Abstract
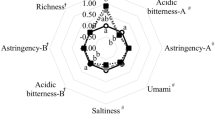
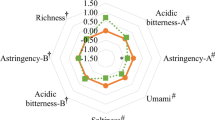
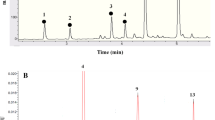
Stevia rebaudiana is an introduced crop in India. The leaf and its extract although sweet have a bitter after taste that precludes commercial acceptability. The composition of the leaf reflected a high nutritive value and polyphenol concentration averaging 4.15% by weight of dried leaf. Variably processed extracts enriched with polyphenols, pigments and a mixture of both were evaluated for sensory attributes by a semi trained panel when added to cofee and lime juice. Presence of polyphenols influenced the acceptability of the sweeteners marginally, while chlorophyll was found unacceptable in any of the extracts. The antioxidant activity of the extracts was synergistic when it was mixed with coffee and lime juice. Complete purification of stevia leaf extracts to obtain pure glycosides is not necessary for it to become a commercially acceptable sweetener.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrewes P, Johanekke LHC Busch, Teun D J, Anneke Groenewegen, Helene A (2003) Sensory properties of virgin olive oil polyphenols: Identification of Deacetoxy-ligstroside aglycon as a key contributor to pungency. J Agric Food Chem 51:1415–1420
Anon (2008) Dr.Duke’s phytochemical and ethnobotanical databases — www.ars-grin.gov/duke. Accessed on 05.09.2008
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis. 15th edn, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC
Arora S, Gawande H, Narendra K, Yarrakula S, Singh VP, Sharma V, Wadhwa BK, Tomer SK, Sharma GS (2008) Textural and structural properties of kalakand made with artificial sweeteners — saccharin, acesulfame-k, sucralose and aspartame. J Food Sci Technol 45:263–266
Awika JM, Rooney LW, Wu X, Prior RL, Zevallos LC (2003) Screening methods to measure antioxidant activity of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and sorghum products. J Agric Food Chem 51:6657–6662
Bonvehi JS, Coll FV (1997) Evaluation of bitterness and astringency of polyphenolic compounds in cocoa powder. Food Chem 60(3):365–370
Brandle JE, Rosa N (1992) Heritability for yield, leaf-stem ratio and stevioside content estimated from a landrace cultivar of Stevia rebaudiana. Can J Plant Sci 72:1263–1266
Chang SS, Cook JM (1983) Stability studies of stevioside and rebaudioside A in carbonated beverages. J Agric Food Chem 31:409–412
Chetana R, Srinivasa PC, Yella Reddy S (2006) Effect of sugar substitutes on moisture sorption characteristics of laddu, an Indian traditional sweet. J Food Sci Technol 43:634–638
Crammer B, Ikan R (1987) Progress in the chemistry and progress of the rebaudiosides. In: Developments in Sweeteners — 3, Grenby TH (ed), Elsevier Applied Science, London, p 45–64
Eriksson CE (1982) Lipid oxidation catalysts and inhibitors in raw materials and processed foods. Food Chem 9:3–19
Fernandez-Escobar R, Moreno R, Garcia-Creus M (1999) Seasonal changes of mineral nutrients in olive leaves during the alternate-bearing cycle. Sci Hort 82:25–45
Fukunaga Y, Miyata T, Nakayasu N, Mizutani K, Kasai R, Tanaka O (1989) Enzymatic transglucosylation products of stevioside: Separation and sweetness evaluation. Agric Biol Chem 48: 1831–1834
Gary CH, Valerie Antoine, Margi Chan, Daiva Nevidomskyte, Martina Koniger (2006) Seasonal changes in photosynthesis, protein composition and mineral content in Rhododendron leaves. Plant Sci 170:314–325
Geuns JMC (2003) Molecules of interest: Stevioside. Phytochem 64:913–921
Harry BW Jr, Allerton R, Harry WD, Hewitt GF (1955) Stevioside I. The structure of the Glucose moieties. J Org Chem 20:875–883
Huang YS, Guo AG, Qian Y, Chen LY, Gu HF (1995) Studies on the variation of steviosides content and selection of type R-A in Stevia rebaudiana. J Plant Res Environ 4:28–32
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New Spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae, and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:191–194
Kalpana R, Khan Md K (2008) Post-harvest management of stevia leaves: A review. J Food Sci Technol 45:391–397
Kennelly EJ (2002) Sweet and non-sweet constituents of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) Bertoni. In: Stevia, the Genus Stevia. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants—Industrial Profiles, Kinghorn AD (ed), Vol 19, Taylor and Francis, London and NY, p 68–85
Kochkiyan V, Markosyan A, Abelyan L, Balayan A, Abelyan V (2006) Combined enzymatic modification of stevioside and rebaudioside A. Appl Biochem Microbiol 42(1):31–37
Kohda H, Kasai R, Yamasaki K, Murakami K, Tanaka O (1976) New sweet diterpeneg Glucosides from Stevia rebaudiana. Phytochem 15:981–983
Kolb N, Herrera JL, Ferreyra DJ, Uliana RF (2001) Analysis of sweet diterpene glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: Improved HPLC Method. J Agric Food Chem 49(10):4538–4541
Kroyer G. Th (1999) The low calorie sweetener Stevioside: Stability and interaction with food ingredients. Lebensm Wiss Technol 32:509–512
Lobov SV, Kasai R, Ohtani K, Tanaka O, Yamasaki K (1991) Enzymic production of sweet stevioside derivatives: Transglucosylation by glucosidases. Agric Biol Chem 55:2959–2965
Masumi K, Emi T, Yohko M, Takahiro U (2008) The taste sensory evaluation of medicinal plants and Chinese medicines. Int J Pharm 351:36–44
Metivier J, Viana AM (1979) The effect of long and short day length upon the growth of whole plants and the level of soluble proteins, sugars and stevioside in leaves of Stevia rebaudiana Bert. J Exp Bot 30:1211–1222
Misnawi JS, Jamilah B, Nazamid S (2004) Sensory properties of cocoa liquor as affected by polyphenol concentration and duration of roasting. Food Qual Prefer 15:403–409
O’Connell JE, Fox PF (2001) Significance and applications of phenolic compounds in the production and quality of milk and dairy products: A review. Int Dairy J 11:103–120
Pignatelli P, Ghiselli A, Buchetti B, Carnevale R, Natella F, Germano G, Fimognari F, Di Santo S, Lenti L, Violi F (2006) Polyphenols synergistically inhibit oxidative stress in subjects given red and white wine. Atherosclerosis 188:78–83
Preys S, Mazerolles G, Courcoux P, Samson A, Fischer U, Hanafi M, Bertrand D, Cheynier V (2006) Relationship between polyphenol composition and some sensory properties in red wines using multiway analysis. Anal Chim Acta 563: 126–136
Ramirez RG, Gonzalez-Rodryguez H, Ramyrez-Orduna R, Cerrillo-Soto MA, Juarez-Reyes AS (2006) Seasonal trends of macro and micro minerals in 10 browse species that grow in northeastern Mexico. Anim Feed Sci Technol 128:155–164
Savita SM, Sheela K, Sharan Sunanda, Shankar AG, Parama Ramakrishna (2004) Stevia rebaudiana — A functional component for food industry. J Hum Ecol 15(4):261–264
Singh G, Asha Kawatra, Sehgal S (2001) Nutritional composition of selected green leafy vegetables, herbs and carrots. Plant Food Hum Nutr 56:359–364
Starrat AN, Kirby CW, Pocs R, Brandle JE (2002) Rebaudioside F, a diterpene glycoside from Stevia rebaudiana. Phytochem 59:367–370
Tadhani MB, Patel VH, Rema Subhash (2007) In vitro antioxidant activity of Stevia rebaudiana leaves and callus. J Food Comp Anal 20(3–4):323–329
Tadhani M Subhash R (2006) Preliminary studies on Stevia rebaudiana leaves: Proximal composition, mineral analysis and phytochemical screening. J Med Sci 6(3):321–326
Virendra VP, Kalpagam P (2008) Assessment of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana)-natural sweetener: A review. J Food Sci Technol 45:467–473
Yuehua von Fircks, Tom Ericsson, Lisa Sennerby-Forsse (2001) Seasonal variation of macronutrients in leaves, stems and roots of Salix dasyclados Wimm. grown at two nutrient levels. Biomass Bioenergy 21:321–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, R., Narayanan, P., Vasudevan, V. et al. Nutrient composition of cultivated stevia leaves and the influence of polyphenols and plant pigments on sensory and antioxidant properties of leaf extracts. J Food Sci Technol 47, 27–33 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-010-0011-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-010-0011-7