Abstract
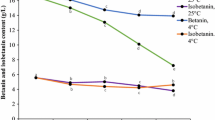
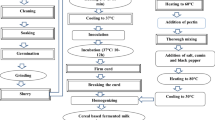
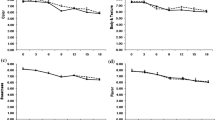
The study was undertaken to study the effect of heat treatment on the storage stability of cardamom flavoured low calorie milk drinks (CFDs). The drinks prepared by replacing sugar with sucralose and adding inulin in milk of 0.5 % fat and 8.5 % milk solid-not-fat were subjected to pasteurization and sterilization and stored at refrigeration and room temperature, respectively. The stored samples were evaluated for changes in physico-chemical and sensory attributes at regular intervals. In pasteurized drinks, the total solids (TS) and pH declined while the total soluble solids (TSS), titratable acidity and viscosity increased significantly (p < 0.01) with storage. A significant reduction in the flavour and body and mouthfeel scores was observed. Standard plate count (SPC) increased in both control and low calorie drinks with storage period. In sterilized CFDs, TS and TSS were not affected appreciably whereas titratable acidity increased and viscosity decreased significantly (p < 0.01) with storage. Though the sensory scores also declined with storage, the drinks obtained high acceptability scores even after 150 days of storage at room temperature. However, the changes in colour components (L, a and b values) indicated increased browning in the drinks with storage time. SPC was not detected until 120 days in control and 135 days in low calorie drink. Yeast and molds were not evident until 135 days in control and 150 days in low calorie drink. The shelf life was found to be 10 and 150 days of pasteurized and sterilized CFDs at refrigeration and room temperature, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1984) Method of microbiological examination of food. American Public Health Association, Washington
Arora S, Nayak SK, Sindhu JS, Seth R (2001) Artificial sweeteners in formulation of dairy products. Indian Food Ind 20:62–66
Arora S, Sharma V, Sharma GS, Wadhwa BK, Singh AK (2006) High potency sweeteners for formulating new dairy products. Indian Dairyman 58:39–45
BIS (1962) IS: 1479 part III bacteriological standards of patsteurized milk. Manak Bhawan, New Delhi
Cano-Ruiz ME, Richter RL (1998) Changes in physico-chemical properties of retort-sterilized dairy beverages during storage. J Dairy Sci 81:2116–2123
Codex (2005) Proposed draft amendments of the codex general standard for food additives. www.codexalimentarius.net accesed on Nov 20, 2008
Cromie SJ (1991) Microbiological aspects of extended shelf life products. Aust J dairy Technol 46(2):101–104
Djmek P (2011) Fluid milk shelf life—from hours to months. http://www.food.lth.se/fileadmin/livsmedelsteknik/pers_hemsidor/TNK201/milk_shelf_life_paper.doc accessed on July 25, 2011
Frazier WC, Westhoff DC (2003) Food microbiology. Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, pp 292–293
Gothwal PP, Bhavadasan MK (1992a) Studies on the browning characteristics in dairy products. Indian J Dairy Sci 45:146–151
Gothwal PP, Bhavadasan MK (1992b) The role of proteins on browning in milk. Indian J Dairy Sci 45:419–423
Goyal SK, Chandra S, Samsher S, Kumari D (2007) Artificial sweeteners: bane or boon in food industry. Processed Food Ind 10(8):21–25
Meilgaard M, Civille GV, Carr BT (1999) Sensory evaluation techniques. CRC Press, Bocan Raton, pp 385–387
Mendonca CR, Zambiazi R, Granada GG (2001) Partial substitution of sugars by the low-calorie sweetener sucralose in peach compote. J Food Sci 66:1195–1200
Meyer S, Riha WE (2002) Optimizing sweetener blends for low-calorie beverages. Food Technol 56(7):42–45
Mittal S, Bajwa U (2011) Effect of fat and sugar substitution on the quality characteristics of low calorie milk drinks. J Food Sci Technol published online Jan 28, 2011 (doi:10.007/s13197-010-oz16-9)
Pelligrino L (1994) Influence of fat content on some heat-induced changes in milk and cream. Neth Milk Dairy J 48:71–80
Petrus RR, Loiola CG, Oliveira CAF (2010) Microbiological shelf life of pasteurized milk in bottle and pouch. J Food Sci 75(1):M36–M40
Porto-Pinto E, Teixeira AM, Lopes-Sopena L, Pires-da-Rosa V, Mello-Luvielmo MD (2003) Sucralose in the development of light milky desserts. Boletim do Centro de Pesquisa e Processamento de Alimentos 21:49–60
Ranganna S (1994) Handbook of analysis and quality control for fruits and vegetables products. Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, pp 9–12, 99–101, 281–307
Shin HS, Lee JH, Pestka JJ, Ustunol Z (2000) Growth and viability of commercial Bifidobacterium spp in skim milk containing oligosaccharides and inulin. J Food Sci 65:884–887
Silva RF (1996) Use of inulin as a natural texture modifier. Cereal Food World 41:792–794
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1968) Statistical methods. Oxford and IBH Publishing Company, New Delhi, p 339
Walstra P, Jenness R (1984) Dairy chemistry and physics. Wiley and Sons, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, S., Bajwa, U. Effect of heat treatment on the storage stability of low calorie milk drinks. J Food Sci Technol 51, 1875–1883 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0714-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0714-z