Abstract
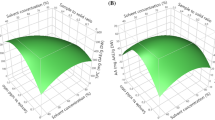
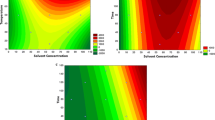
Solid-liquid extraction of phytic acid (PA) from rice bran was optimized by the maximization of the yield using response surface methodology. A Box-Behnken design was used to monitor the effects of three processing parameters of extraction on the PA yield, including ratio of acid solution to raw material (mL/g), hydrochloric acid concentration (mol/L), and extraction time (h). The results showed that the optimal conditions were acid solution/raw material of 8.5:1 (mL/g), HCl concentration 0.62 mol/L and extraction time 5.5 h. Validation tests indicated that the actual yield of PA was (2.15 ± 0.02)% with RSD = 1.92% (n = 5) under the optimized conditions, which was in good agreement with predicted yield. Antioxidant assays suggested that the extracted PA had weaker DPPH, hydroxyl and superoxide free-radical-scavenging capabilities than vitamin C at the same concentration of 0.5 mg/mL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn HJ, Kim JH, Yook HS, Byun MW (2003) Irradiation effects on free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of phytic acid. J Food Sci 68:2221–2224
Ajay P, Ramana KV, Bawa AS (2010) Simplification and optimization of deMan Rogosa Sharpe (MRS) medium for enhanced production of bacteriocin by Weissella paramesenteroides DFR-8. J Food Sci Technol 47(3):258–265
Amaro R, Murillo M, González Z, Escalona A, Hernández L (2009) Optimization of the treatment of wheat samples for the determination of phytic acid by HPLC with refractive index detection. J AOAC Int 92:873–878
Garg SK, Singh DS (2010) Optimization of extrusion conditions for defatted soy-rice blend extrudates. J Food Sci Technol 47(6):606–612
Ghiselli A, Nardini M, Baldi A, Scaccini C (1998) Antioxidant activity of different phenolic fractions separated from an Italian red wine. J Agri Food Chem 46:361–367
Grases F, Simonet BM, March JG, Prieto RM (2000) Inositol hexakisphophate in urine: the relationship between oral intake and urinary excretion. BJU Int 85:138–142
Grases F, Sanchis P, Perello J, Isern B, Prieto RM (2007) Effect of crystallization inhibitors on vascular calcifications induced by vitamin D–A pilot study in Sprague-Dawley rats. Cir J 71:1152–1156
Itagi HBN, Singh V (2011) Preparation, nutritional composition, functional properties and antioxidant activities of multigrain composite mixes. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0267-6
Latta M, Eskin M (1980) A simple and rapid colorimetric method for phytate determination. J Agri Food Chem 28:1313–1315
Liang J, Li F, Fang Y, Yang W, An X, Zhao L, Xin Z, Hu Q (2010) Response surface methodology in the optimization of tea polyphenold-loaded chitosan nanoclusters formulations. Euro Food Res Technol 231:917–924
Mahajan BVC, Kaur T, Gill MIS, Dhaliwal HS, Ghuman BS, Chahil BS (2010) Studies on optimization of ripening techniques for banana. J Food Sci Technol 47(3):315–319
Muralidhar RV, Chirumamila RR, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) A response surface approach for the comparison of lipase production by Candida cylindracea using two different carbon sources. Biochem Eng J 9:17–23
Myers RH, Montgomery DC (2002) Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product in Optimization using Designed Experiments. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, pp 521–690
Norazalina S, Norhaizan ME, Hairuszah I, Norashareena MS (2010) Anticarcinogenic efficacy of phytic acid extracted from rice bran on azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:259–268
Qi HM, Zhang QB, Zhao TT, Chen R, Zhang H, Niu XZ, Li Z (2005) Antioxidant activity of different sulfate content derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol 37:195–199
Schröterová L, Hasková P, Rudolf E, Cervinka M (2010) Effect of phytic acid and inositol on the proliferation and apotosis of cells derived from colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 23:787–793
Shampine LF, Thompson S (2001) Solving DDEs in MATLAB. Appl Nume Math 37:441–458
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T (1992) Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agri Food Chem 40:945–948
Wu P, Tian JC, Walker CE, Wang FC (2009) Determination of phytic acid in cereals–A brief review. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:1671–1676
Xu Q, Kanthasamy AG, Reddy MB (2008) Neuroprotective effect of the natural iron chelator, phytic acid in a cell culture model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicology 245:101–108
Acknowledgements
Financial supports for this work from the Education Bureau Project for Scientific Research of Zhejiang Province (No. Y200803745) and the Key Brainstorm Project for Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province (No. 2007 C12019) were gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H.W., Bai, X.L. Optimization of extraction conditions for phytic acid from rice bran using response surface methodology and its antioxidant effects. J Food Sci Technol 51, 371–376 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0521-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0521-y