Trends Food Sci Tech 11:347–356
Ramchandran L, Shah NP (2008) Growth, proteolytic and ACE-I activities of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus and rheological properties of low-fat yogurt as influenced by the addition of Raftiline HP. J Food Sci 73:368–374
Ramchandran L, Shah NP (2009a) Effect of exopolysaccharides on the proteolytic and angiotensin-I converting enzyme-inhibitory activities and textural and rheological properties of low-fat yogurt during refrigerated storage. J Dairy Sci 92:895–906
Ramchandran L, Shah NP (2009b) Effect of exopolysaccharides and inulin on the proteolytic, angiotensin-I-converting enzyme- and alpha-glucosidase-inhibitory activities as well as on textural and rheological properties of low-fat yogurt during refrigerated storage. Dairy Sci Technol 89:583–60
Ramchandran L, Shah NP (2010) Characterization of functional, biochemical and textural properties of synbiotic low-fat yogurts during refrigerated storage. LWT Food Sci Technol 43:819–827
Ramchandran L, Shah NP (2011) Yogurt can beneficially affect blood contributors of cardiovascular health status in hypertensive rats. J Food Sci 76:131–136
Rautio M, Jousimies-somer H, Kauma H, Pietarinen I, Saxelin M, Tynkkynen S, Koskela M (1999) Liver abscess due to a Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain indistinguishable from L. rhamnosus strain GG. Clin infect diseases 28:1159–1160
Saarela M, Mogensen G, Fonden R, Mättö J, Mattila-Sandholm T (2000) Probiotic bacteria: safety, functional and technological properties. J Biotechnol 84:197–215
Salminen S, Ouwehand A, Benno Y, Lee Y (1999) Probiotics: how should they be defined? Trends Food Sci Tech 10:107–110
Seppo L, Jauhiainen T, Poussa T, Korpela R (2003) A fermented milk high in bioactive peptides has a blood pressure–lowering effect in hypertensive subjects. Am J Clin Sci 77:326–330
Sipola M, Finckenberg P, Santisteban J, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H, Nurminen ML (2001) Long-term intake of milk peptides attenuates development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Phys Pharm 52:745–54
Tsai JS, Chen TJ, Sun Pan B, Gong SD, Chung MY (2008) Antihypertensive effect of bioactive peptides produced by protease-facilitated lactic acid fermentation of milk. Food Chem 106:552–558
Vasiljevic T, Kealy T, Mishra VK (2007) Effects of β-Glucan addition to a probiotic containing Yogurt. J Food Sci 72:405–411
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the University of Tehran and Iranian center of excellence for application of modern technologies for producing functional foods and drinks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakerian, M., Razavi, S.H., Ziai, S.A. et al. Proteolytic and ACE-inhibitory activities of probiotic yogurt containing non-viable bacteria as affected by different levels of fat, inulin and starter culture. J Food Sci Technol 52, 2428–2433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1202-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1202-9